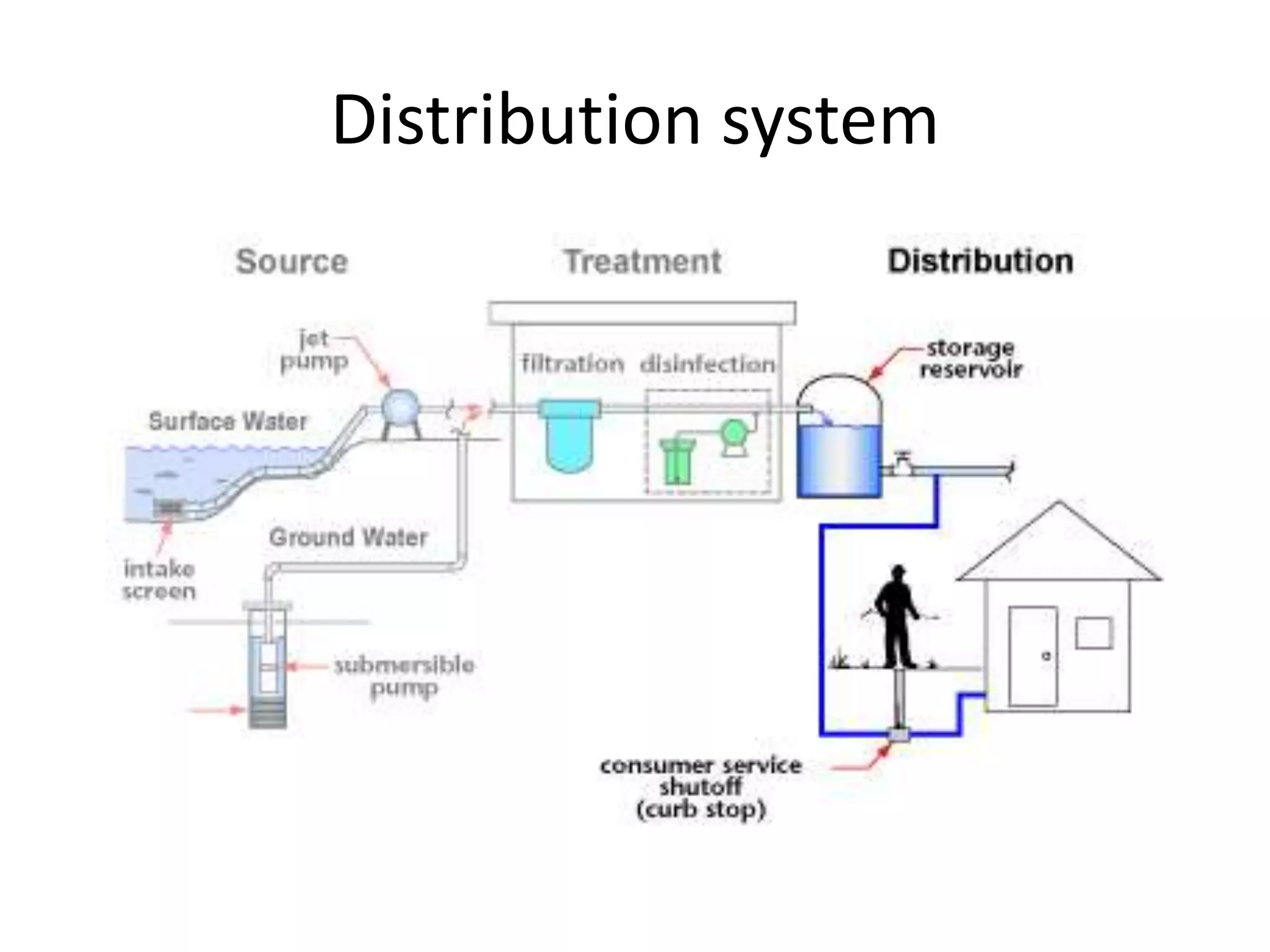
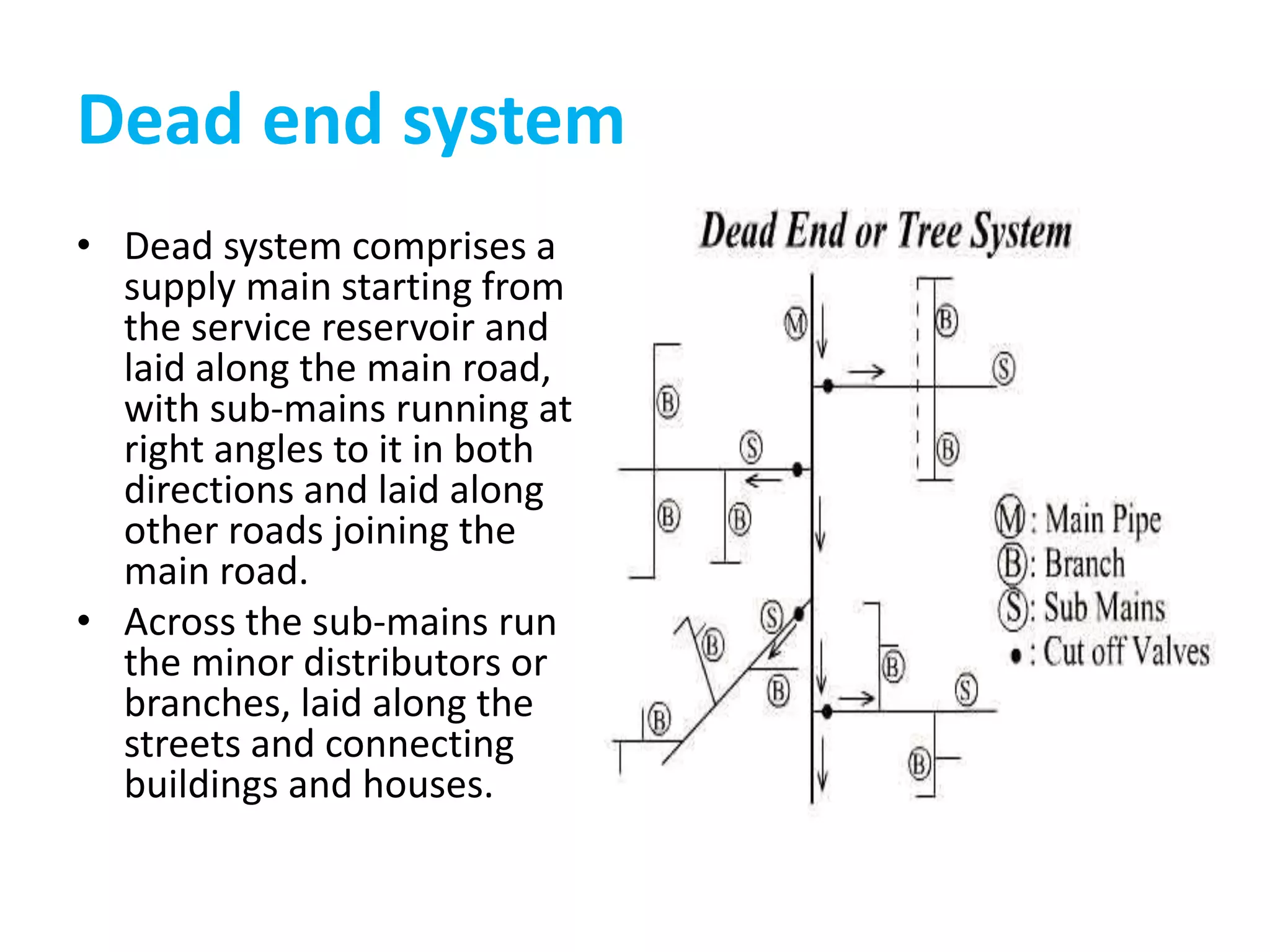
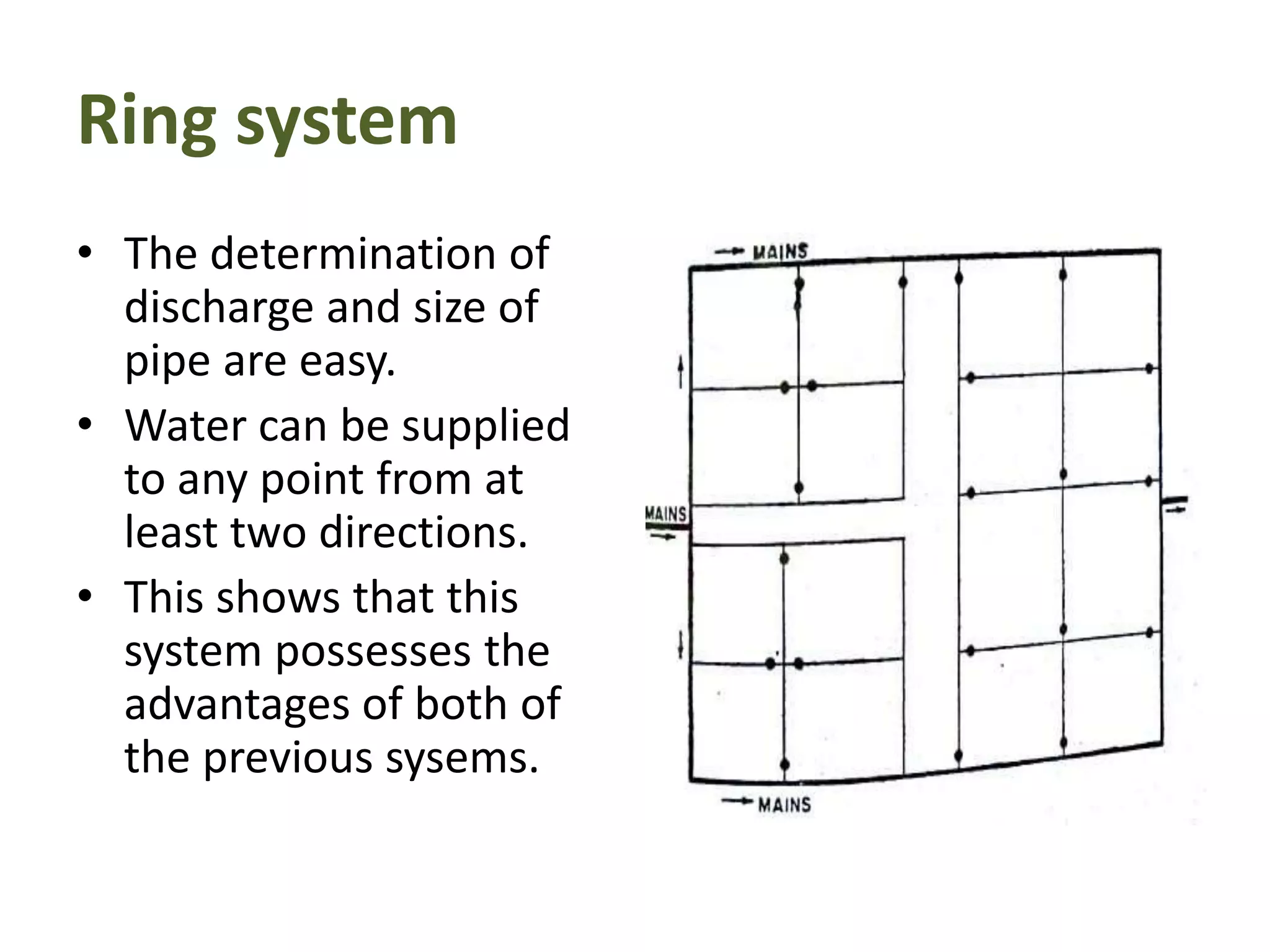
