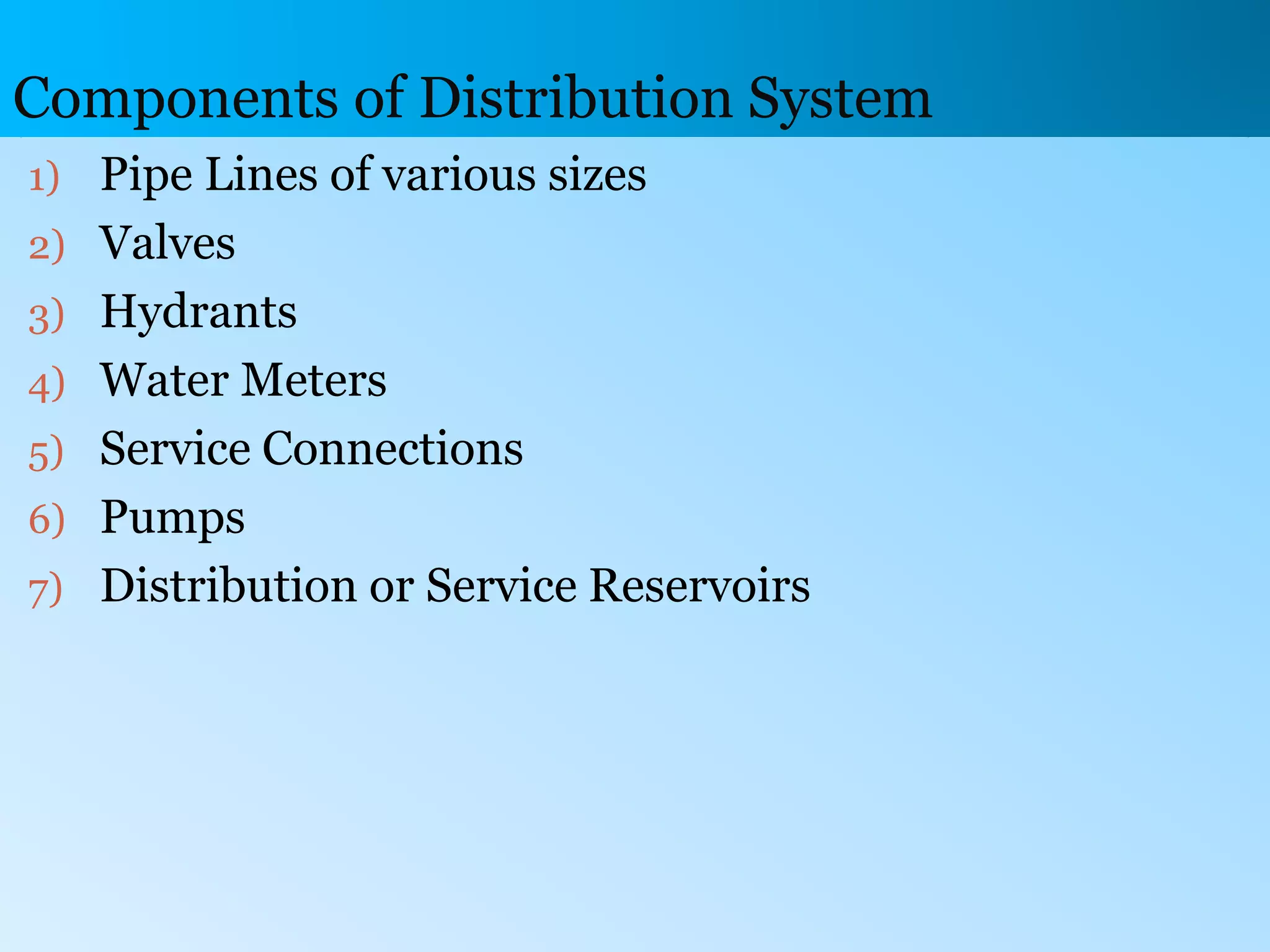
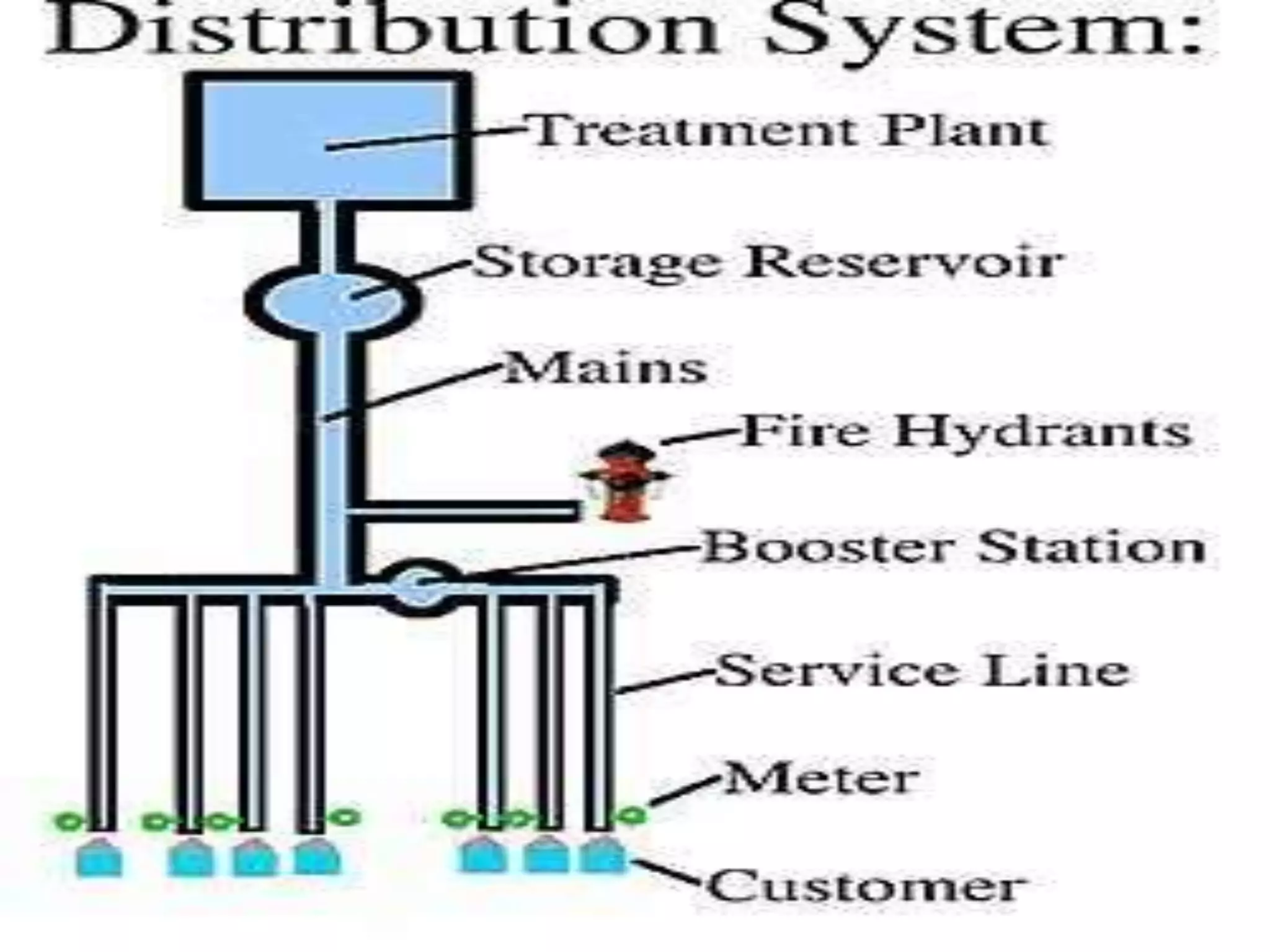
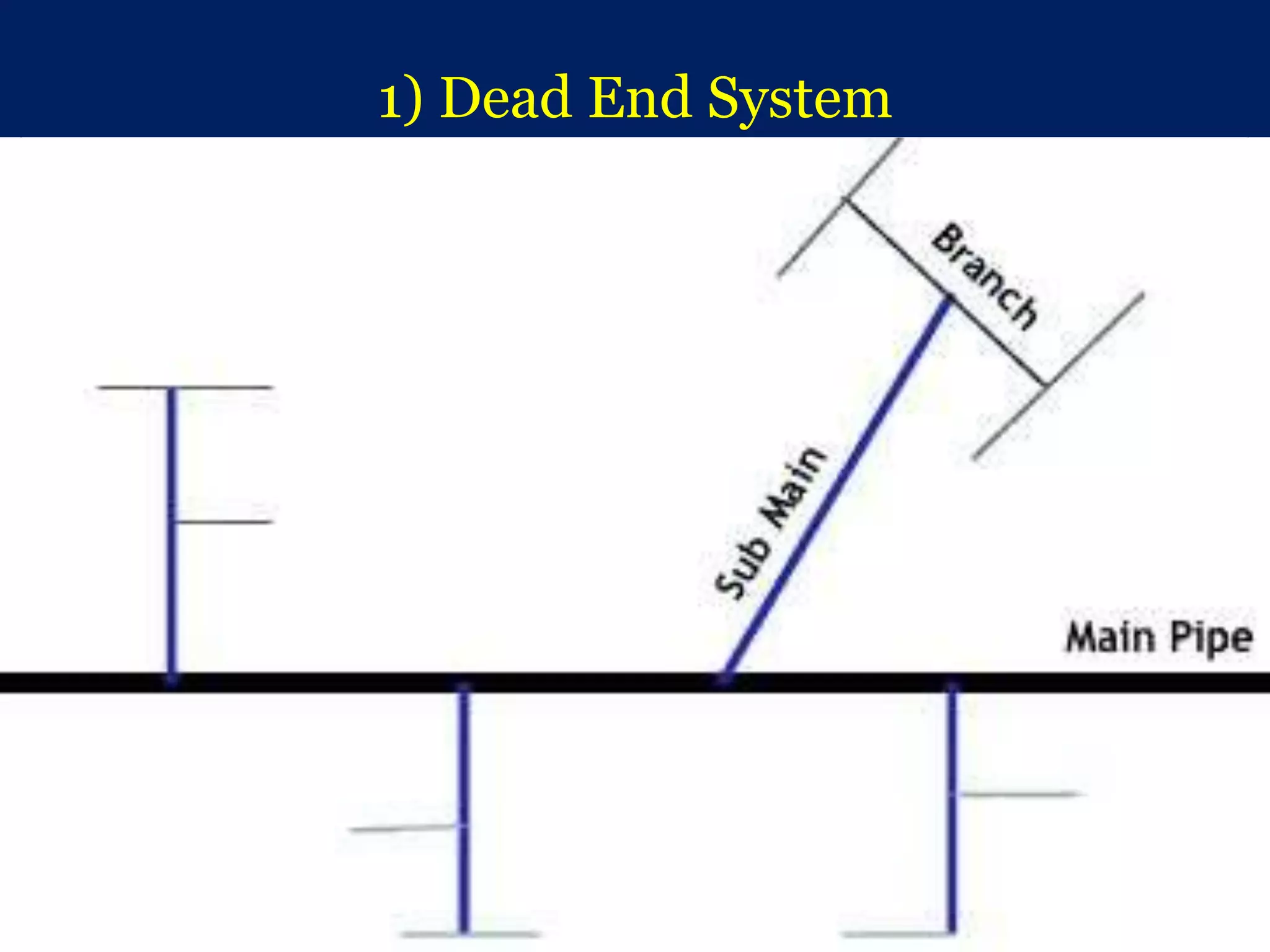
