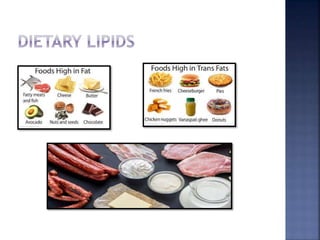
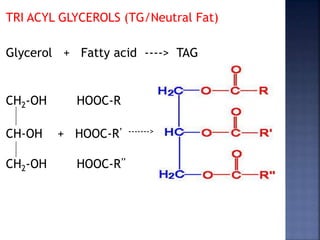
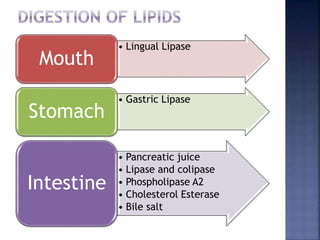
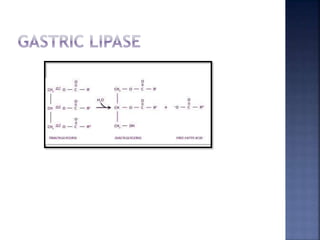
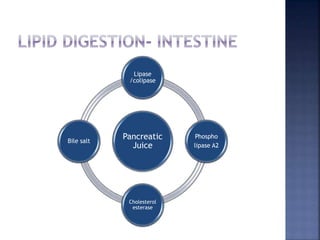
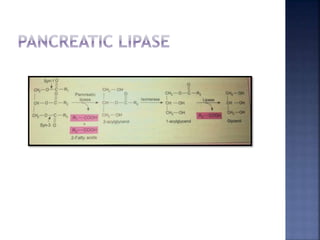
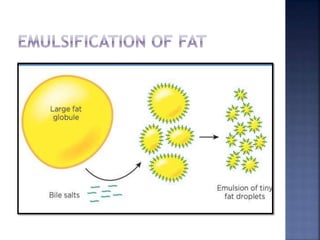
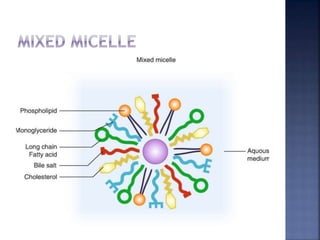
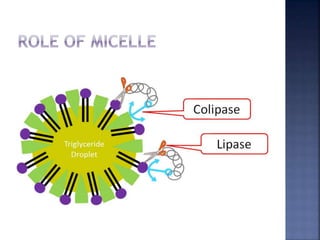
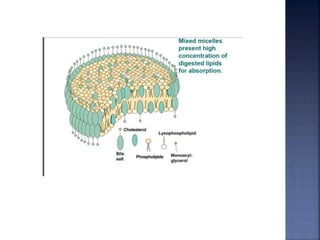
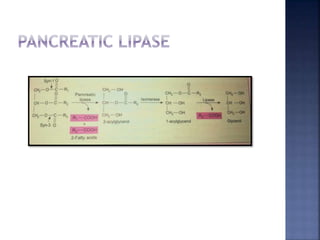
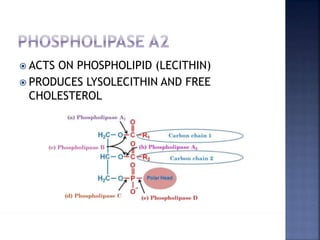
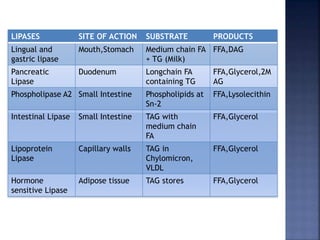
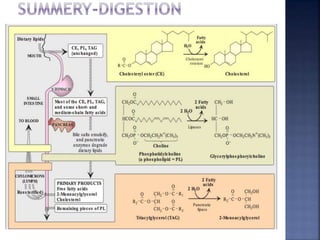
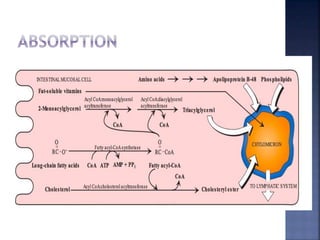
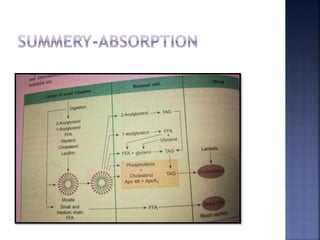
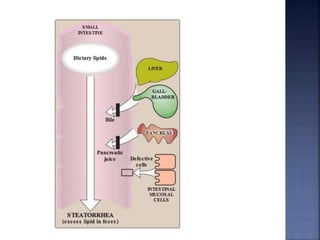
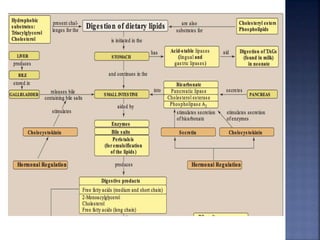
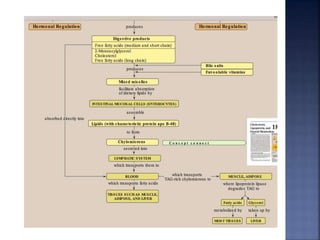
This document summarizes fat digestion and absorption. It notes that most dietary fat consists of triglycerides which are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol by lingual lipase in the mouth, gastric lipase in the stomach, and pancreatic lipase in the small intestine. Bile salts are also required to emulsify fat into micelles to allow absorption. The fatty acids and glycerol are reassembled into triglycerides and incorporated into lipoproteins for transport through the lymphatic system and blood. Disorders that can interfere with fat digestion or absorption include pancreatic problems causing steatorrhea, gallstones obstructing bile flow, and intestinal diseases impairing absorption.