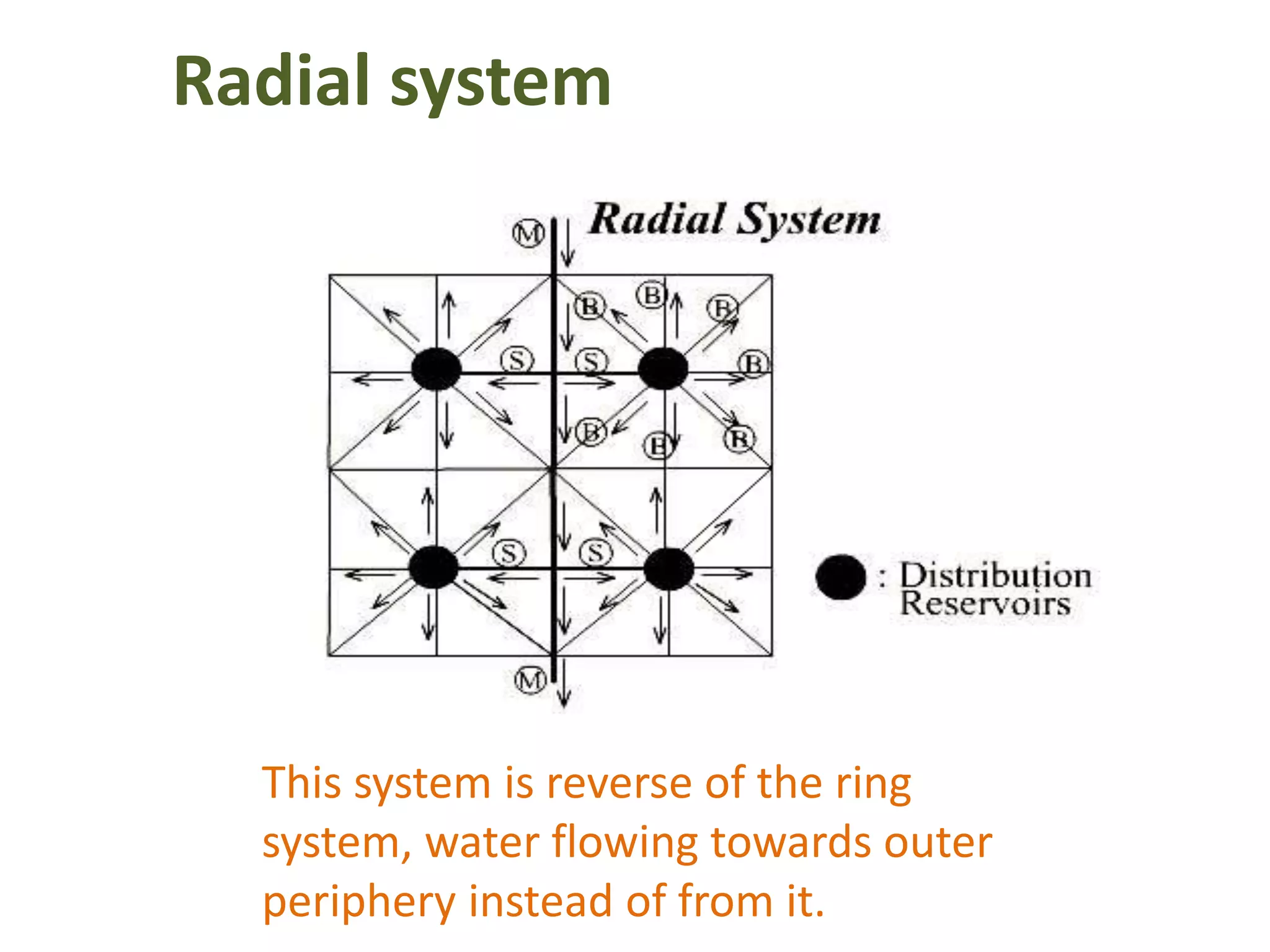
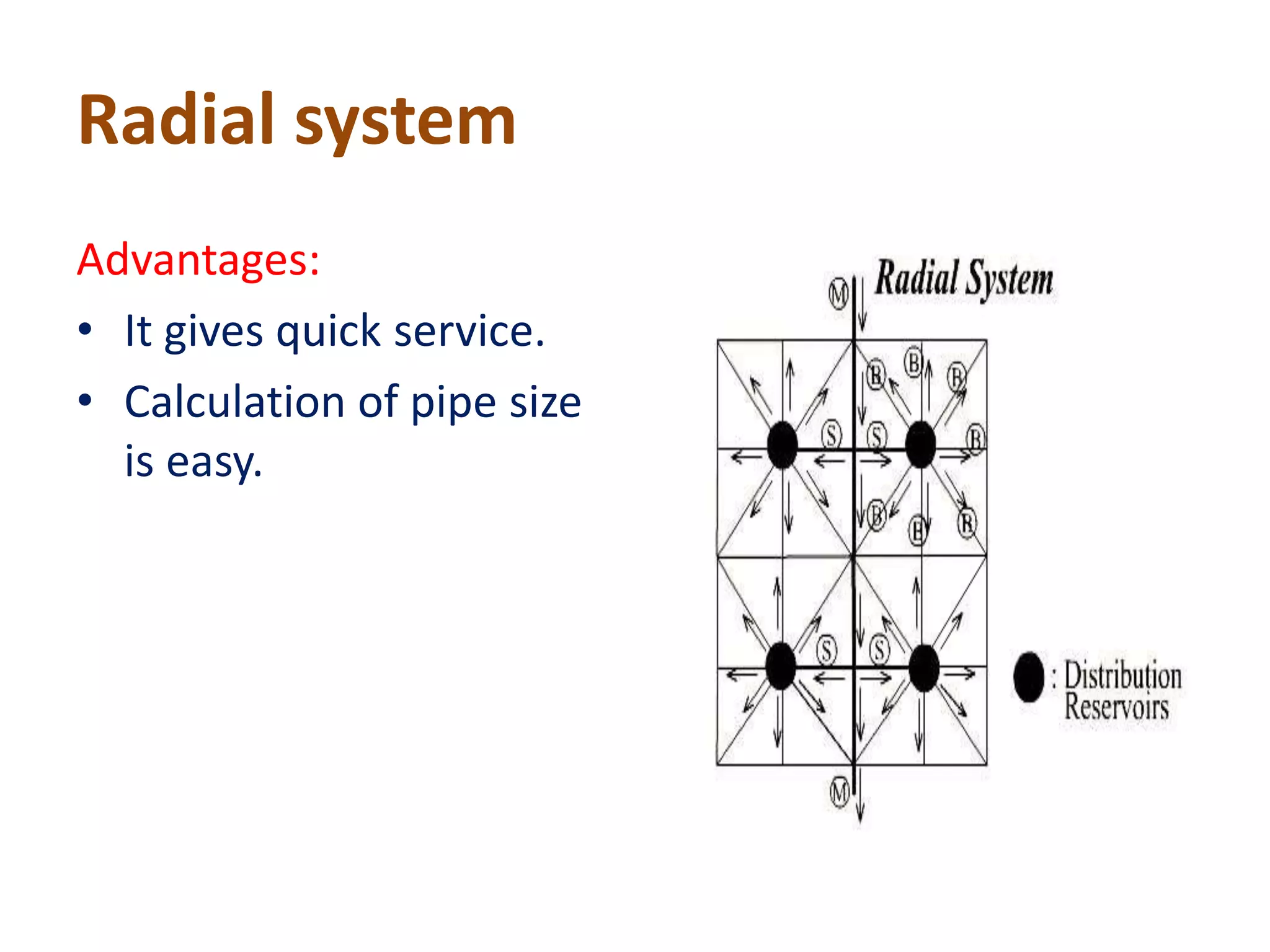
The document details various water distribution systems, describing their components, layout types, and requirements for efficiency and water quality. It outlines four main layout types: dead end, grid iron, ring, and radial systems, each with its advantages and disadvantages in terms of maintenance and efficiency. A good distribution system should ensure consistent water quality, adequate pressure during emergencies, and minimal disruption during repairs.