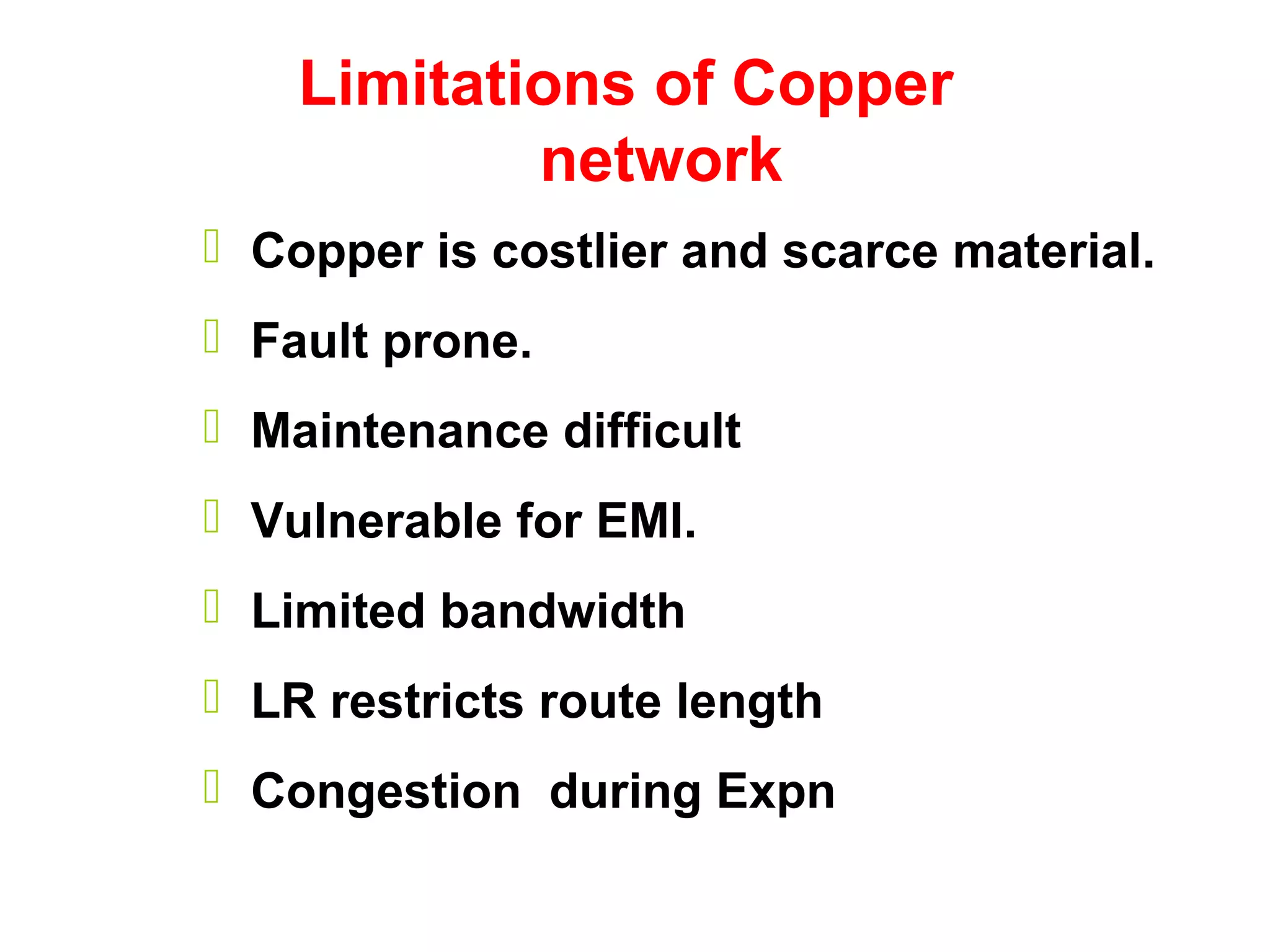
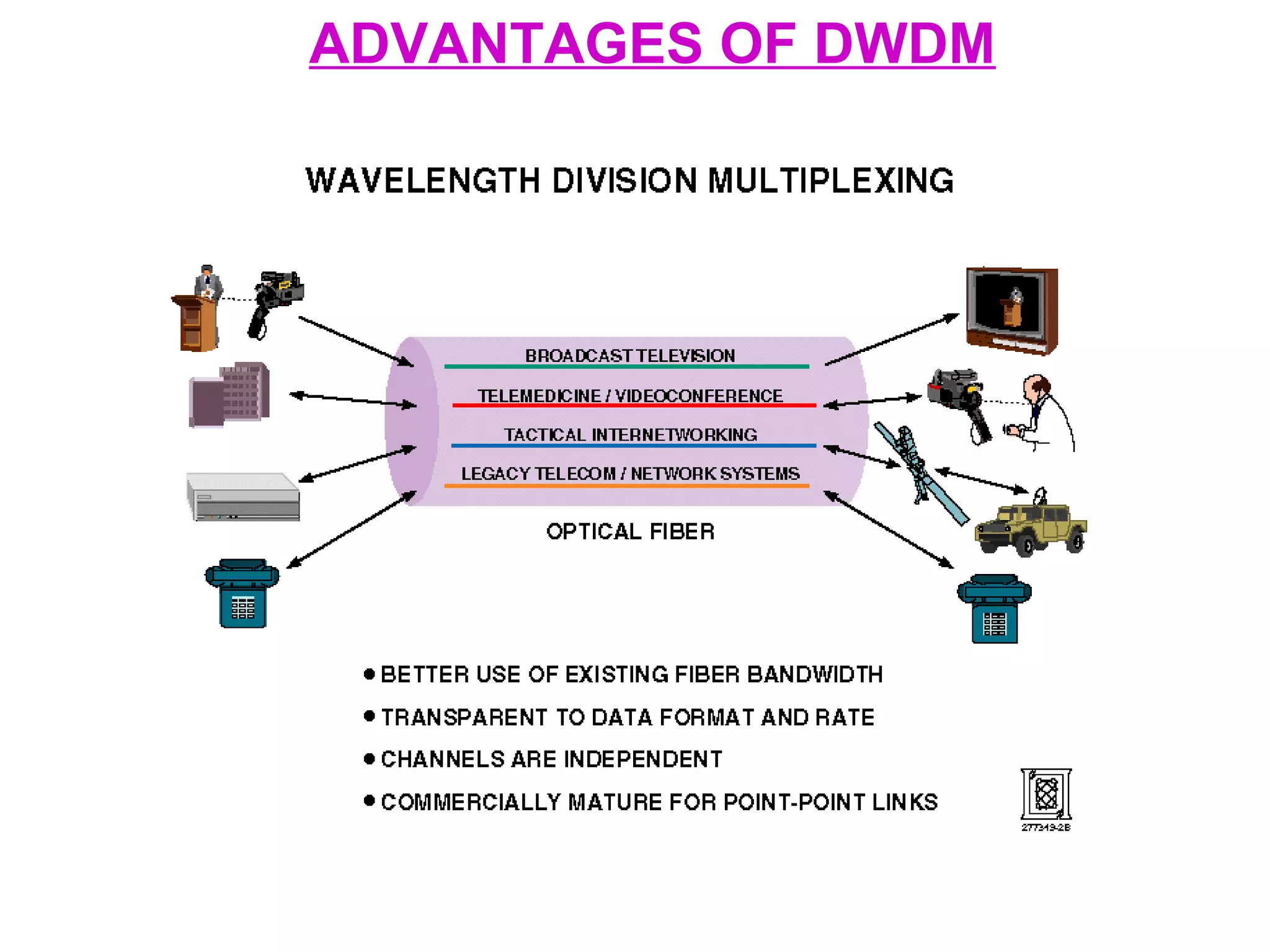
- Copper networks have limitations such as being costly, fault-prone, difficult to maintain, and having limited bandwidth. Optical fiber cables address these issues with advantages like unlimited bandwidth, low loss, electromagnetic immunity, small size, and greater safety.
