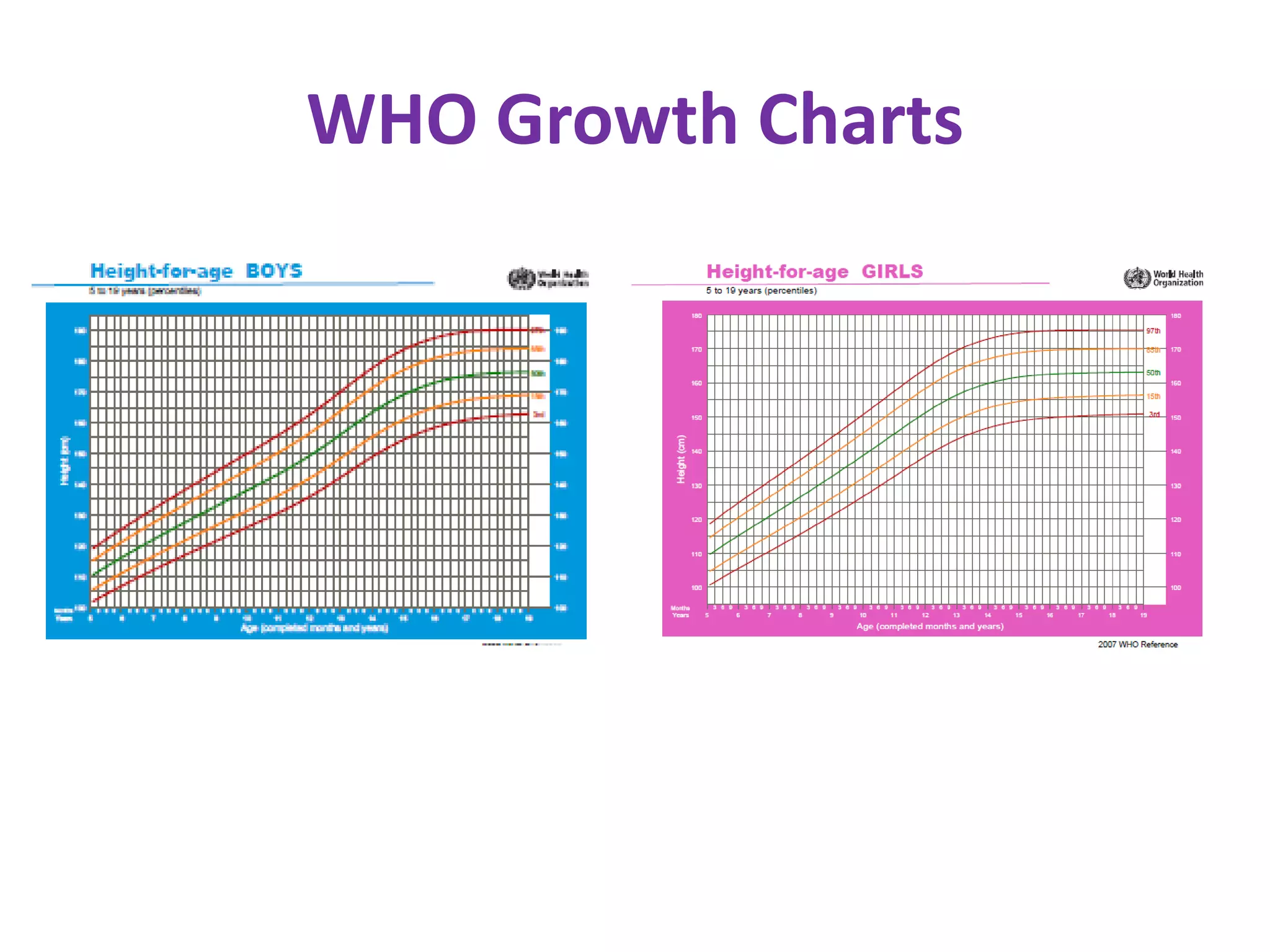
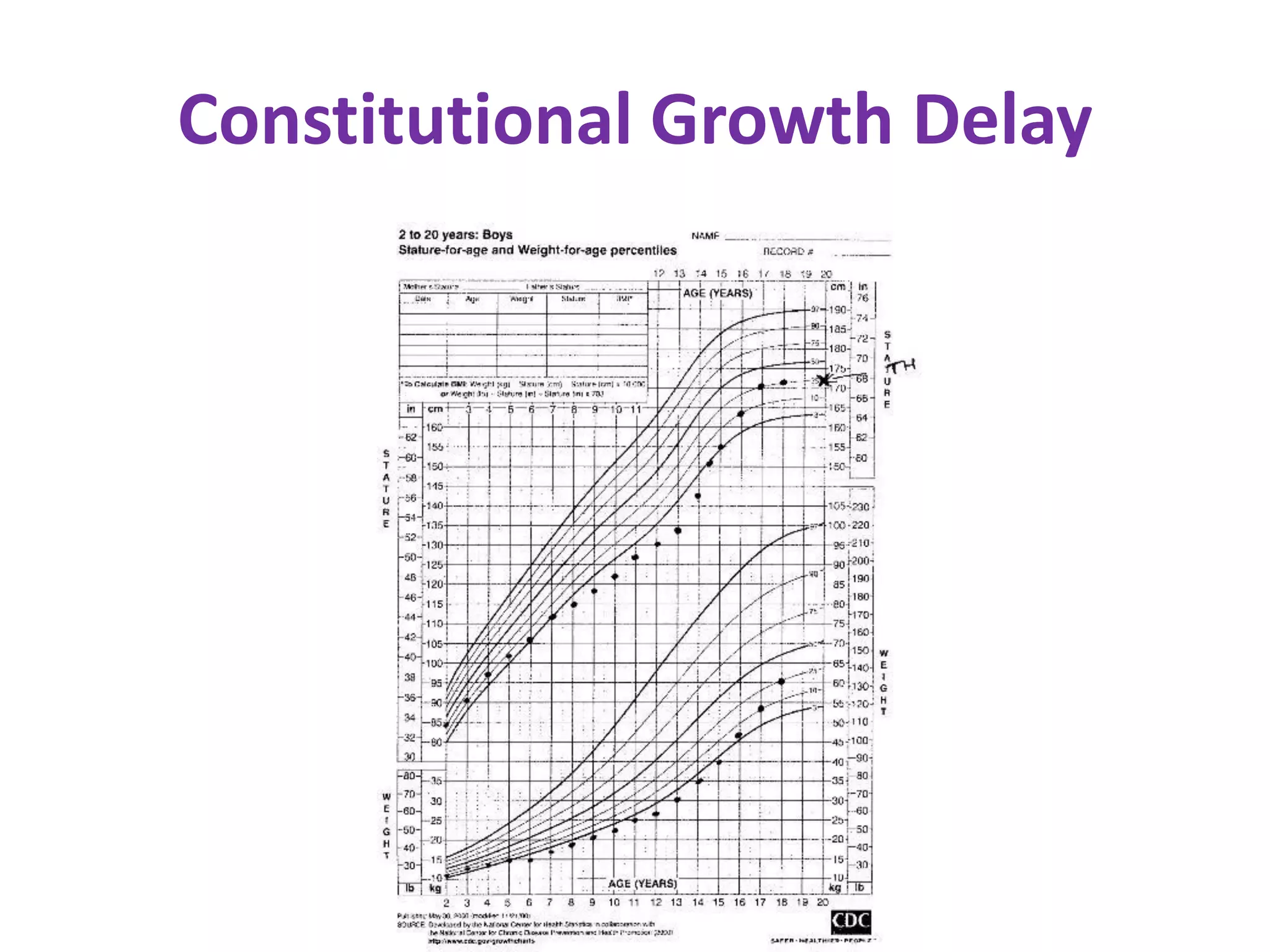
This document provides guidance on evaluating and managing short stature in children. It discusses evaluating a short child by taking a history including birth details, illnesses, nutrition, and parental heights. Physical examination involves measuring height, weight, body proportions, and examining parents. Growth charts are used to assess if a child's height is below standard deviations. Potential causes of short stature discussed include familial, constitutional growth delay, chronic diseases, psychosocial, chromosomal, genetic syndromes, and endocrine disorders. Initial investigations include blood tests and bone age x-ray. Advanced tests may include skeletal survey, karyotype, growth hormone stimulation. Management depends on the identified cause and may include counseling, disease treatment, hormone therapy.