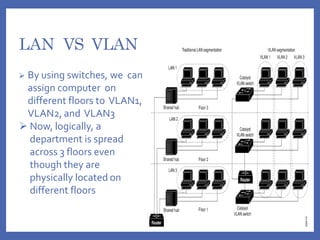
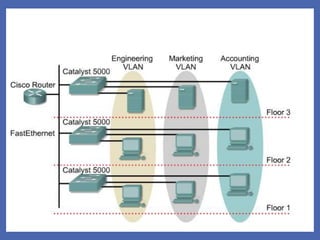
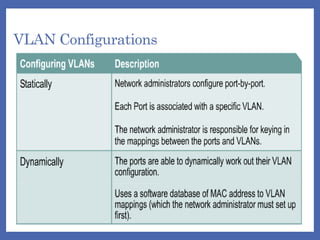
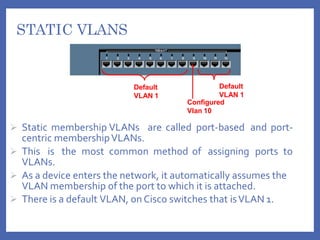
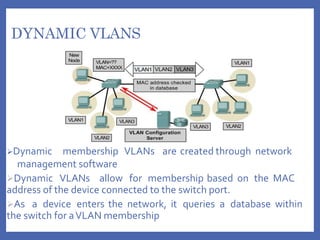
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) logically segments devices within a network, allowing users in different physical locations to communicate as if they are on the same LAN. VLANs can be configured as static or dynamic, with static VLANs assigned based on port connection and dynamic VLANs based on device MAC addresses. Using VLANs improves performance, administration, and security while enabling the formation of virtual workgroups.





![• Switch(config-if)switchport mode
[access|trunk]
• An access port means that the port (interface)
can only belong to a single VLAN.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vlancn-210617084607/85/VLAN-VIRTUAL-LAN-COMPUTER-NETWORKS-11-320.jpg)

