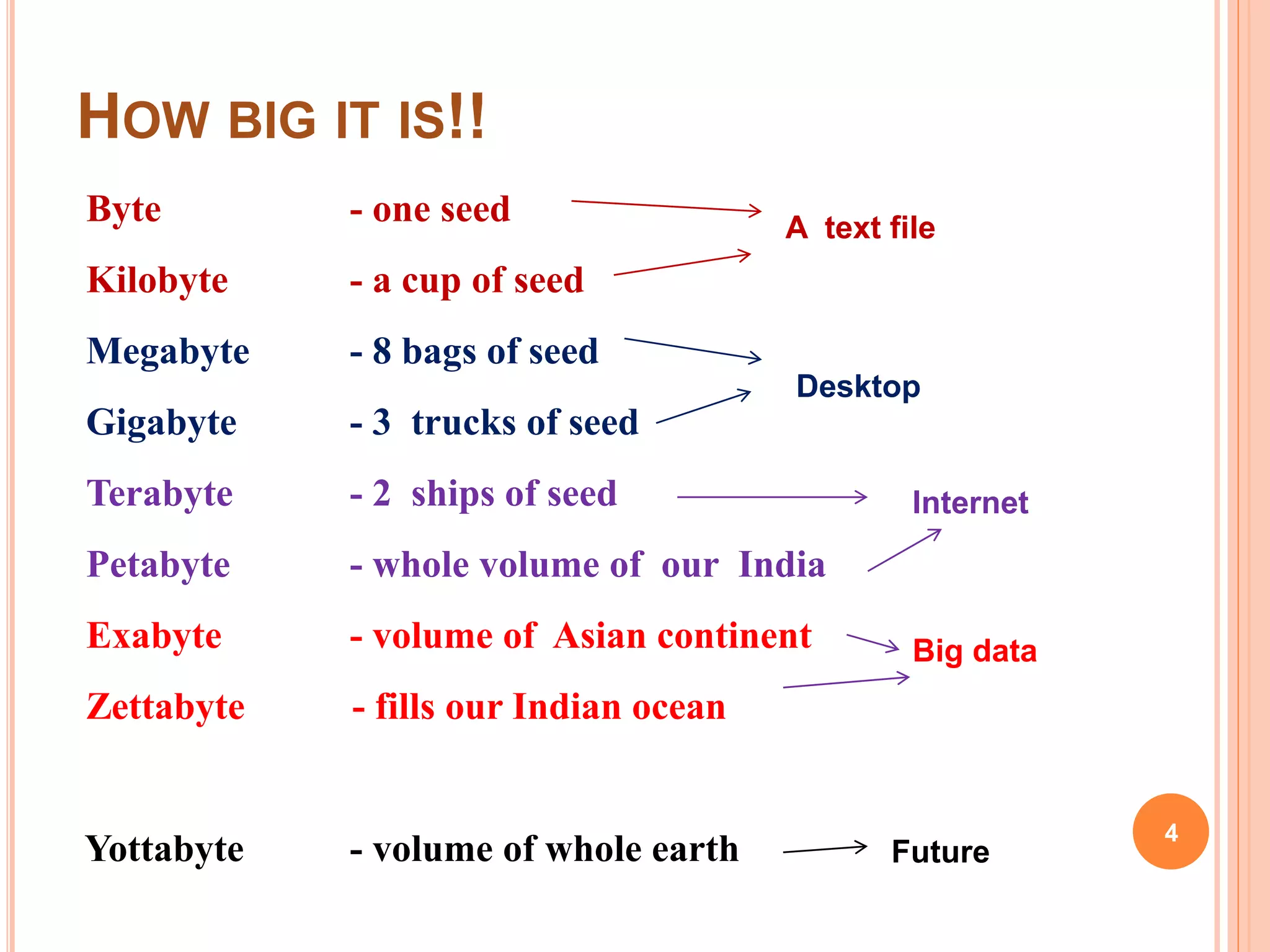
