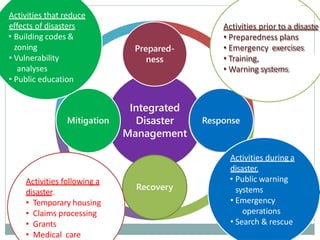
The document provides a comprehensive overview of disaster, including its definitions, types (natural and man-made), and the roles of disaster nursing in responding to emergencies. It outlines the goals, principles, and phases of disaster management, emphasizing the importance of preparedness, response, and recovery. The document highlights the critical role of nurses in disaster situations to assess needs, provide care, and coordinate resources effectively.