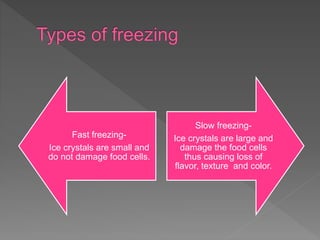
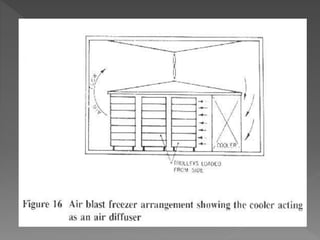
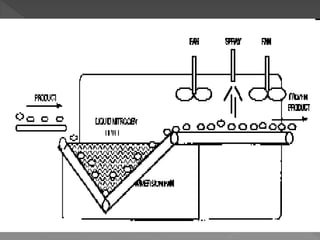
Freezing is a method of food preservation that involves lowering the food's temperature to below the freezing point. It allows food to be preserved by slowing microbial growth and preventing spoilage. There are different freezing methods like air blast freezing, which uses cold air circulated over food on a conveyor belt, and immersion or spray freezing, which sprays or immerses food in refrigerated liquid. The key is freezing food quickly to form small ice crystals that do not damage cells and affect quality. Larger ice crystals from slow freezing can damage texture and flavor.