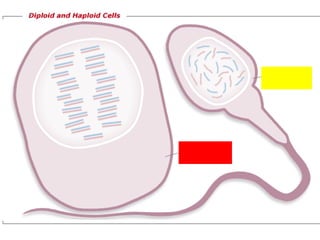
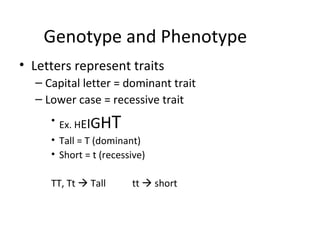
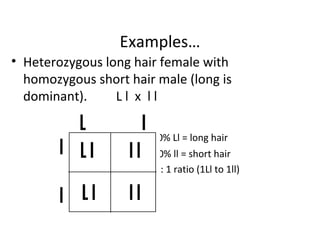
The document discusses basic genetics concepts including genes, alleles, genotypes, phenotypes, dominant and recessive traits, Mendel's laws of inheritance, and using Punnett squares to determine the probability of offspring inheriting traits from parents. It defines key terms like genotype as the genetic makeup of an individual, phenotype as the observable expression of genes, and explains how dominant traits will always be expressed over recessive traits in a heterozygous individual. Dominant traits are represented by capital letters while recessive traits are lowercase. Punnett squares allow predicting the likelihood of traits being passed from parents to offspring based on the parents' genotypes.