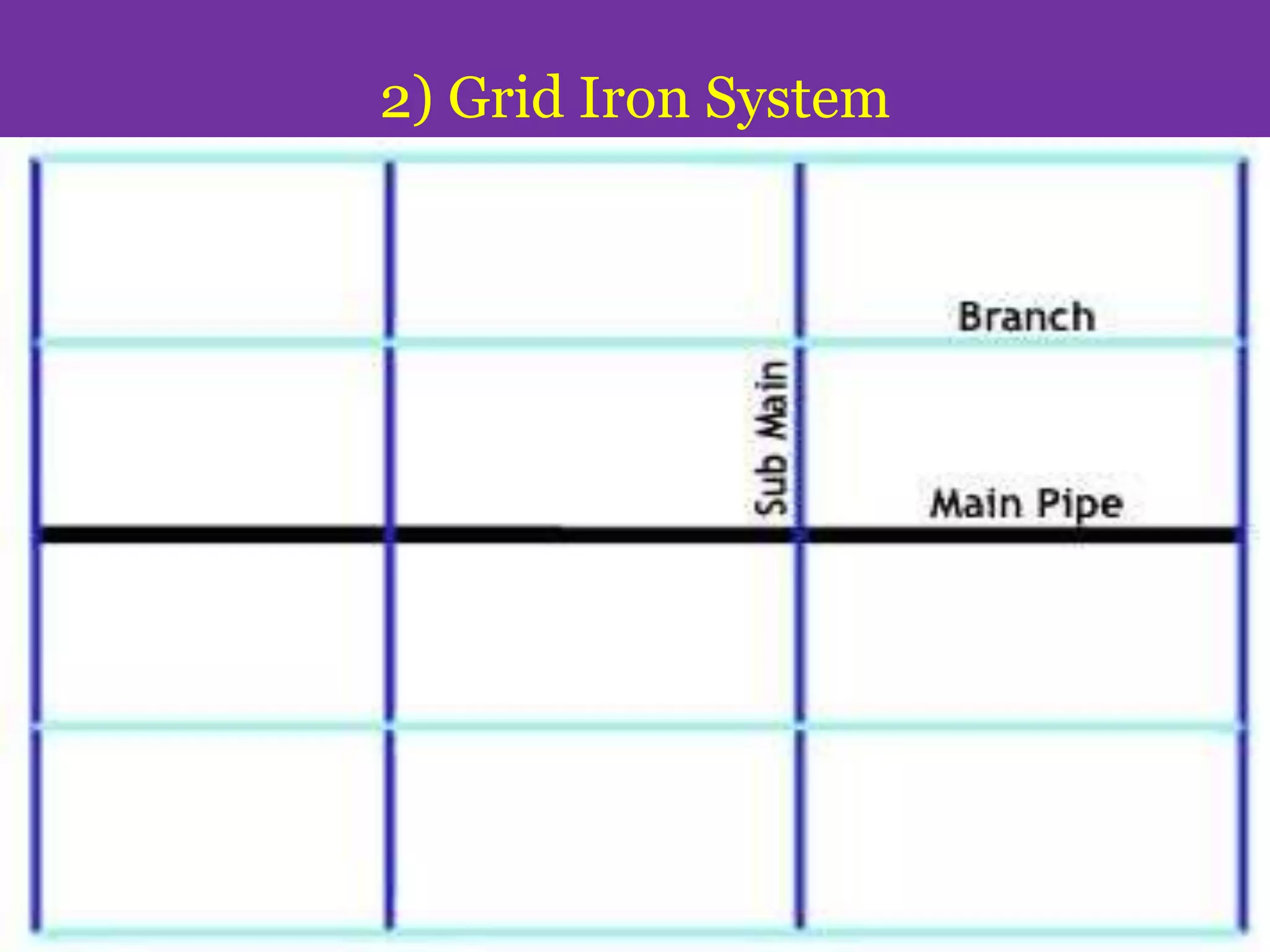
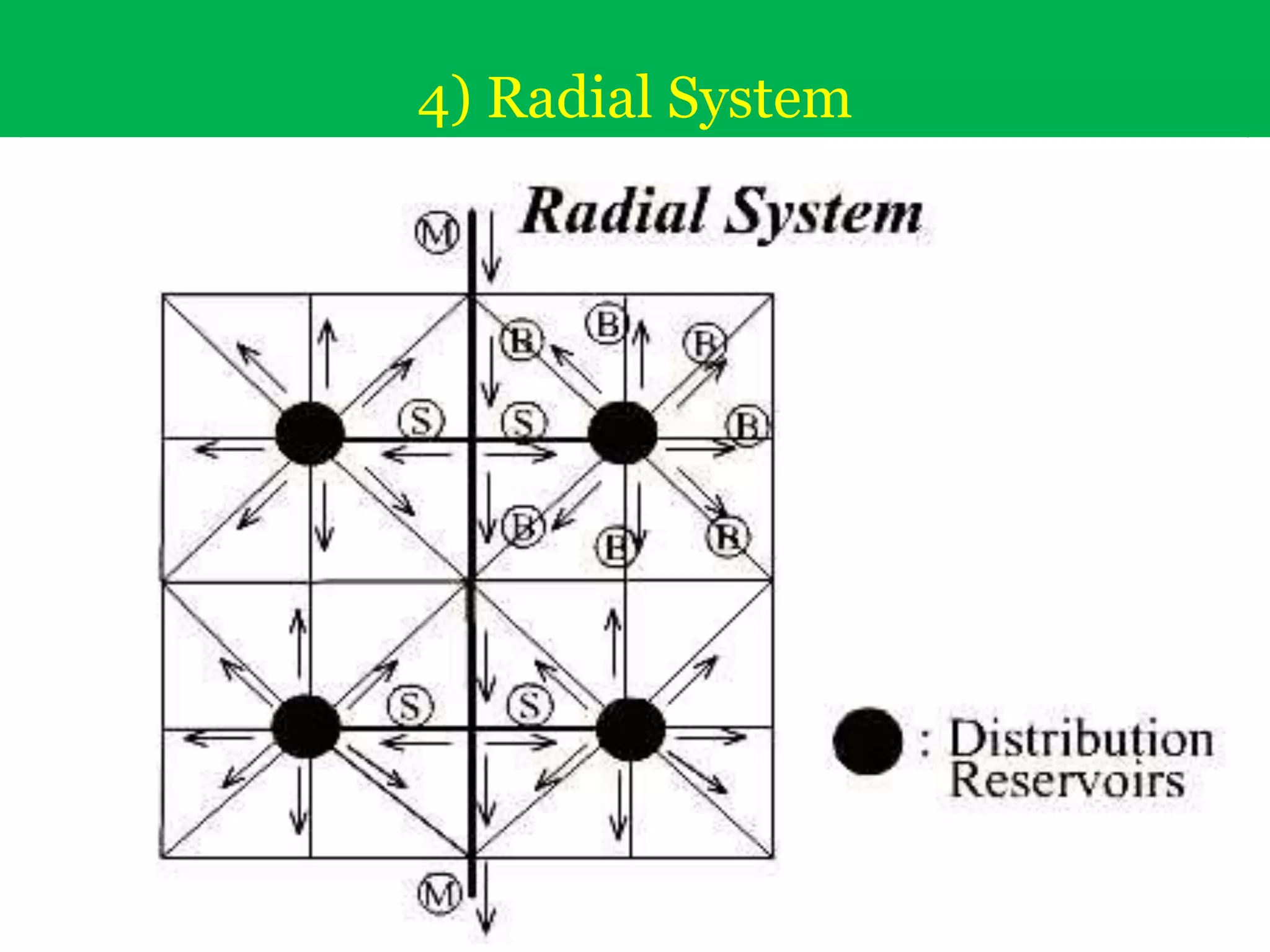
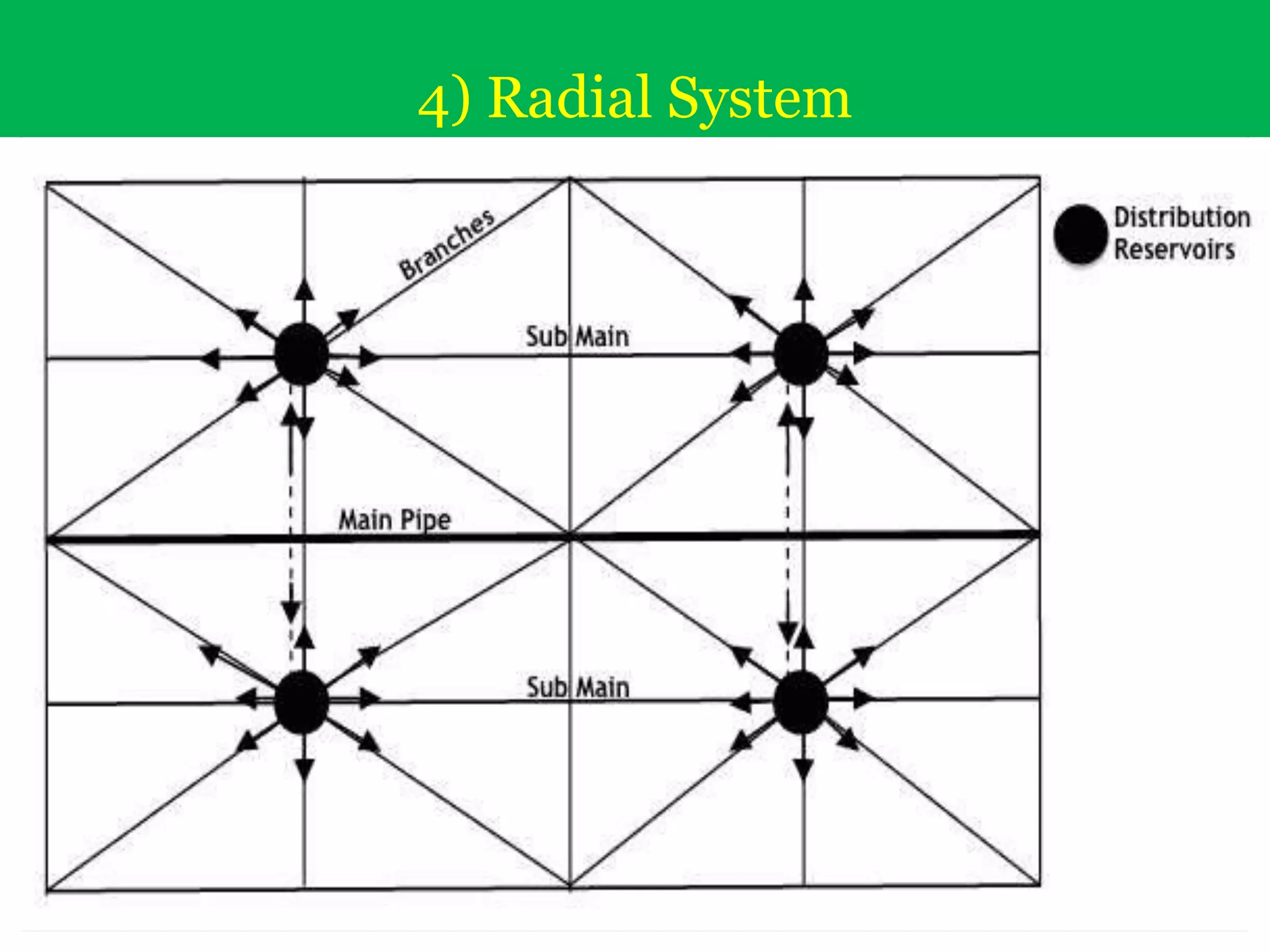
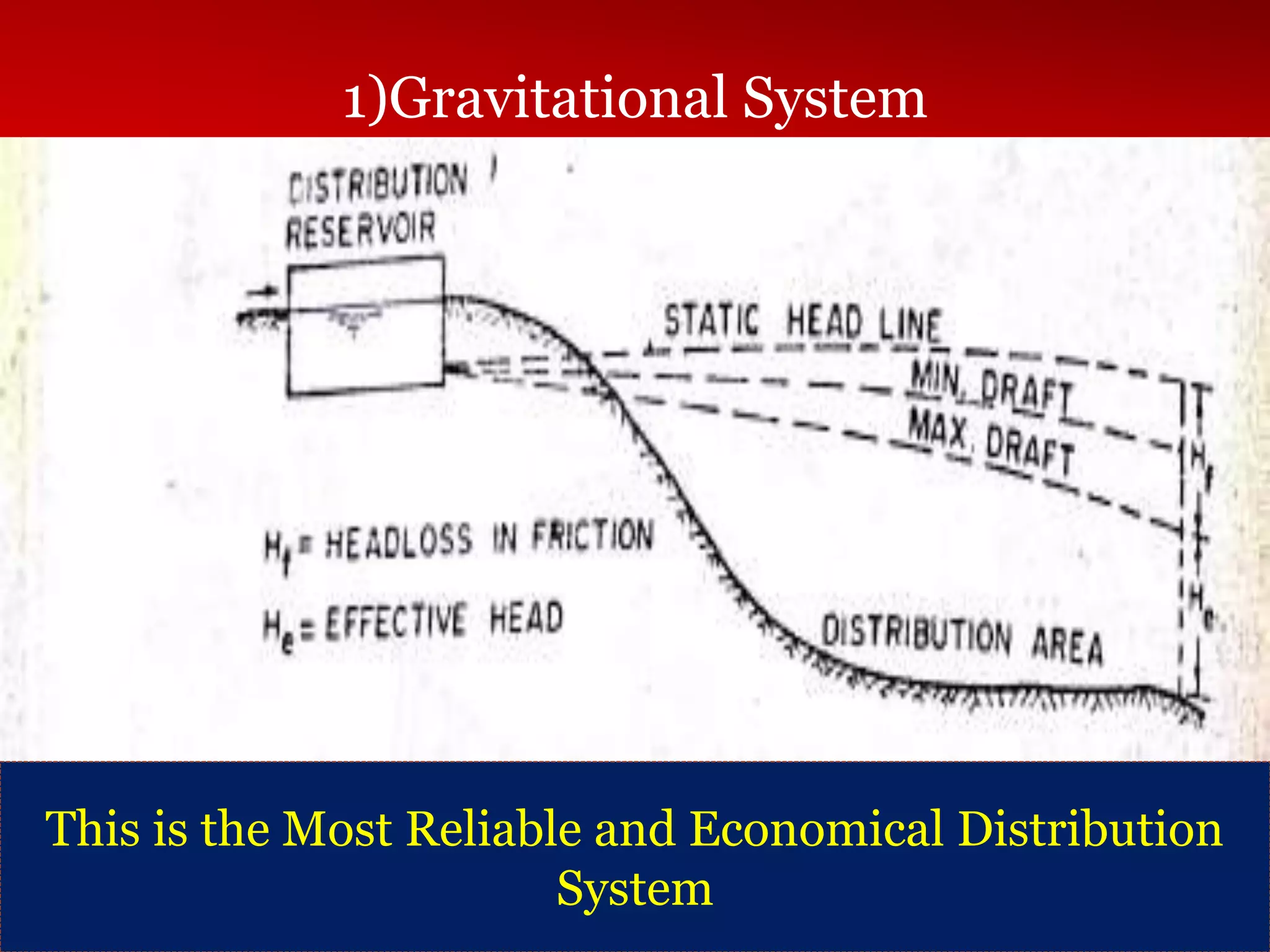