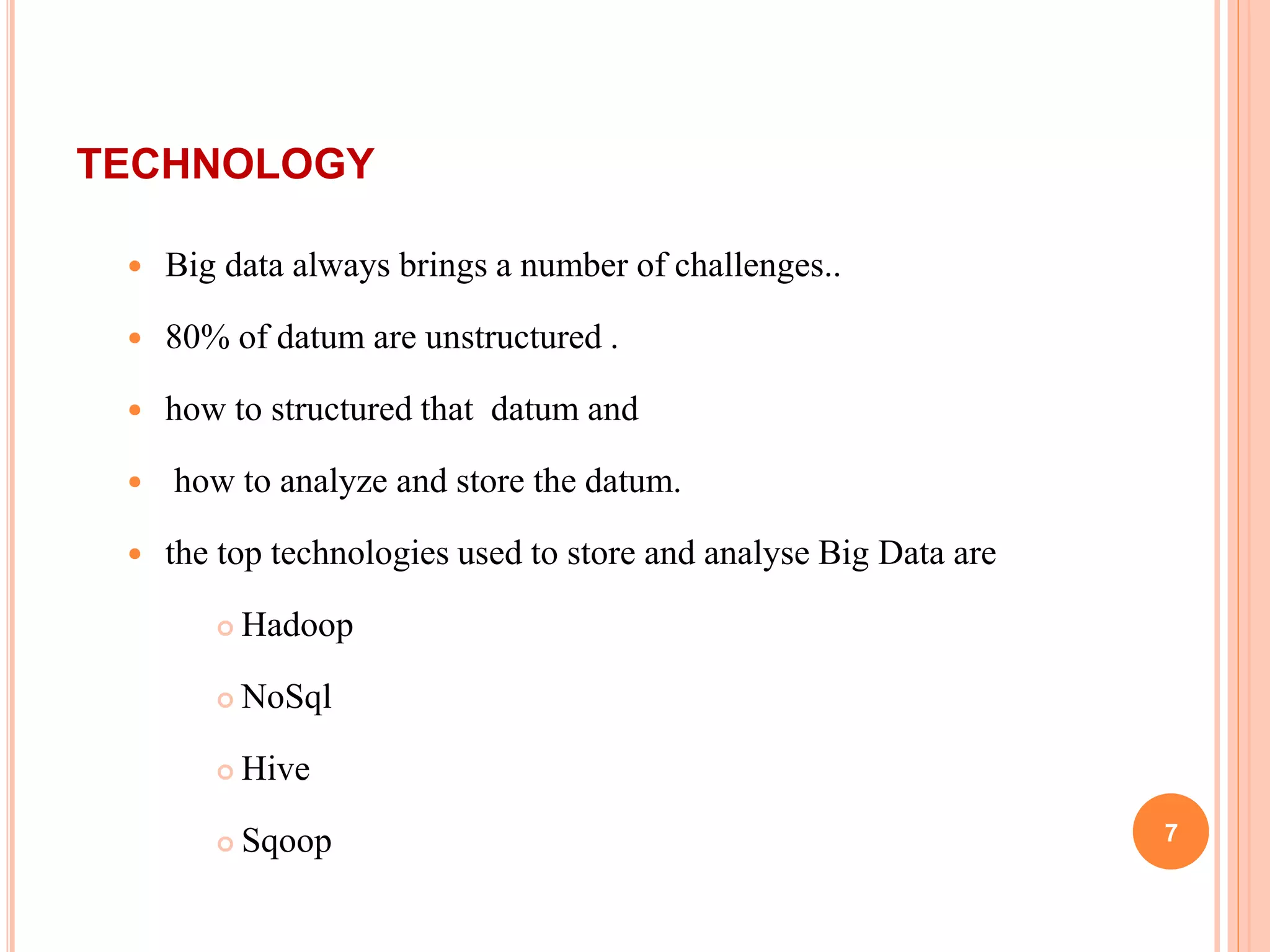
