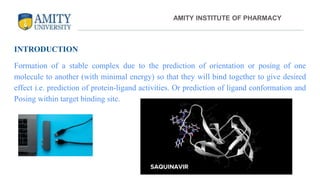
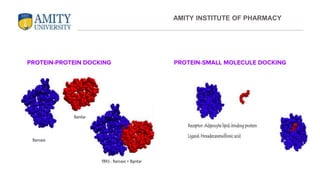
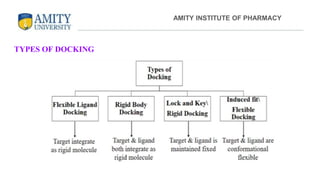
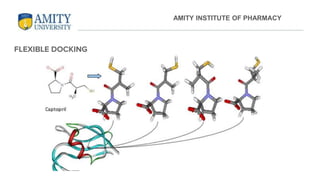
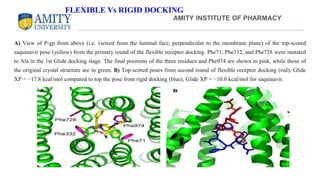
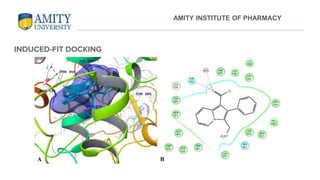
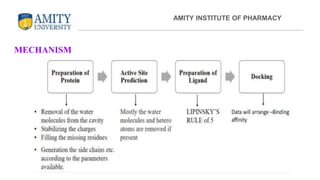
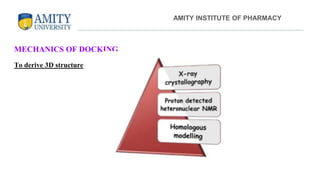
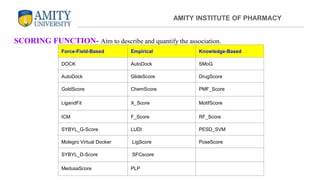
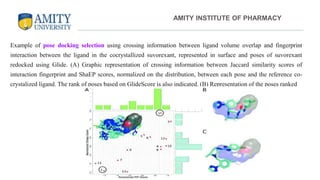
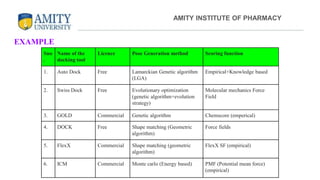
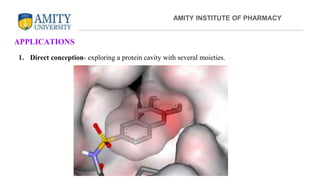
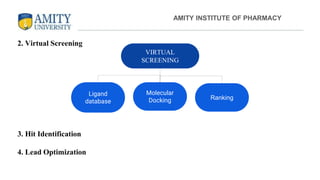
The document discusses molecular docking, focusing on the prediction of protein-ligand interactions and the stability of complex formations. It compares different docking methodologies, including flexible and rigid docking, and outlines various scoring functions and docking tools used in the process. Additionally, it highlights applications like virtual screening, hit identification, and lead optimization in drug discovery.