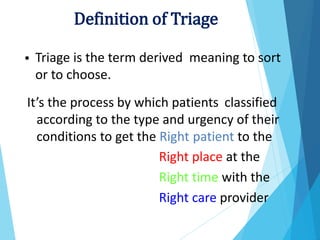
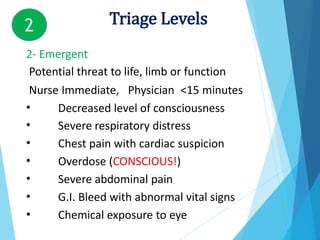
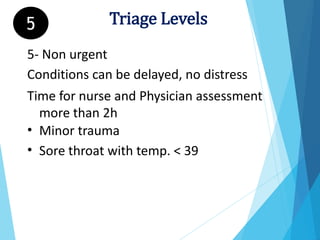
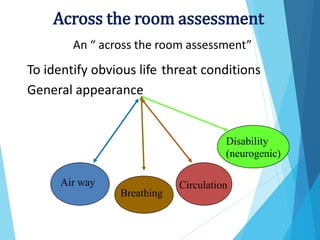
Triage is the process of prioritizing patients based on the urgency of their condition. It aims to direct patients to the right care provider and level of care in a timely manner. During triage, patients are assessed and assigned a color code of red, yellow, green, or black to indicate if their condition is immediate, delayed, minor, or expectant. This determines the order and priority of treatment. The triage nurse's role is to quickly assess patients, maintain privacy, control crowds, communicate with staff, and direct patients to the appropriate care.