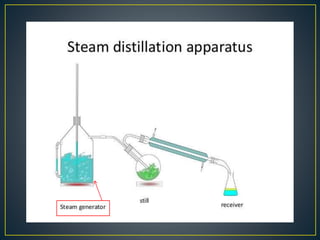
Distillation is a process used to separate mixtures based on differences in their boiling points. It involves heating the mixture to vaporize its components, cooling the vapors to condense them back to liquid, and collecting the condensed liquids separately. There are several types of distillation including simple distillation, fractional distillation, and steam distillation. Distillation is commonly used in pharmaceutical manufacturing to purify water and organic compounds or extract volatile plant constituents. Purified water and water for injection are both prepared using distillation methods to remove impurities, microbes, and pyrogens.