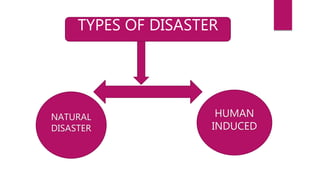
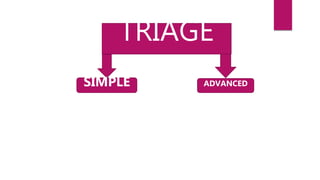
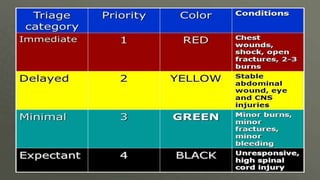
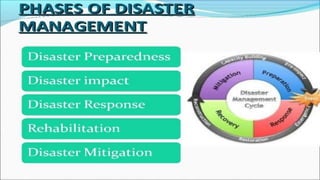
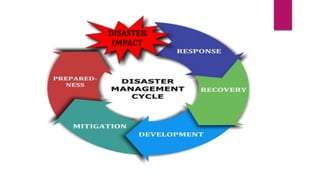
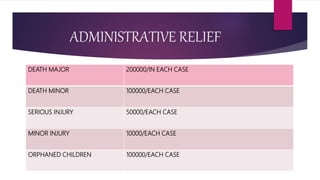
This document discusses disaster nursing. It begins by defining a disaster as any event that causes significant damage, loss of life, or deterioration of health beyond local capacity to respond. It then discusses types of disasters, recent disasters in India, and levels of disaster classification. Key elements of disaster nursing are identified as hazards, vulnerability, capacity, and risk. The document outlines principles of triage and its aims. Phases of disaster management are discussed including preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation. International organizations involved in disaster relief are identified. The document emphasizes the goals and principles of disaster nursing in providing care and meeting needs during and after disasters.