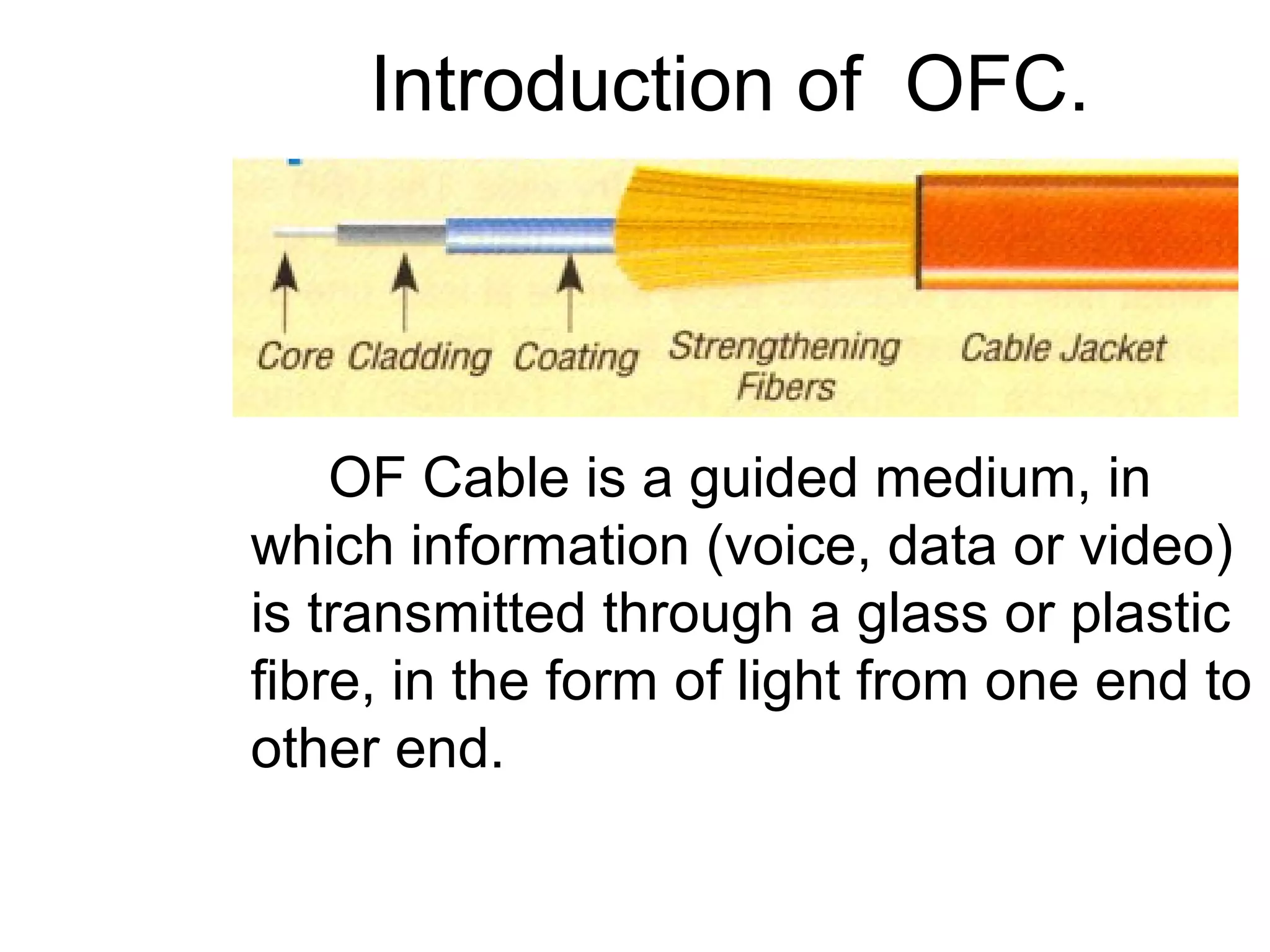
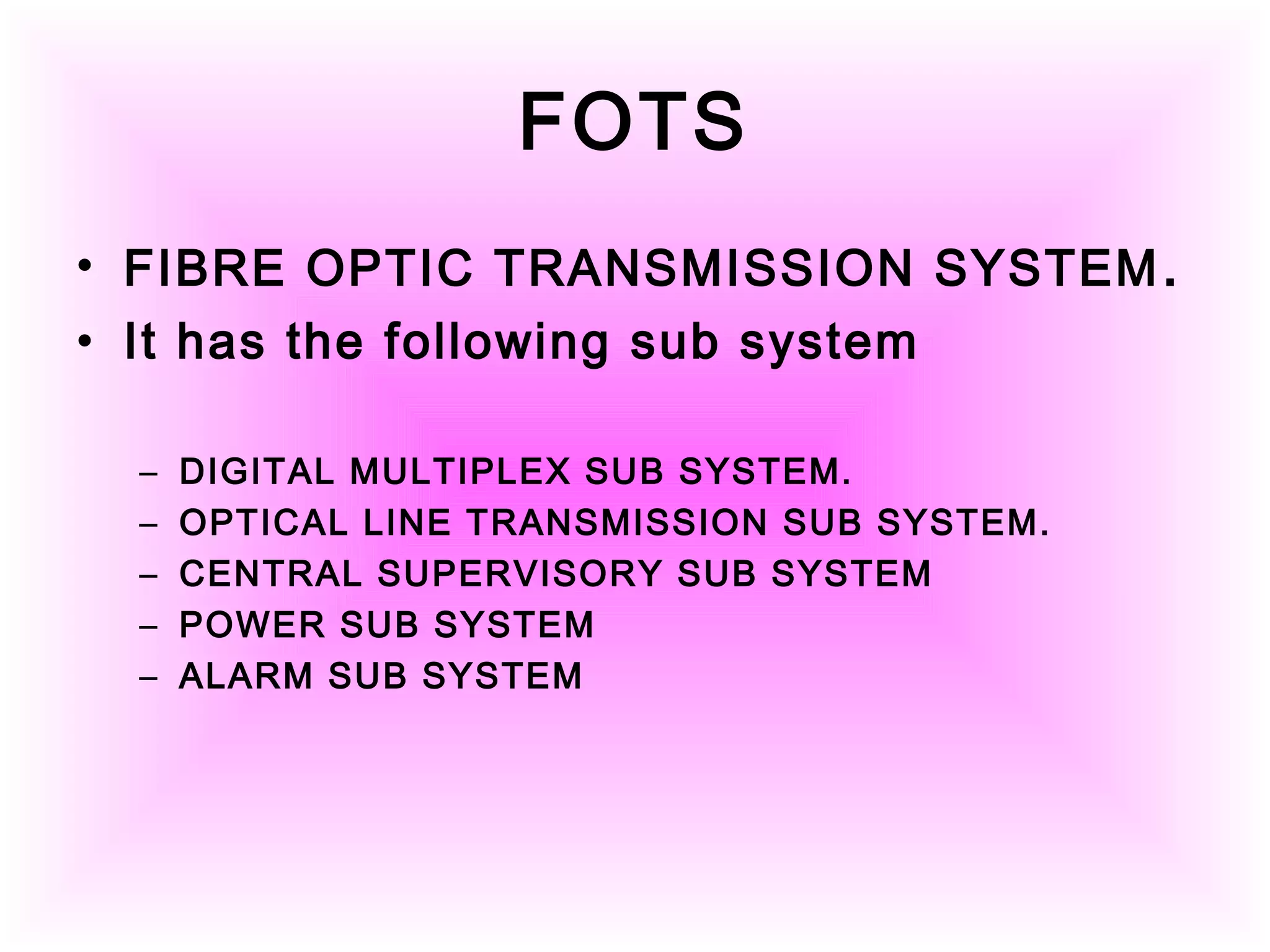
- Optical fiber cable is a guided medium that transmits