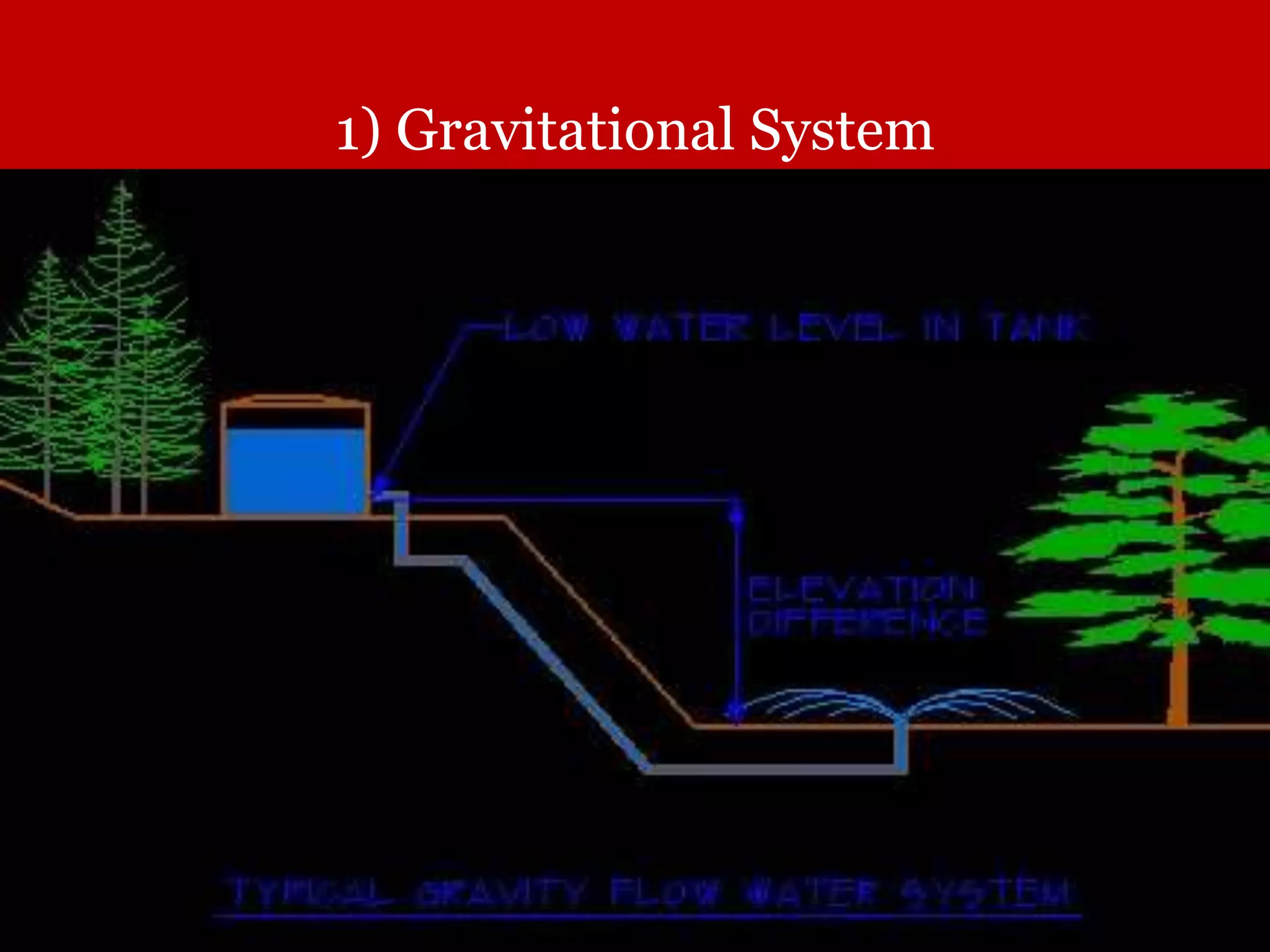
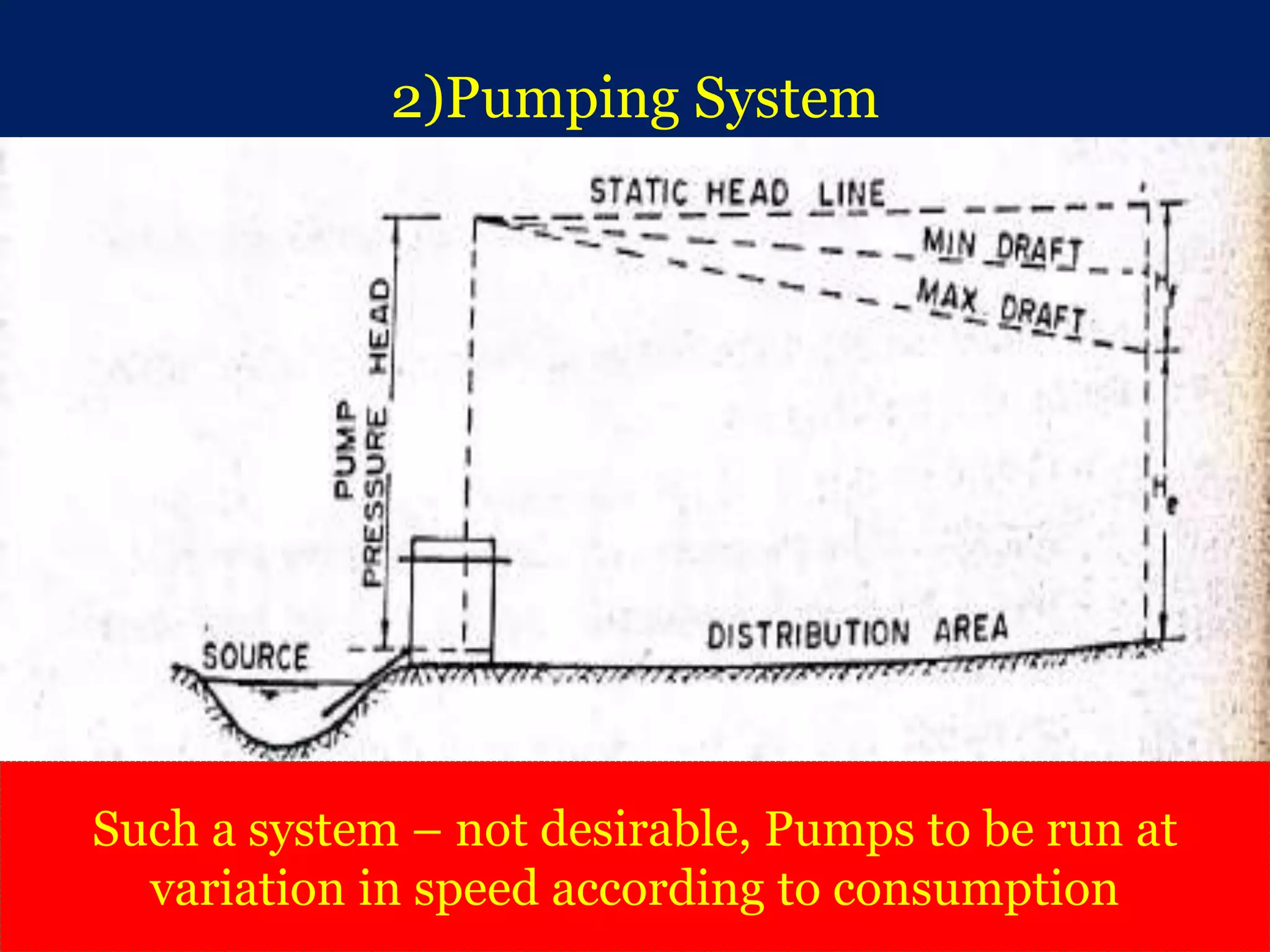
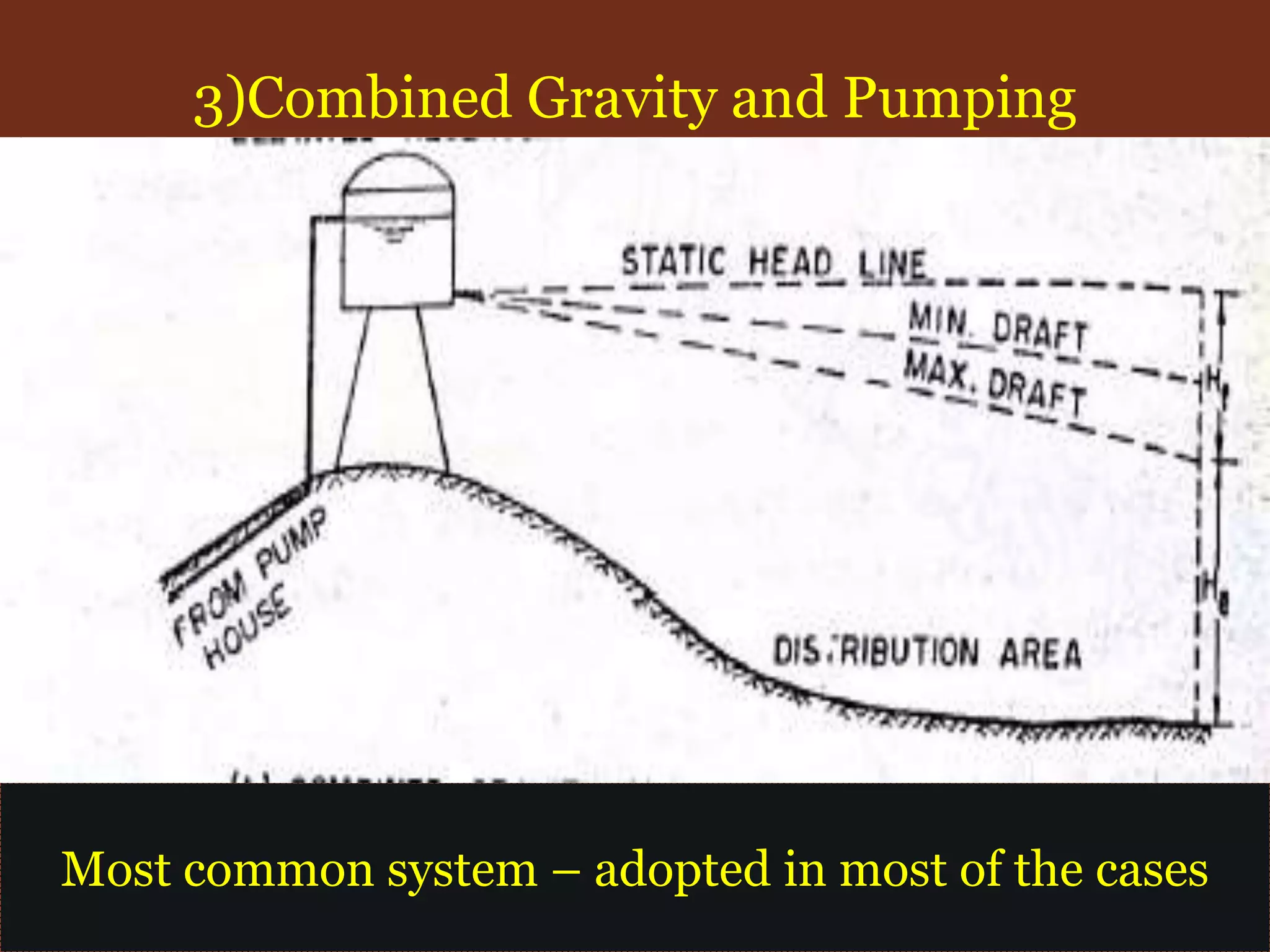