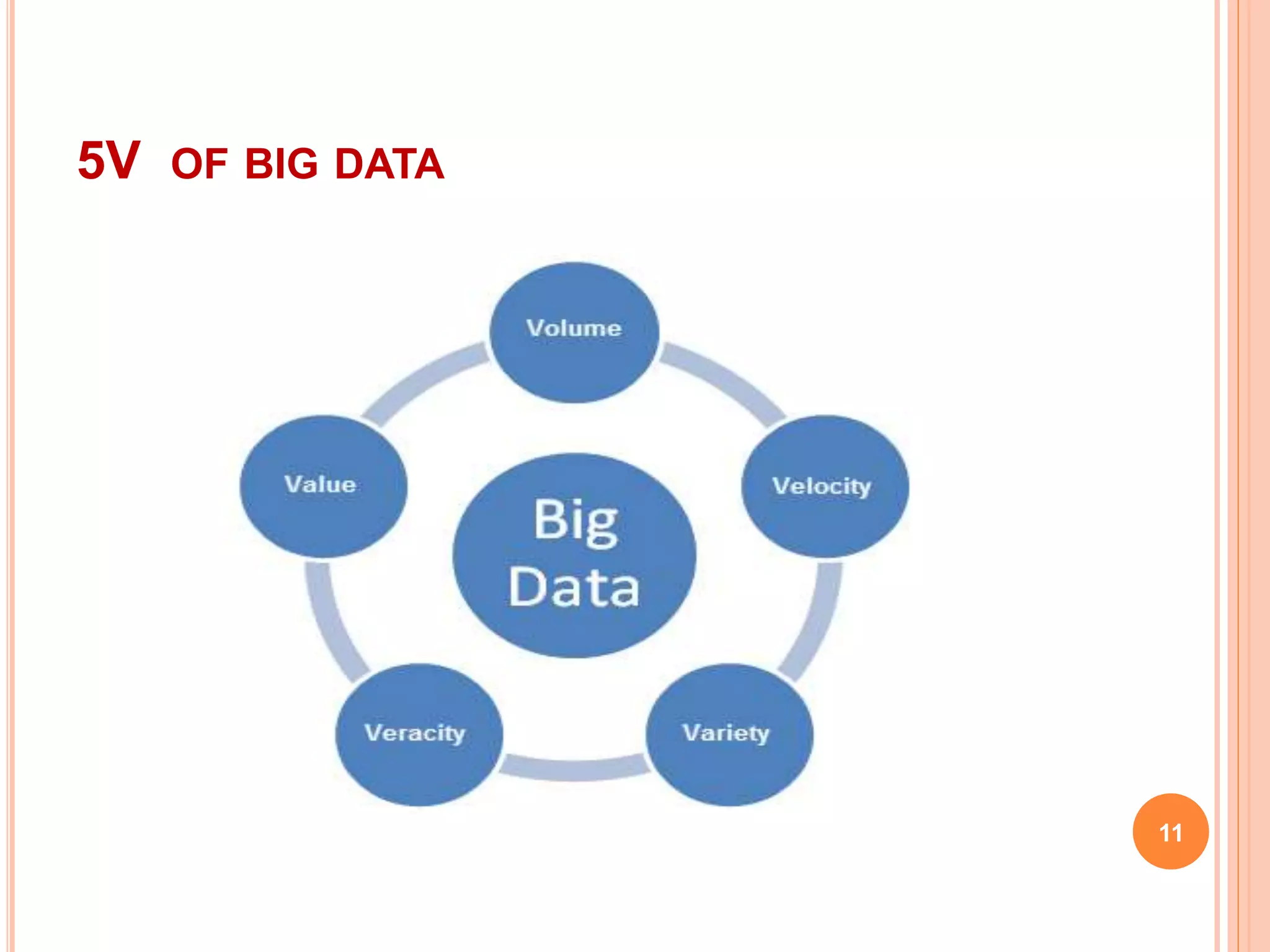
