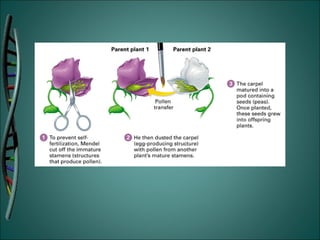
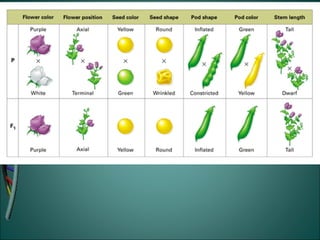
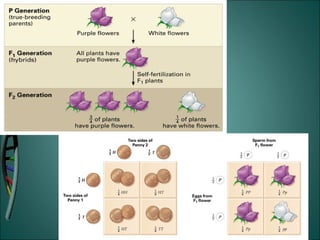
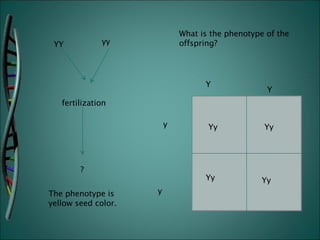
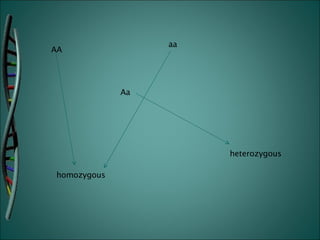
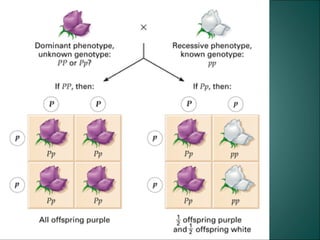
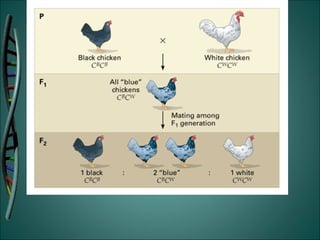
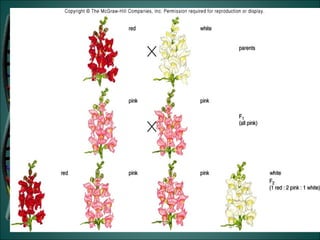
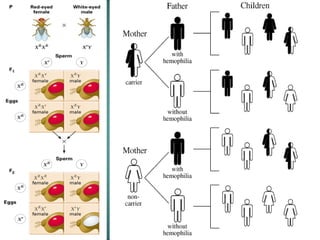
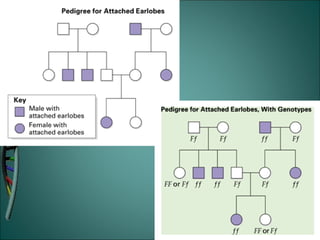
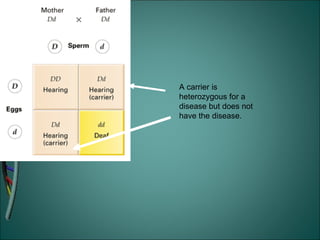
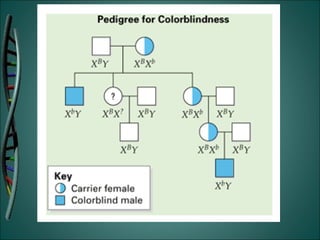
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied heredity through experiments with pea plants in his garden. He discovered the basic rules of genetics, including that traits are passed from parents to offspring and certain traits are dominant over recessive traits. Mendel studied seven observable traits in pea plants and used cross-pollination to determine which traits were dominant. His laws of segregation and independent assortment established that organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent, and that genes assort independently during reproduction.