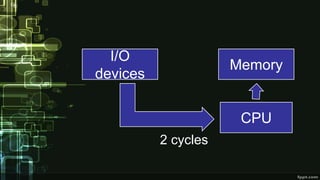
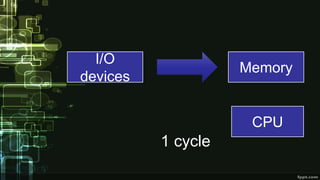
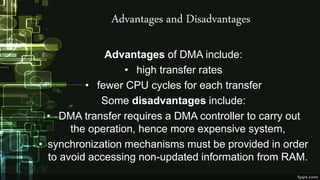
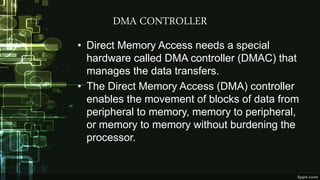
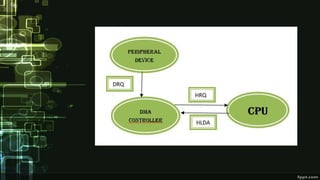
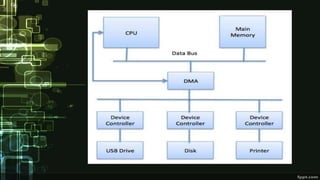
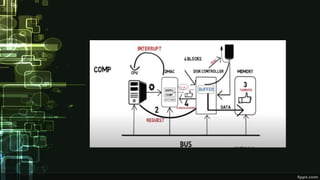
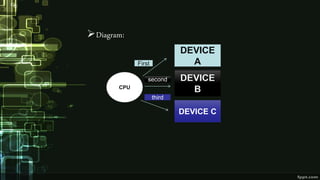
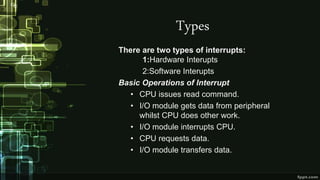
This document provides information about direct memory access (DMA) and input/output (I/O) techniques used by operating systems. It lists six group members and their topics which include DMA, how it works, and comparisons of polling and interrupts. DMA allows hardware devices to access memory independently of the CPU. The operating system uses DMA hardware by instructing a device driver to transfer data to a buffer, then the disk controller performs the DMA transfer to that address. Polling checks device status periodically while interrupts use hardware signals to notify the CPU when a device needs attention.