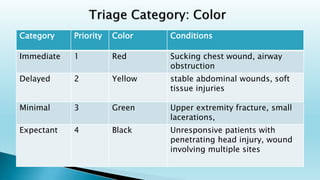
Disaster management involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from disasters. The document defines a disaster and outlines the phases of disaster management including mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. It also discusses the roles and responsibilities of nurses in disaster situations, which include assessment, rescue, recovery efforts, and addressing the psychological impacts on victims.