information in the form of light through glass or plastic fibers. It is used in telecom networks, undersea cables, and other applications requiring high bandwidth or immunity to electromagnetic interference.
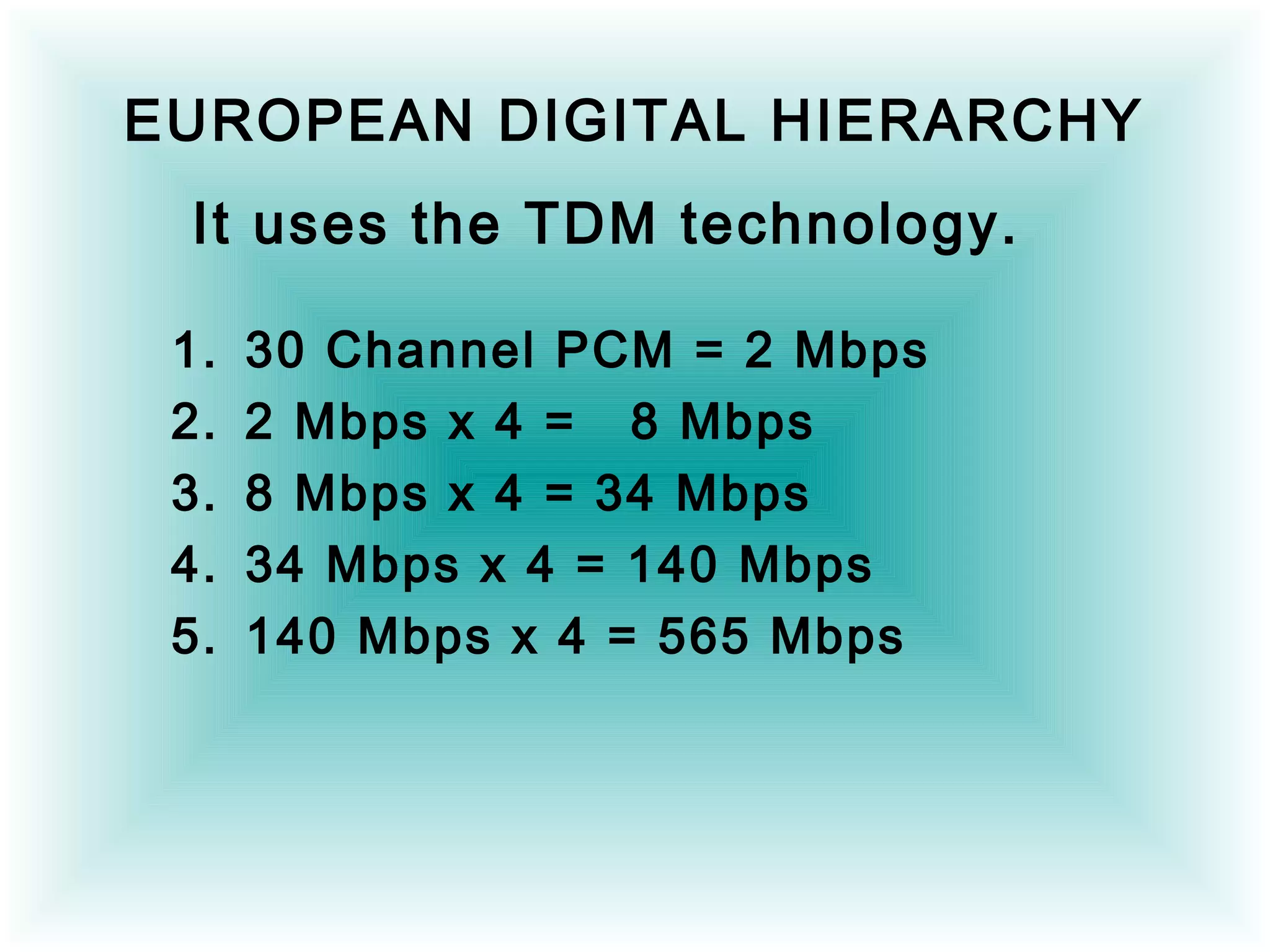
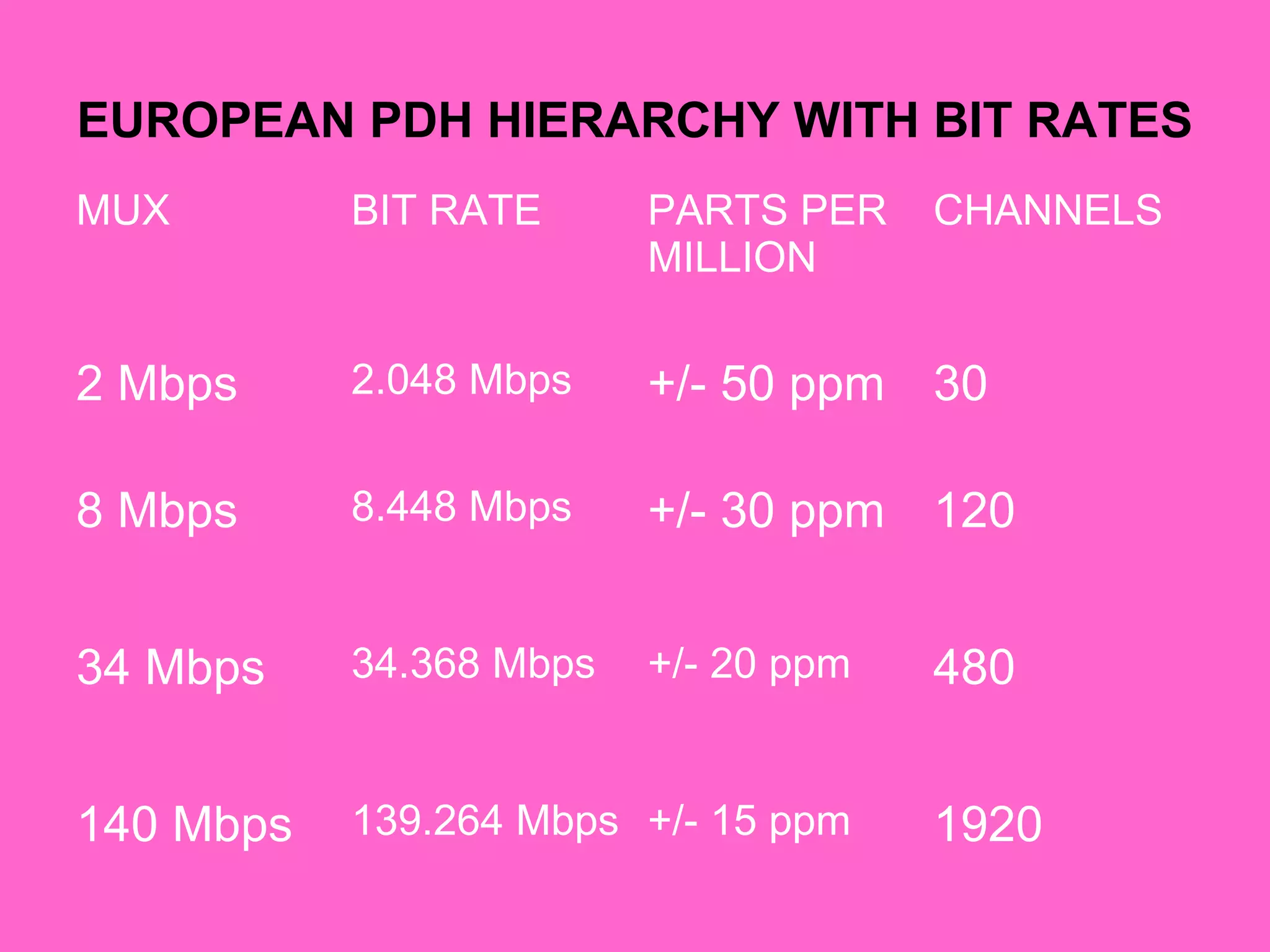
