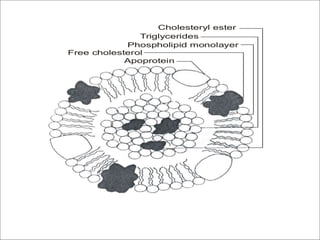
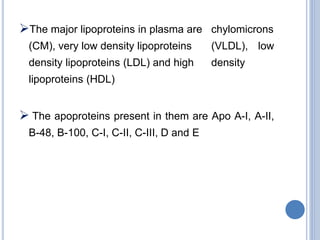
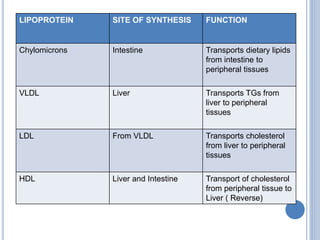
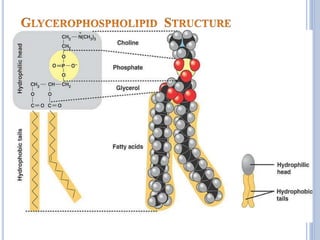
This document provides information about lipids. It begins by defining lipids as compounds that are relatively insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are then classified into three main categories: simple lipids like fatty acids and triglycerides, compound lipids containing additional non-lipid components like phospholipids and glycolipids, and derived lipids which are hydrolysis products of other lipids. The document focuses on the structures, functions and examples of important lipids like fatty acids, triglycerides and phospholipids.




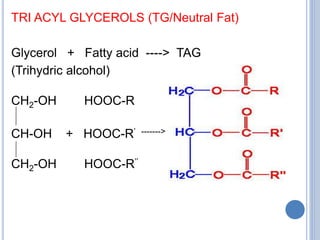
![1. Simple lipids – esters of FA + alcohol
Fats - esters of FA + Glycerol
eg. TAG
Fat in liquid state is known as -----
Waxes – solid esters of long chain FA
+
high mol.wt MHA
[ monohydric alcohols]
eg. Bees wax
sperm oil
H2COH
HCOH
H2COH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidchemistry-190224072909/85/Lipid-chemistry-5-320.jpg)






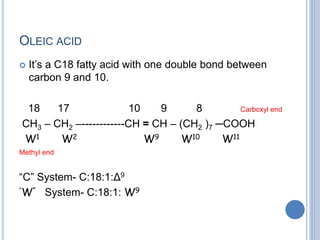
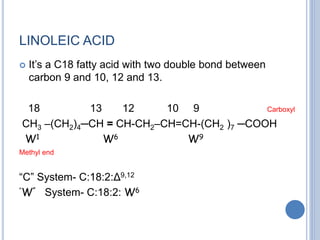
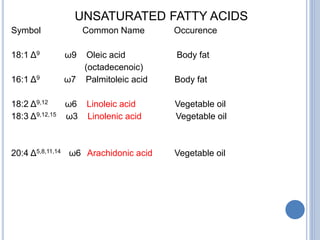
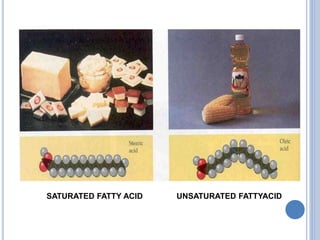
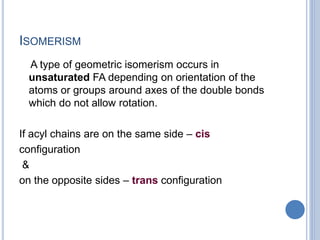
![ Based on the nature of the hydrocarbon chain
- Saturated FA [ - anoic]
- Unsaturated FA [ - enoic]
- Branched chain FA – phytanic acid
- Hydroxy FA – cerebronic, ricinoleic acid
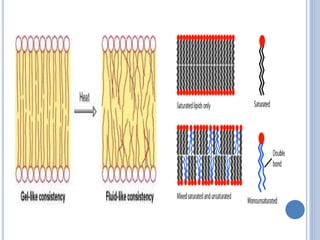
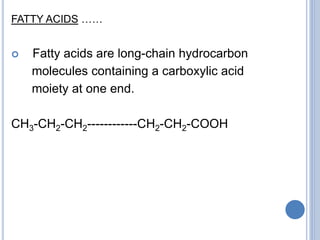
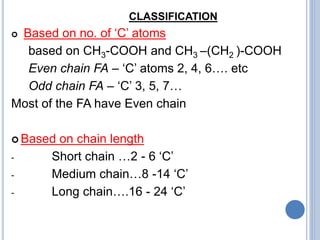
Fatty acids that contain no carbon-carbon
double bonds are termed saturated fatty acids;
those that contain double bonds are
unsaturated fatty acids.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidchemistry-190224072909/85/Lipid-chemistry-17-320.jpg)
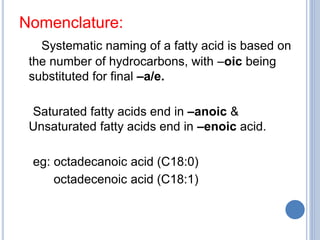












