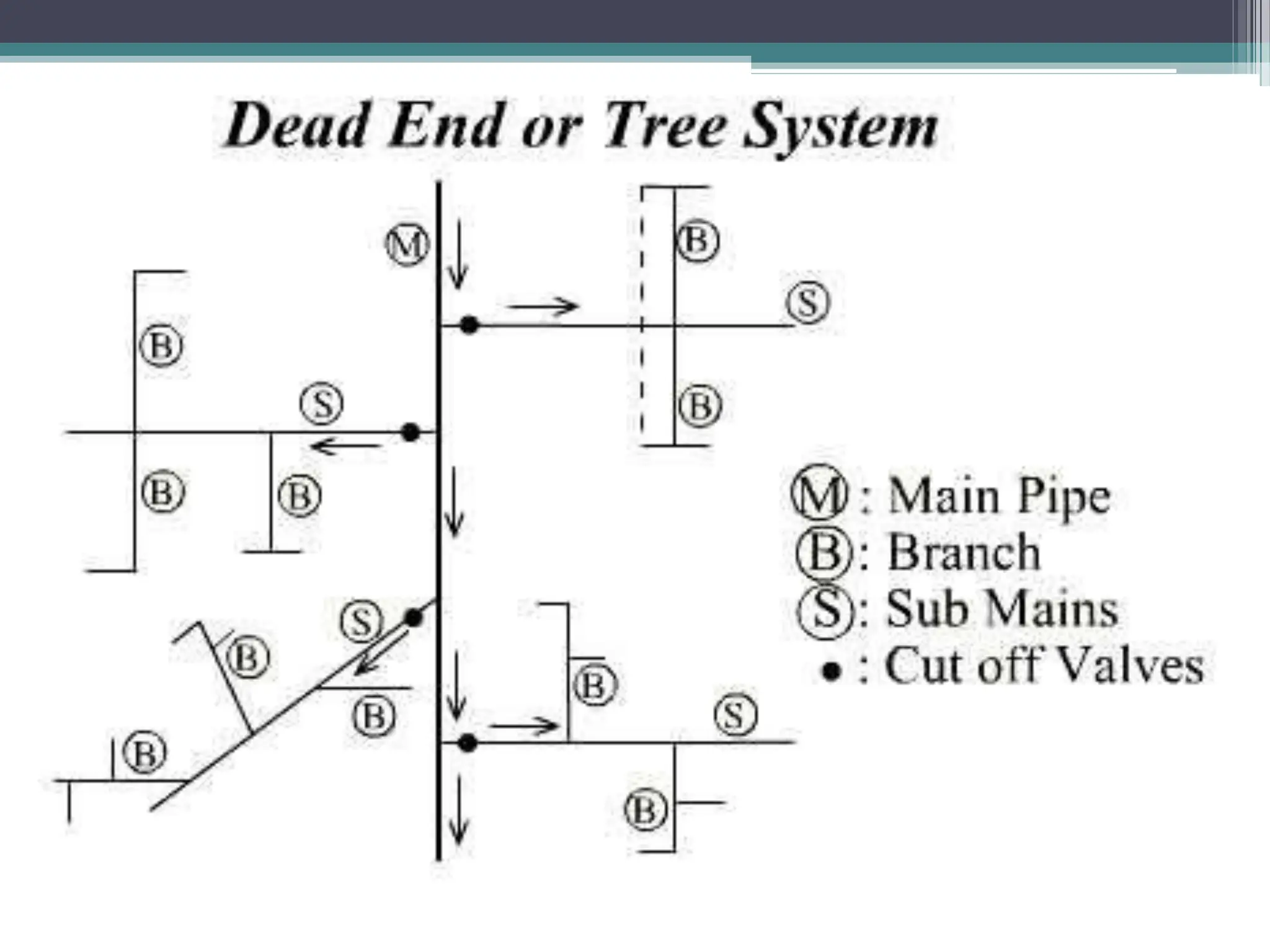
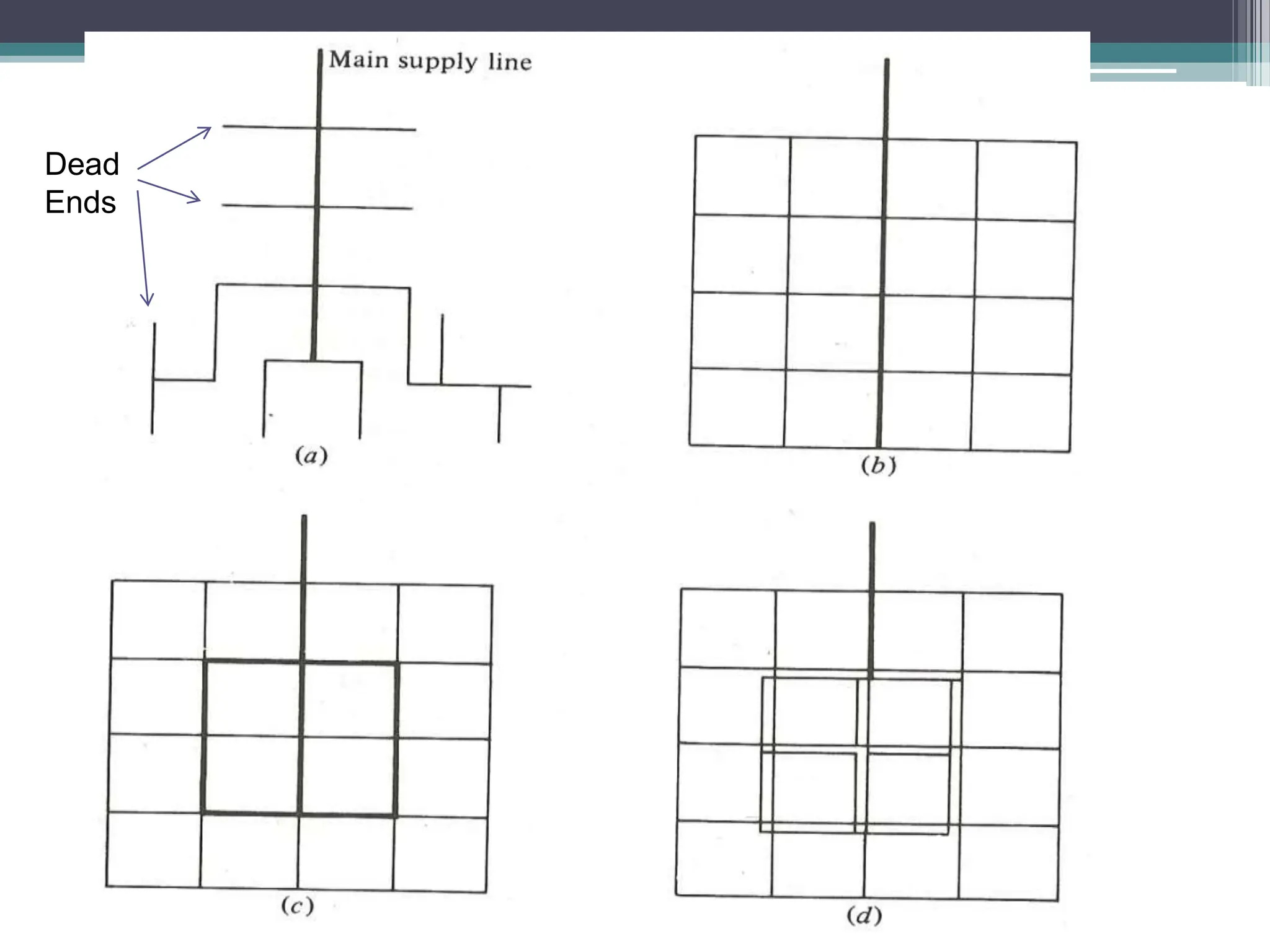
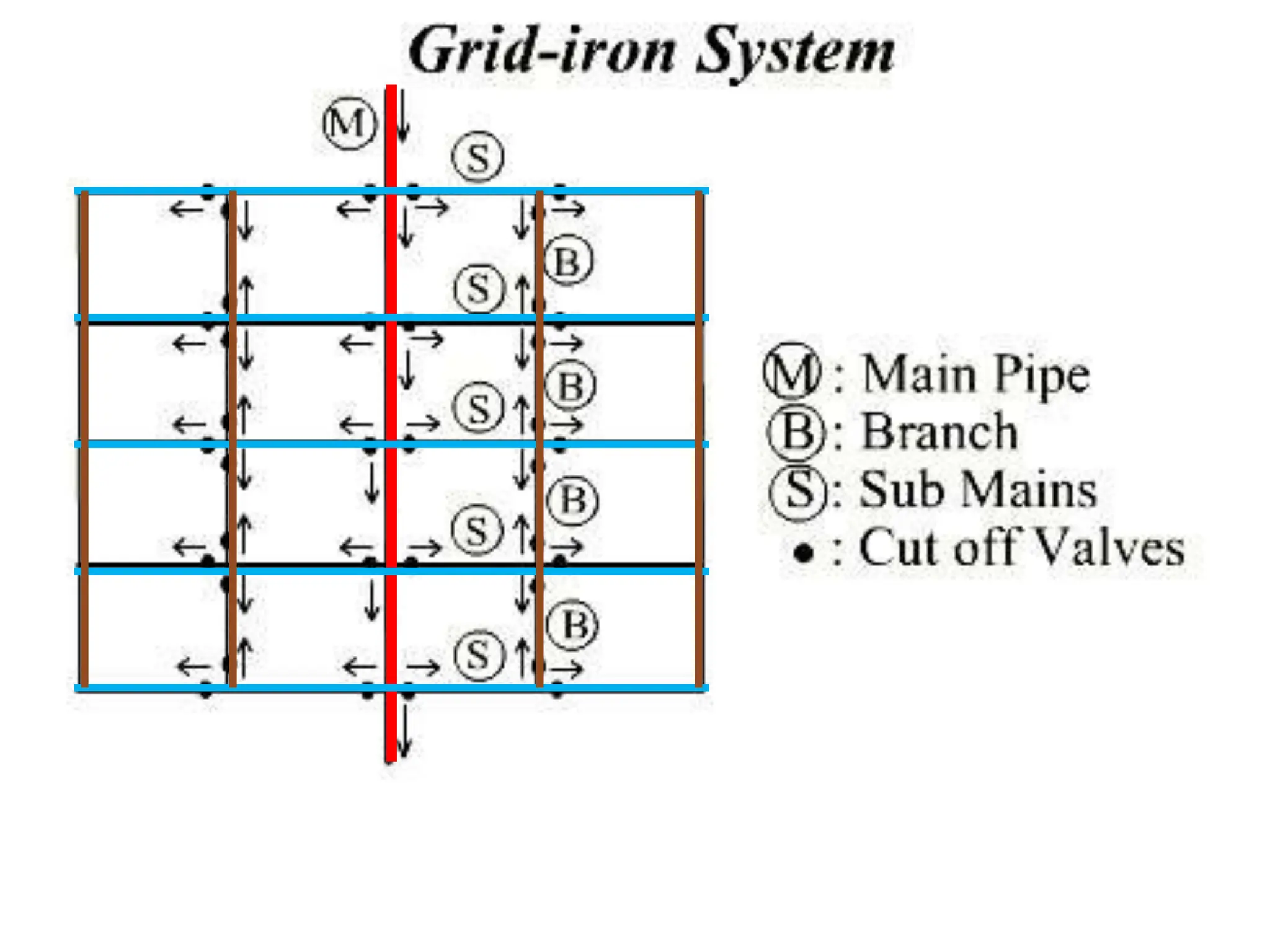
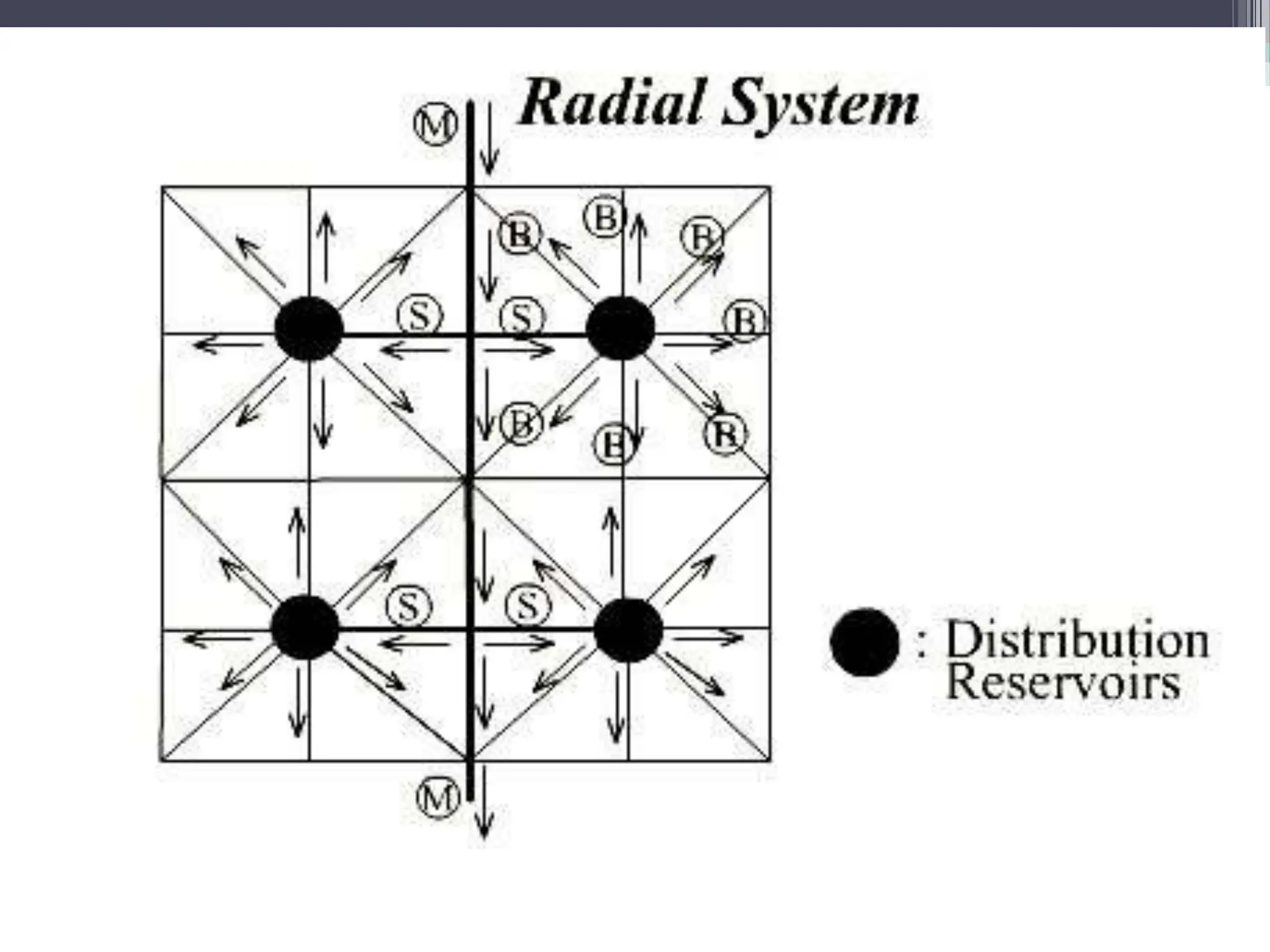