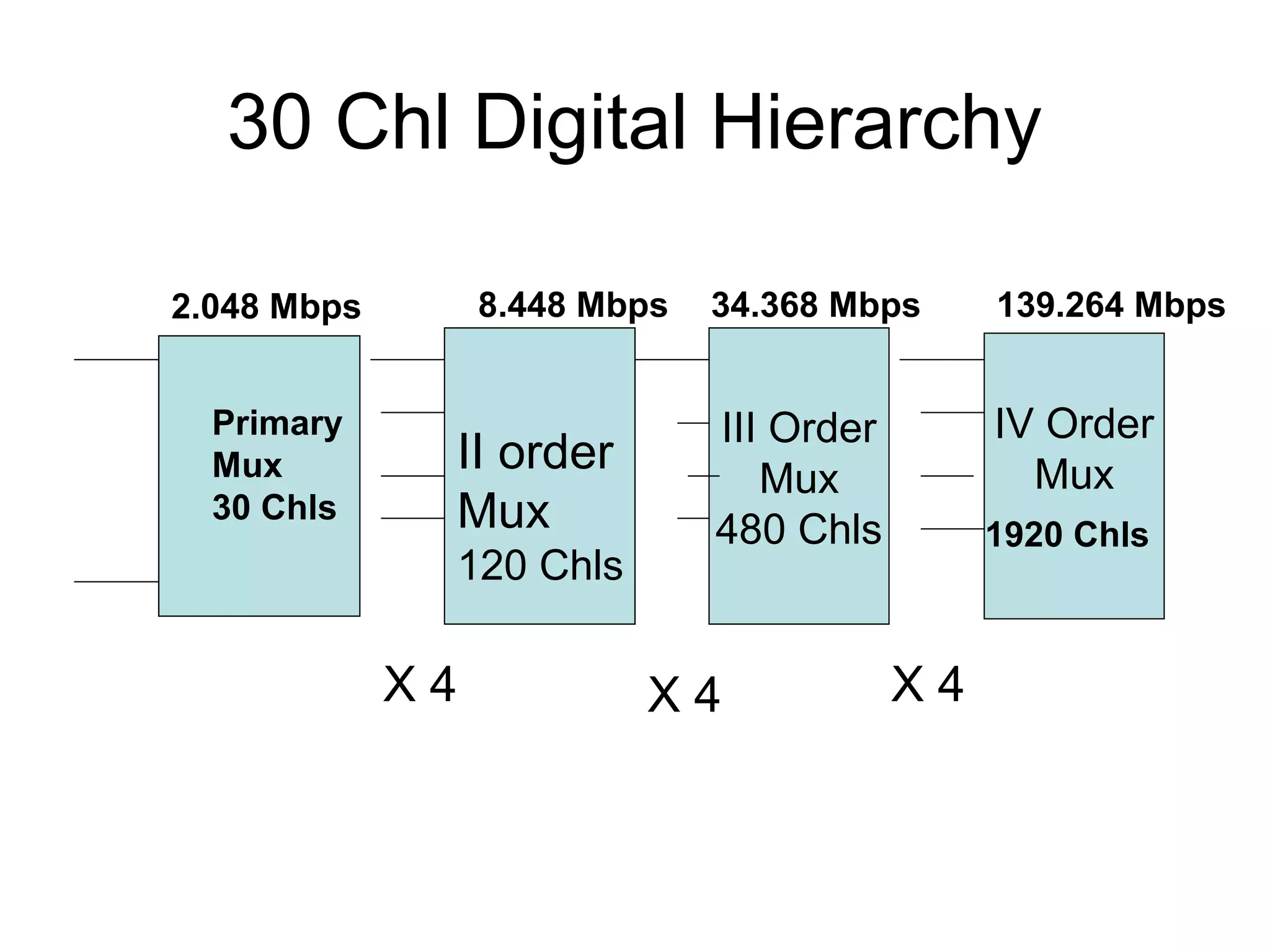
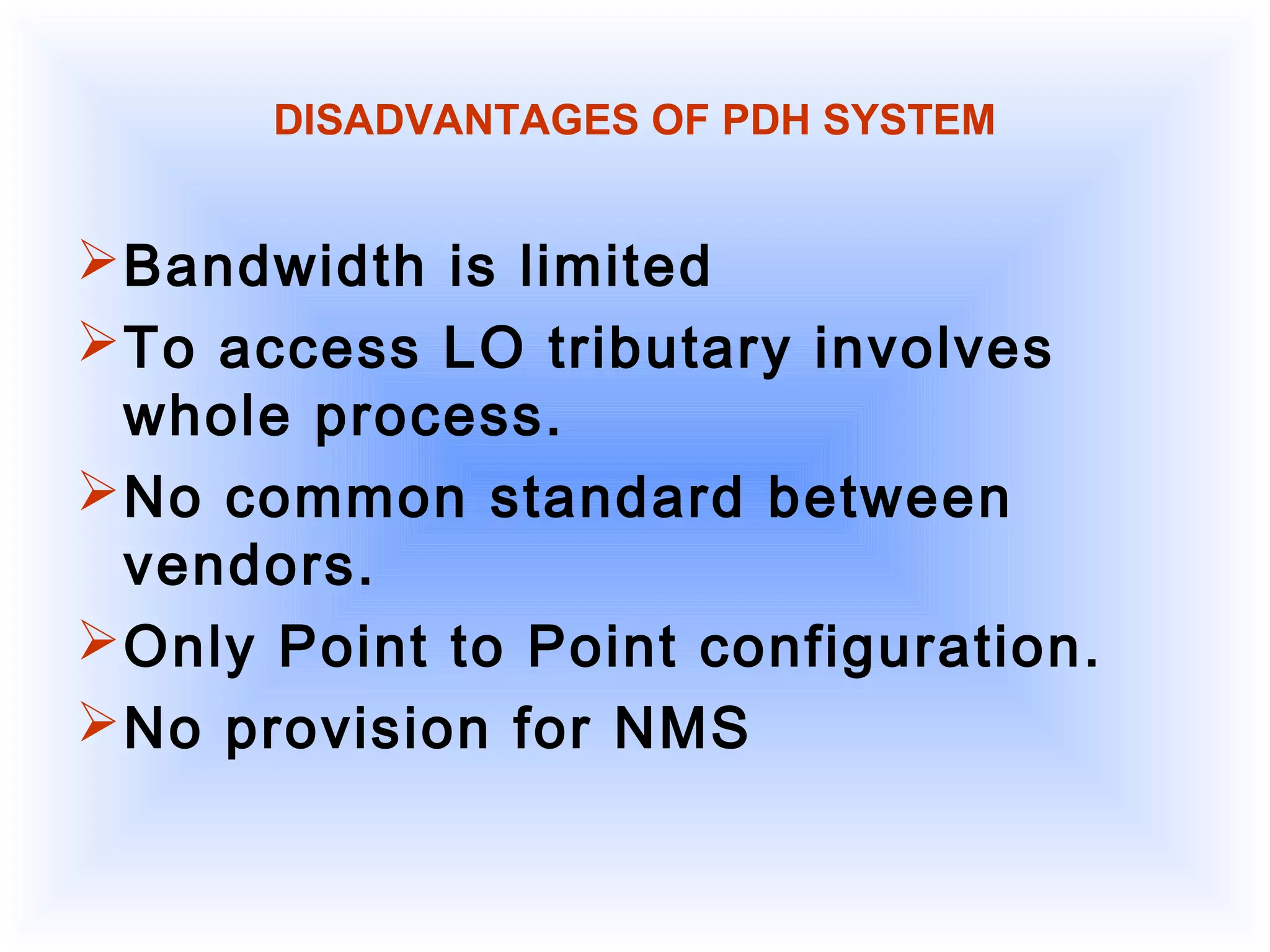
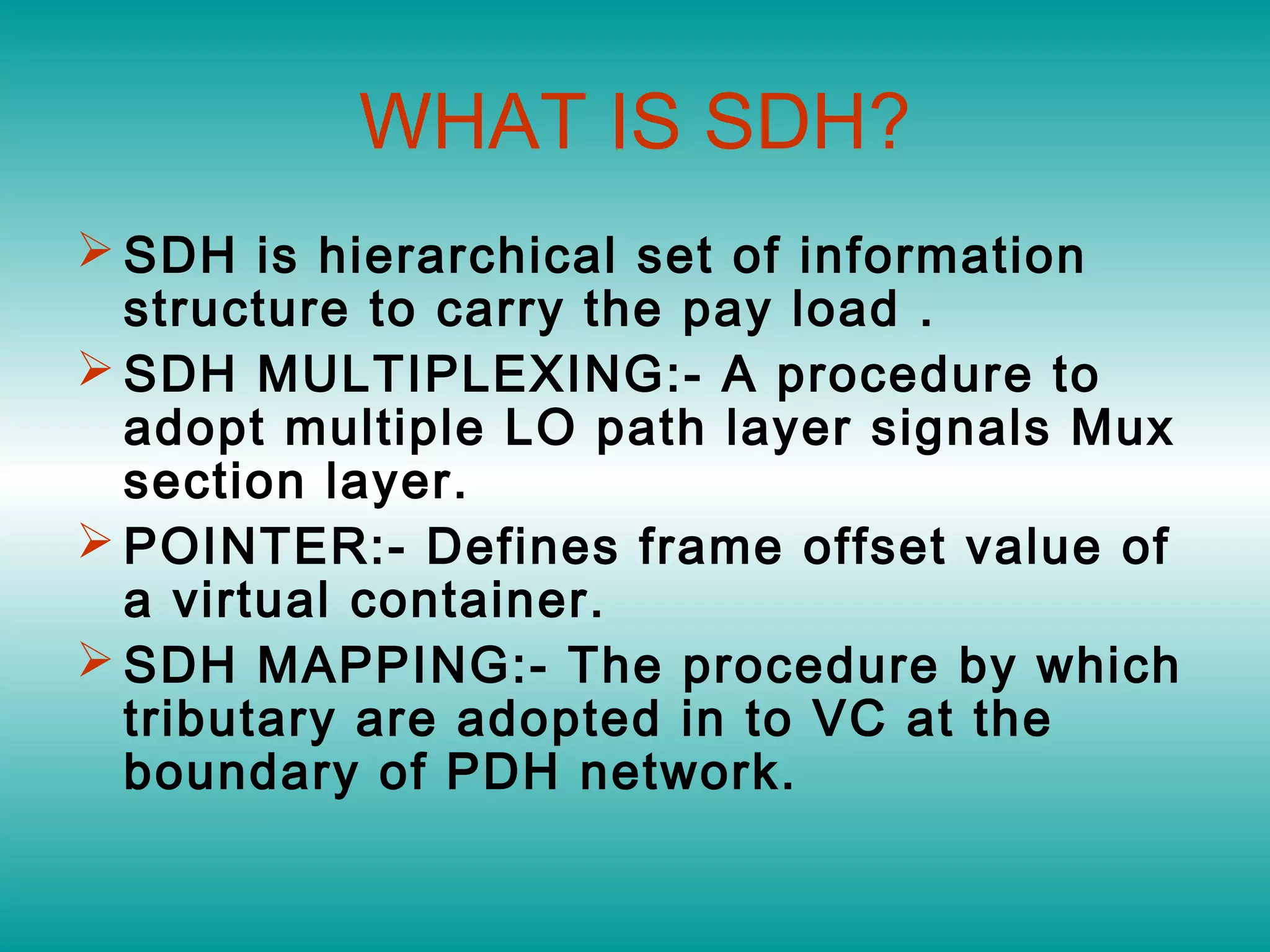
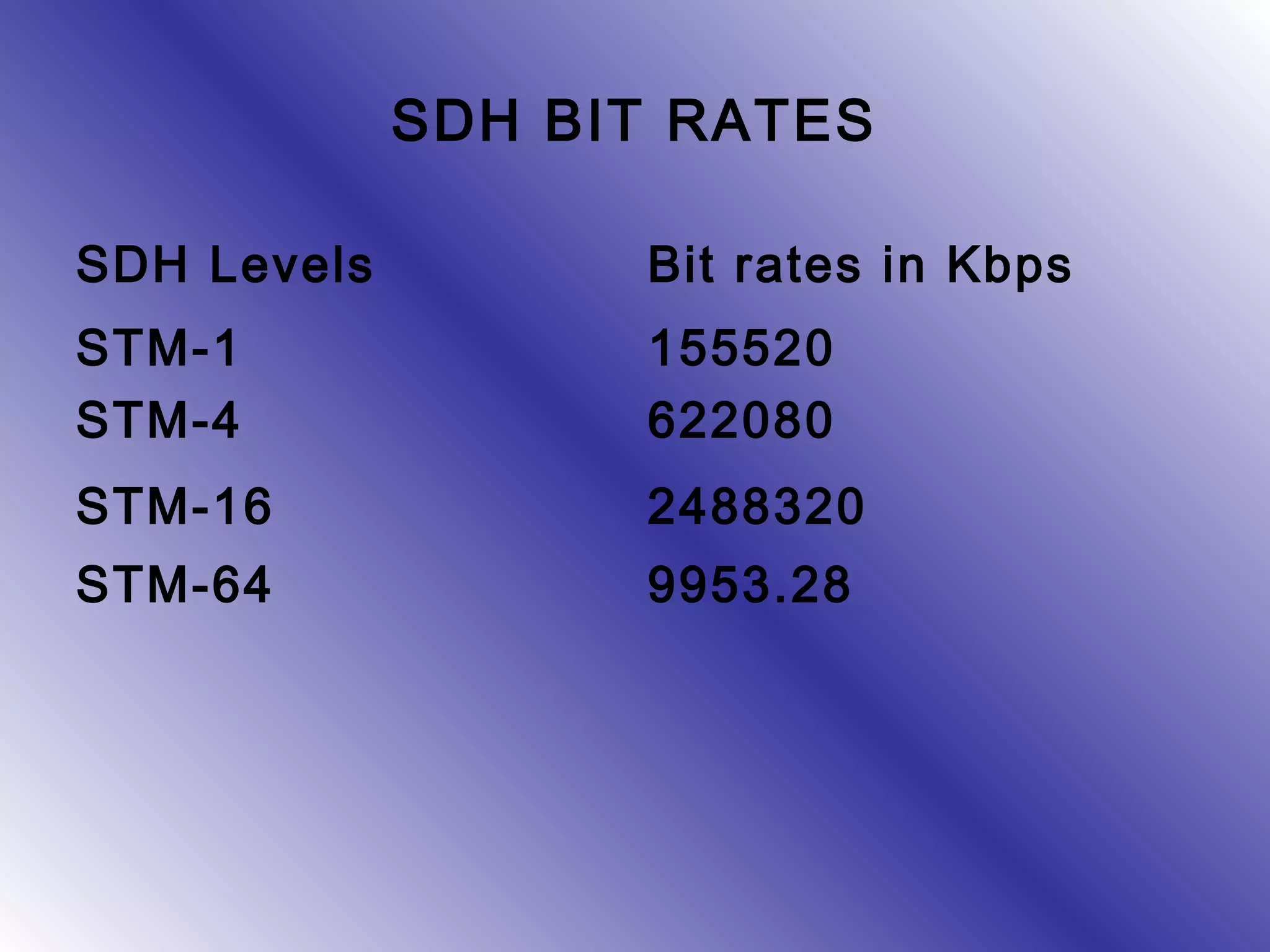