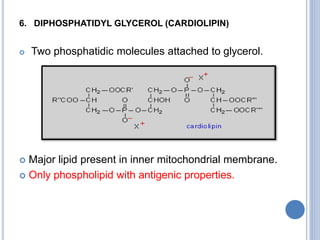
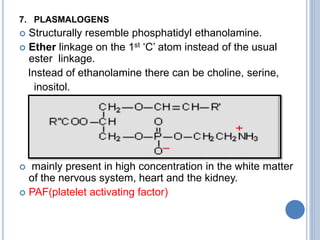

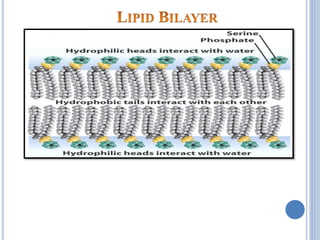
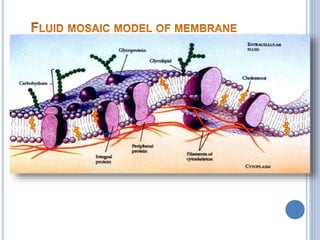
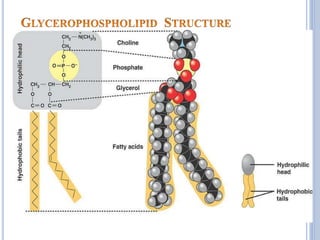
![Functions of PL
major constituents of cellular membrane
PL in gen & lecithin in particular are amphipathic polar head
– glycerol, phosphocholine, non-polar tail – hydrocarbon
chains of FA.
As a constituent of lung surfactant- DPL, phosphatidyl
glycerol, sphingomyelin. [LS ratio] >2 indicates lung maturity
Low levels of surfactant – RDS (prematurity)
Constituent of lipoproteins
Contain polyenoic FA, esterifies cholesterol.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidchemistry-190224072909/85/Lipid-chemistry-47-320.jpg)

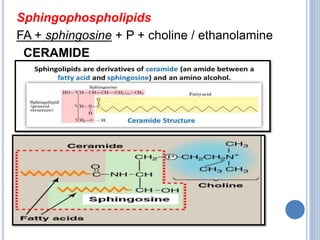



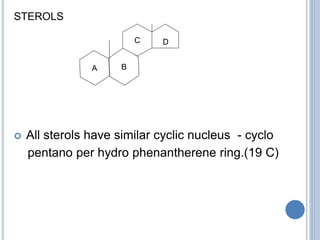
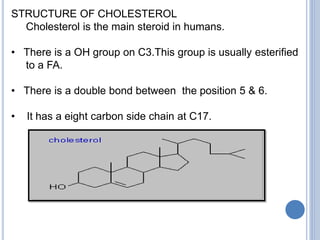
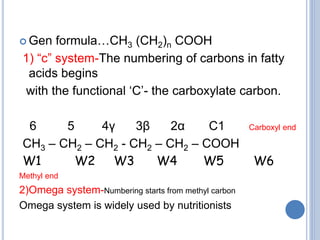
![Functions:
Cholesterol & its esters are major constituents of
plasma membrane and lipoproteins.
It is the precursor of steroid hormones, bile acids,
& Vit D.
[Steroid hormones ----adrenal cortex - cortisol,
cortisone & aldosterone, testis- testosterone, ovary-
estradiol, placenta -progesterone.
Bile acids---cholic, chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic,
lithocholic acids].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidchemistry-190224072909/85/Lipid-chemistry-55-320.jpg)