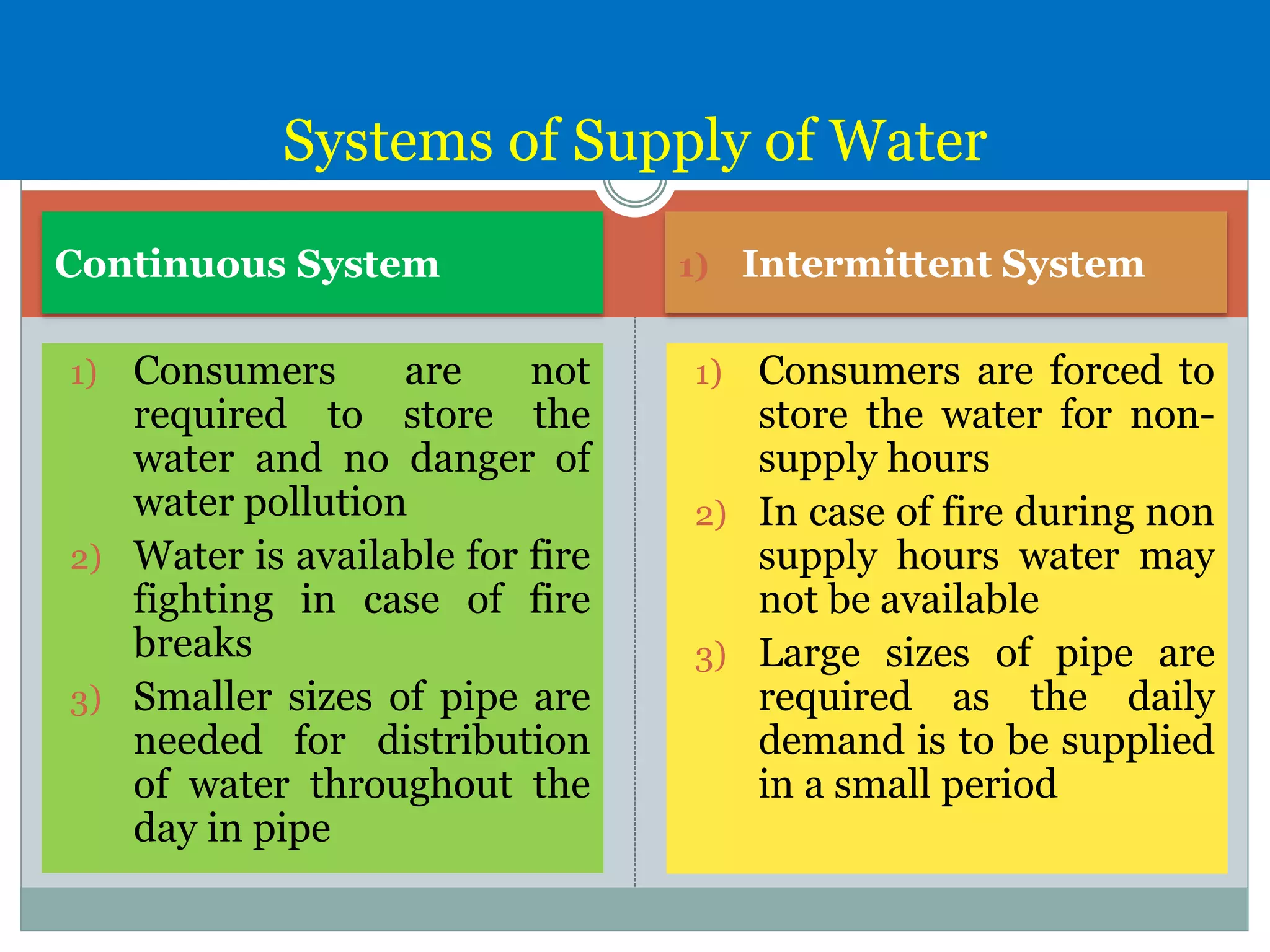
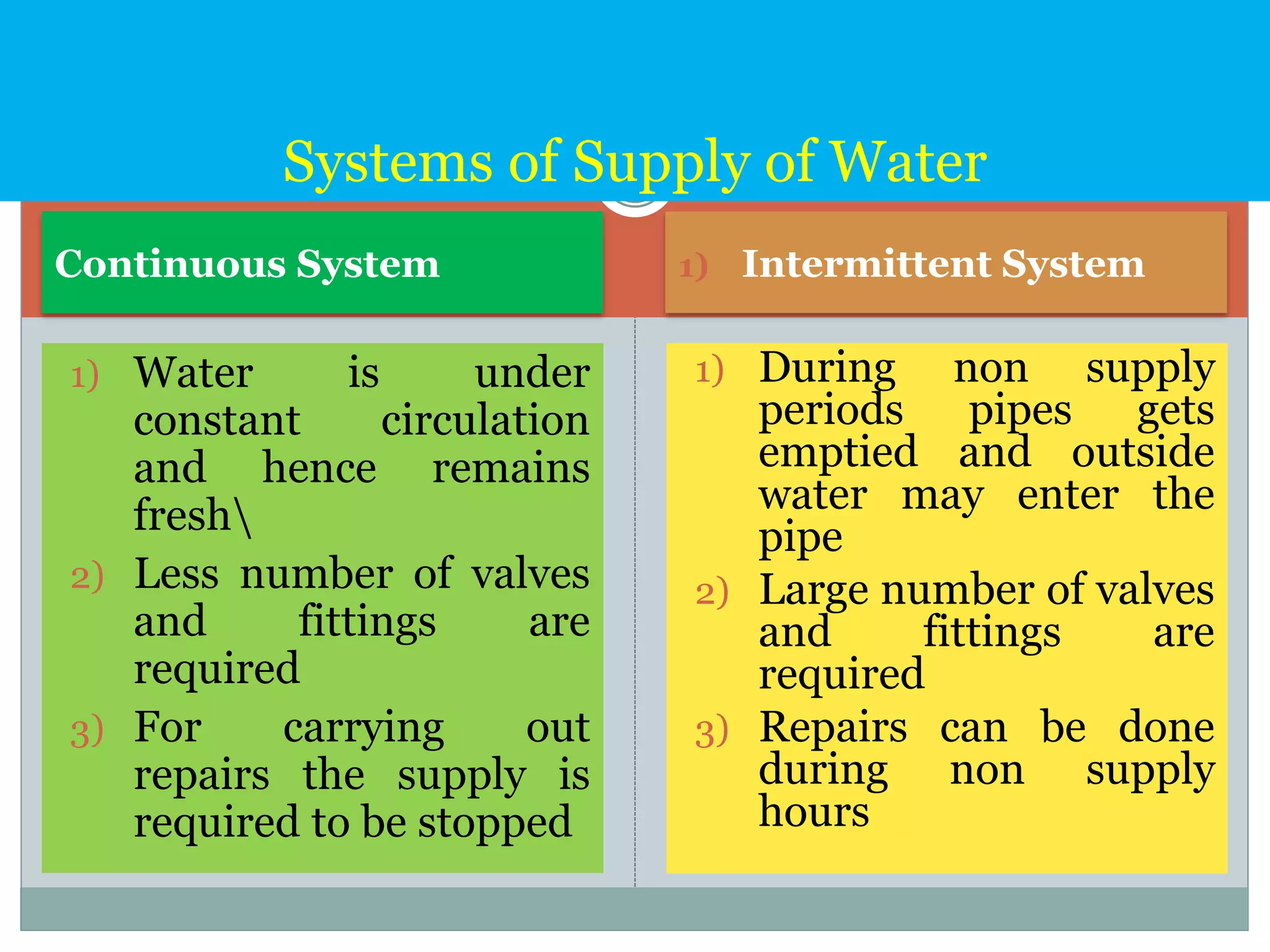
The document discusses water distribution systems, highlighting their main function of transporting water from treatment plants to homes and detailing the key components such as pipes, valves, hydrants, and reservoirs. It outlines various layouts and methods, including dead end, grid iron, ring, and radial systems, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it explains the importance of distribution reservoirs in managing water supply and maintaining constant pressure, while also considering the effects of different designs on efficiency and emergency response.