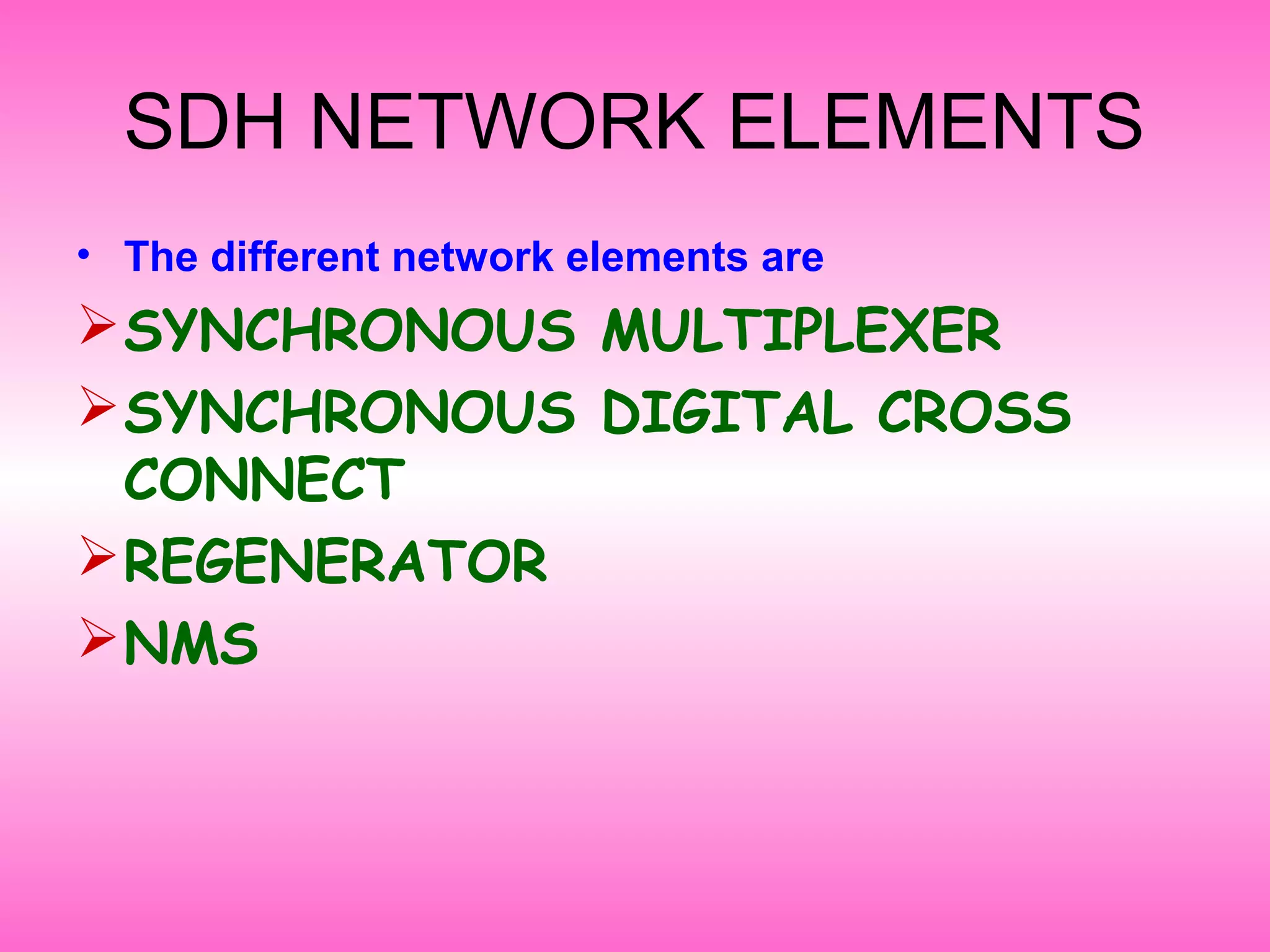
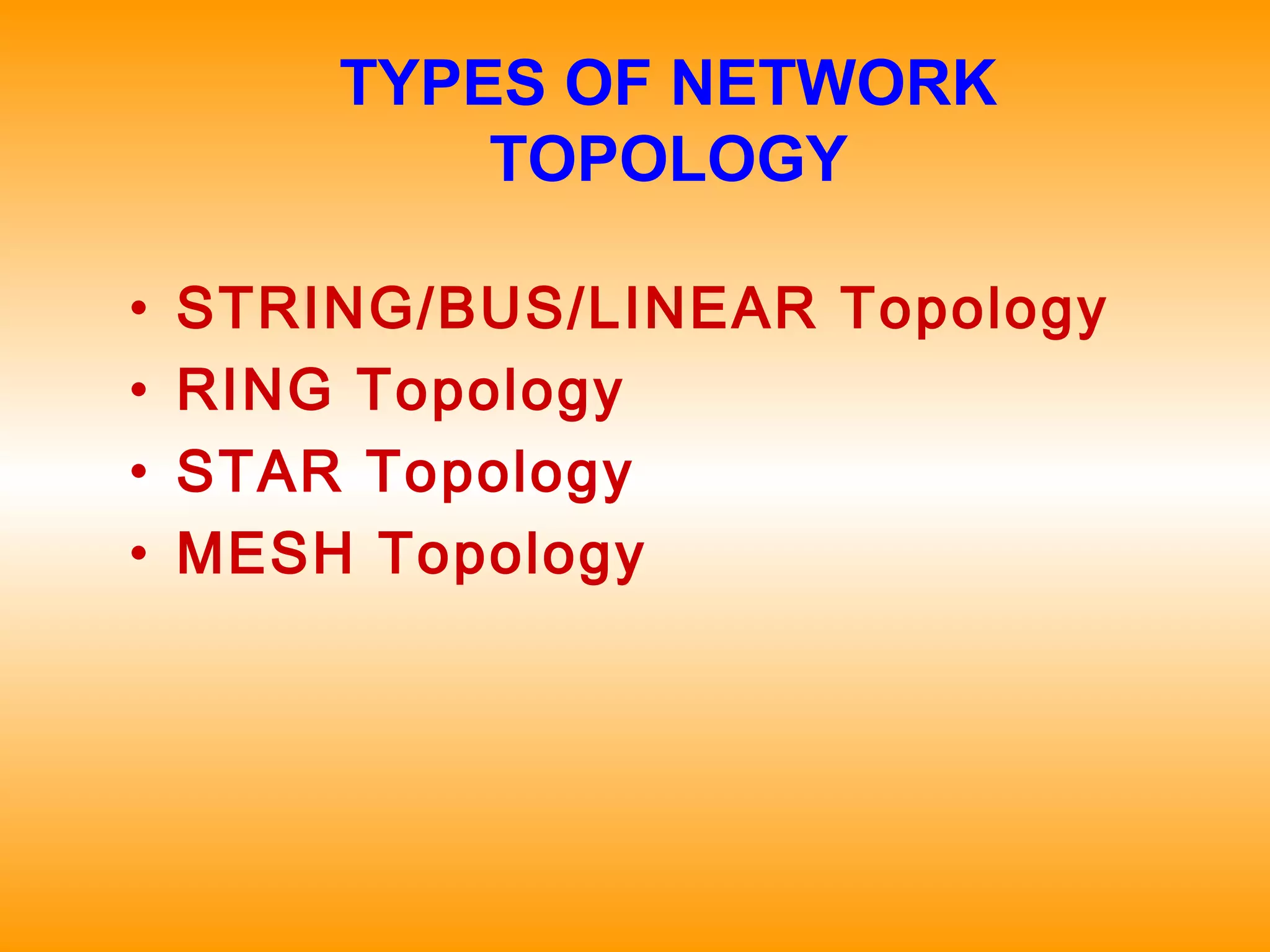
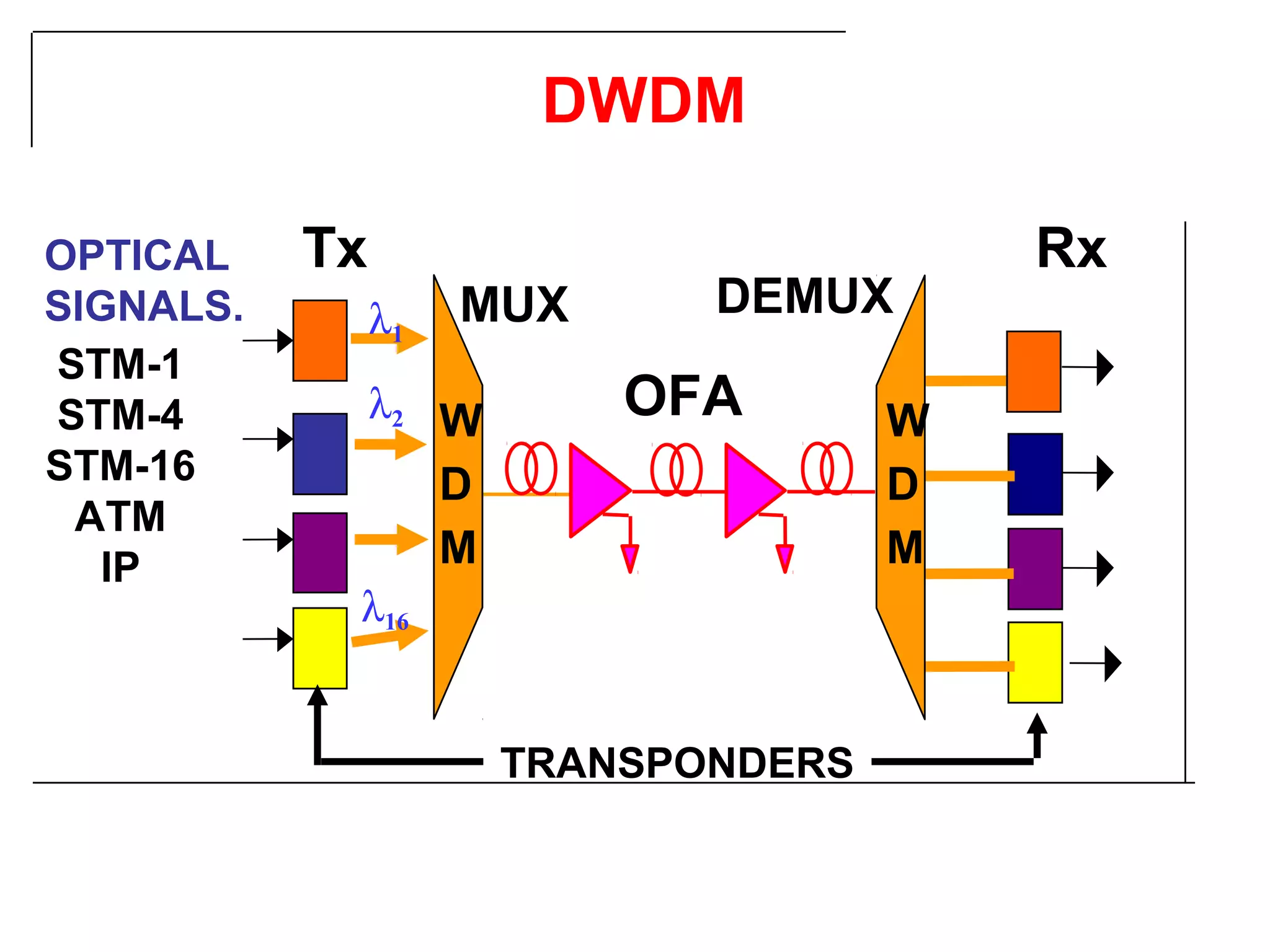
