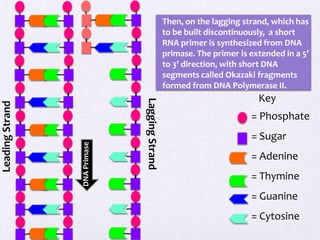
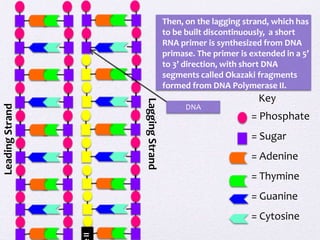
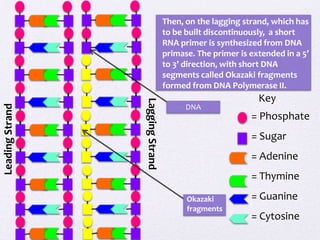
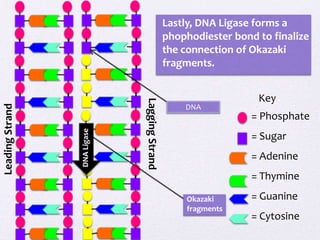
DNA replication involves unwinding the DNA double helix using the enzyme helicase. On the leading strand, DNA polymerase III continuously adds nucleotides to form the leading strand. On the lagging strand, which is discontinuous, RNA primers are added by primase and DNA polymerase II builds Okazaki fragments by adding nucleotides between primers. The primers are later removed and replaced with DNA to form a continuous DNA strand.