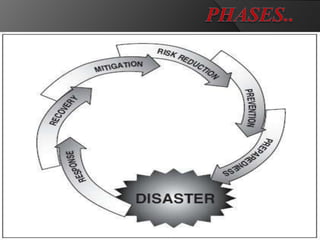
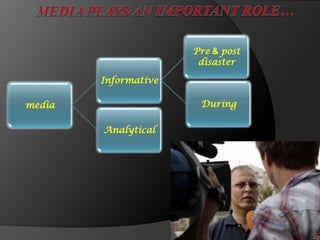
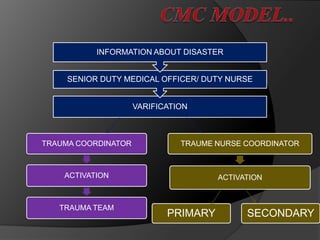
This document discusses disaster nursing and classifies different types of disasters. It defines a disaster as an event that causes damage, destruction, loss of life, and deterioration of health services beyond the normal capacity of the affected community. Disasters are classified as natural (e.g. floods, earthquakes), man-made (e.g. fires, wars), technological (e.g. industrial accidents), or complex emergencies. The document outlines the phases of a disaster from pre-impact planning to post-impact recovery. It discusses challenges for nursing in disasters and the importance of preparation, training, and an all-hazards approach to planning.