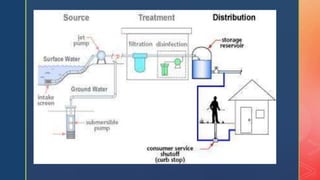
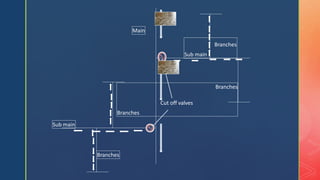
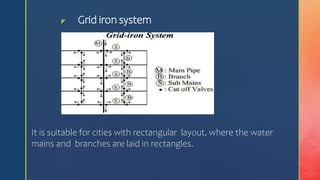
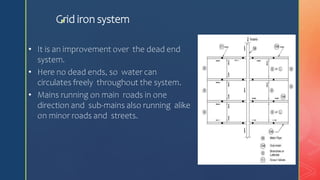
The document discusses distribution systems and pipe layouts. It defines the distribution system as delivering water from pumping stations or conduits throughout a community. Key points:
1. Distribution systems include reservoirs, pipes, valves, and other infrastructure to supply water from its source to points of usage.
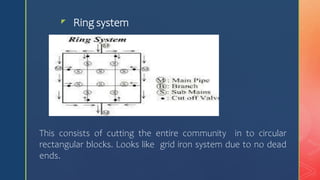
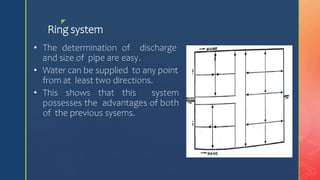
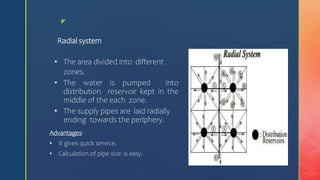
2. Common pipe layouts are dead-end, gridiron, ring, and radial systems. Gridiron systems have fewer dead ends allowing better water circulation.
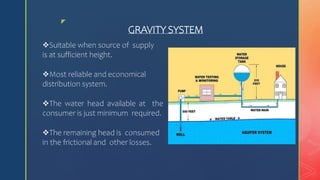
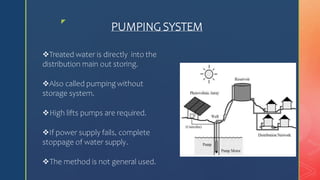
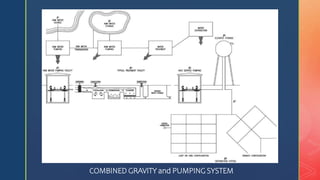
3. Distribution requires sufficient water pressure delivered reliably. Systems include gravity, pumping, or combined approaches using reservoirs to store water for high demand periods.