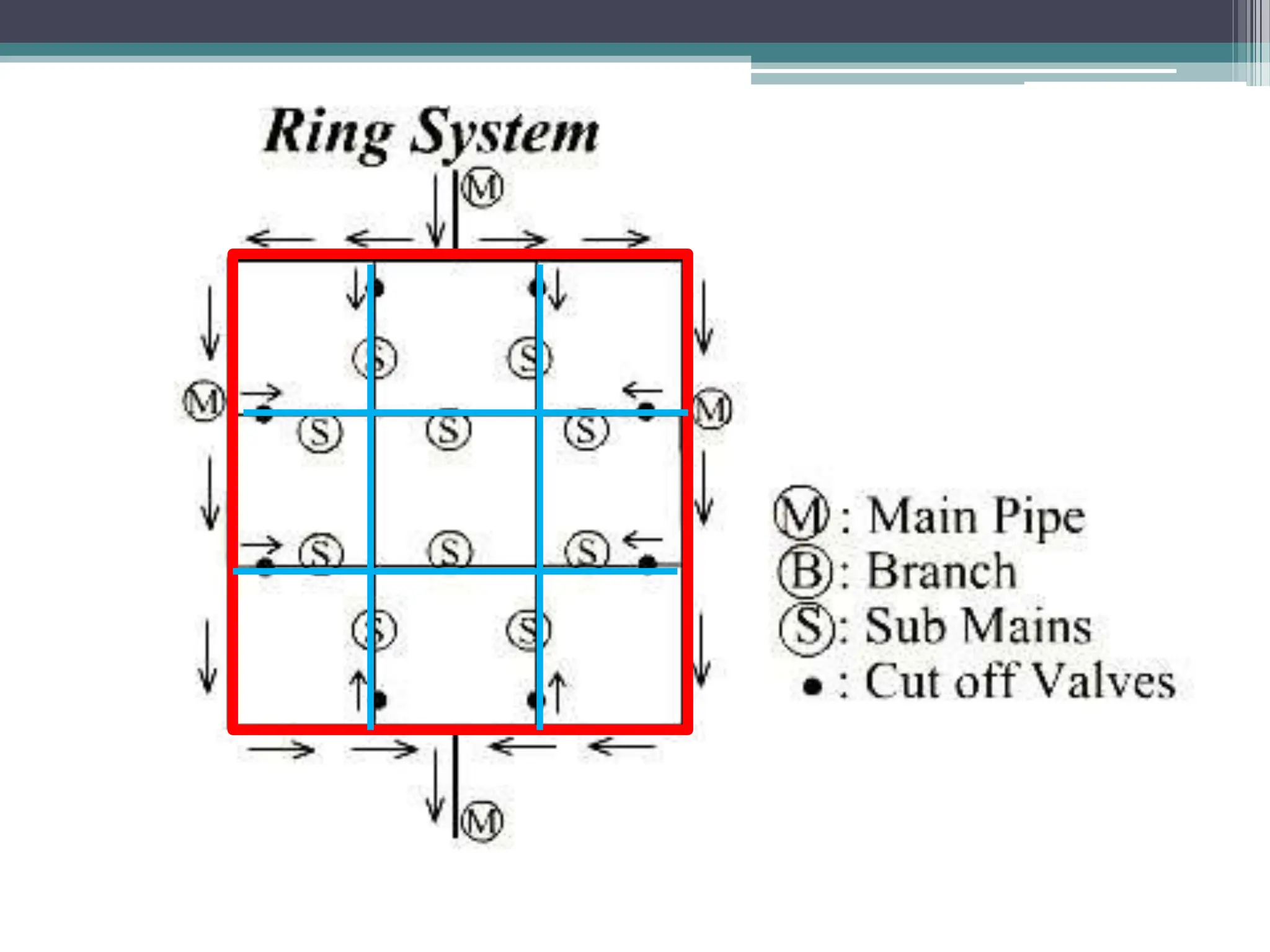
The document discusses various water distribution systems, including the dead end system, grid iron system, radial system, and ring system, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. The dead end system is simple and cost-effective but suffers from stagnation and maintenance issues, while the grid iron system ensures better water circulation but requires more infrastructure. The radial and ring systems provide quick service and flexible water supply, respectively, with their own unique benefits and challenges.