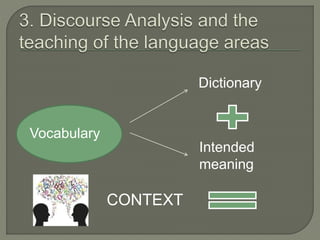
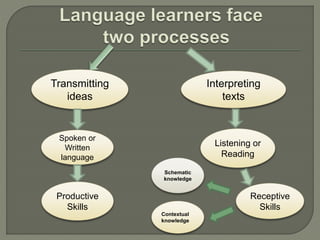
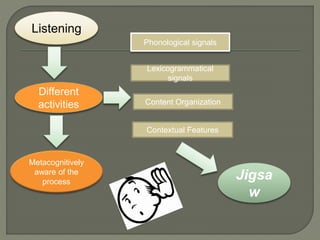
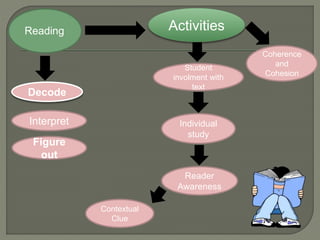
The document explores the relationship between discourse analysis and language teaching, emphasizing the importance of shared knowledge and context in the learning process. It discusses various aspects such as discourse in the classroom, language skills, and the features of discourse communities that contribute to effective communication. The conclusion advocates for improved training for language teachers in discourse analysis and the development of a discourse-oriented curriculum.