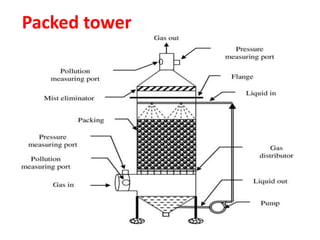
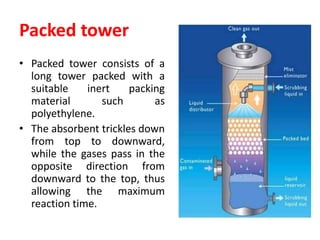
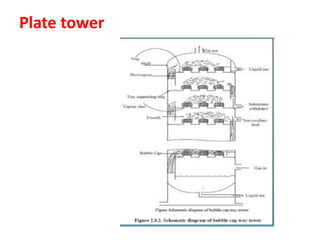
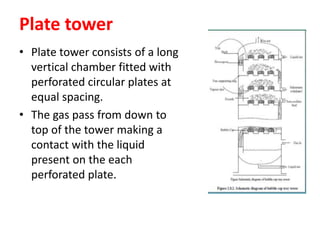
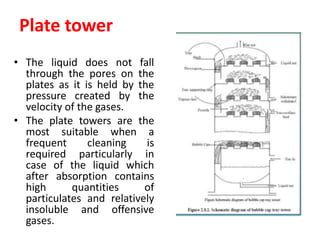
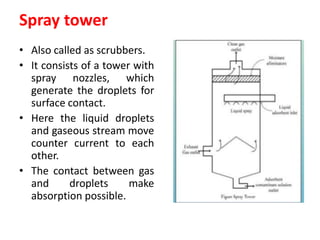
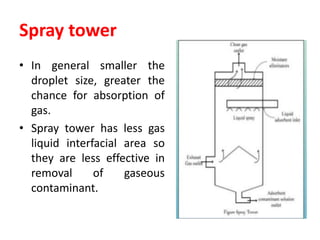
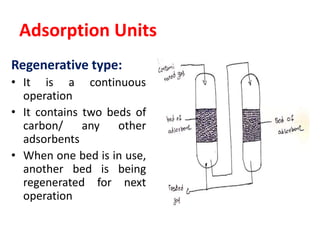
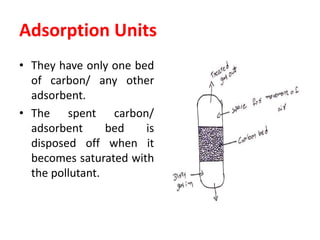
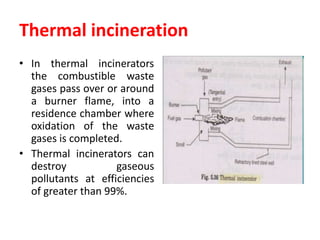
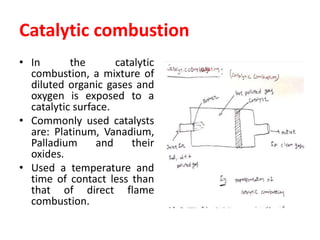
The document discusses methods for controlling gaseous pollutants, including absorption, adsorption, and combustion. Absorption involves passing polluted gases through liquid absorbents like in a packed tower, plate tower, or spray tower. Adsorption uses solid adsorbents like activated carbon to concentrate pollutants on surfaces. Combustion destroys pollutants through direct flame, thermal incineration using a residence chamber, or catalytic combustion using catalysts to aid oxidation. Overall, the document outlines common industrial processes for removing gaseous pollutants from emission streams.