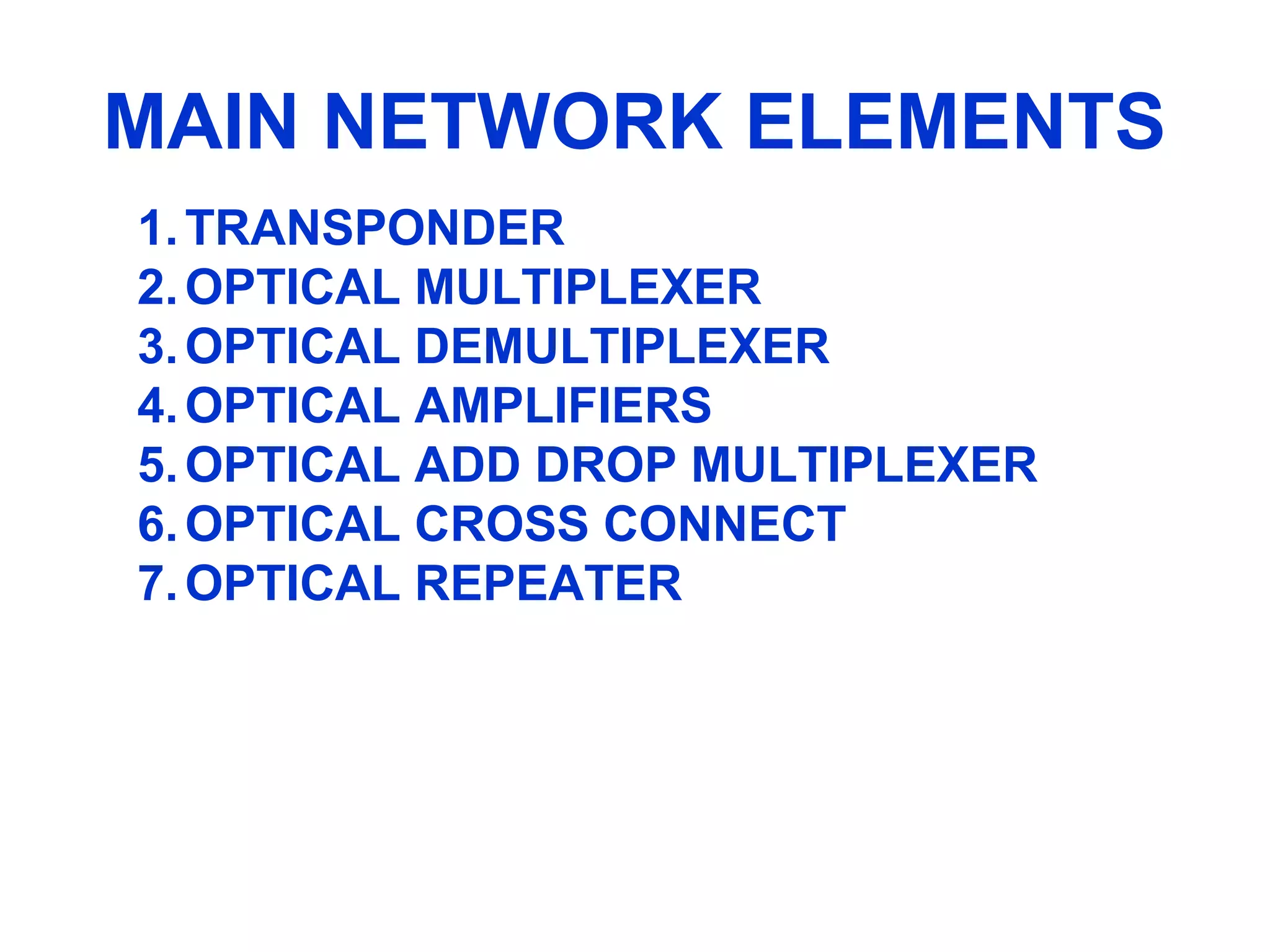
- Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) was developed to overcome disadvantages of Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) networks like limited bandwidth and lack of common standards. SDH allows direct access to lower