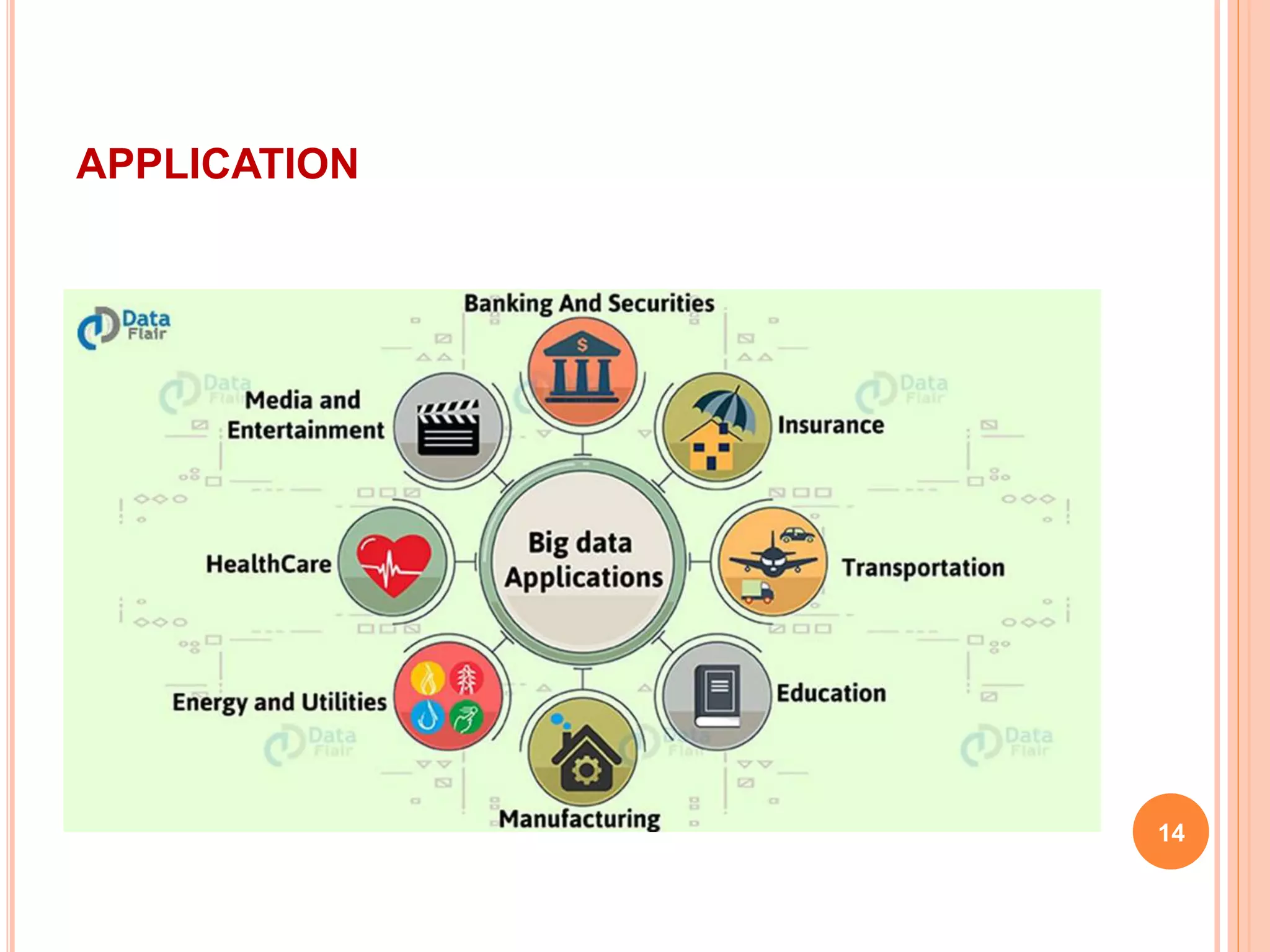
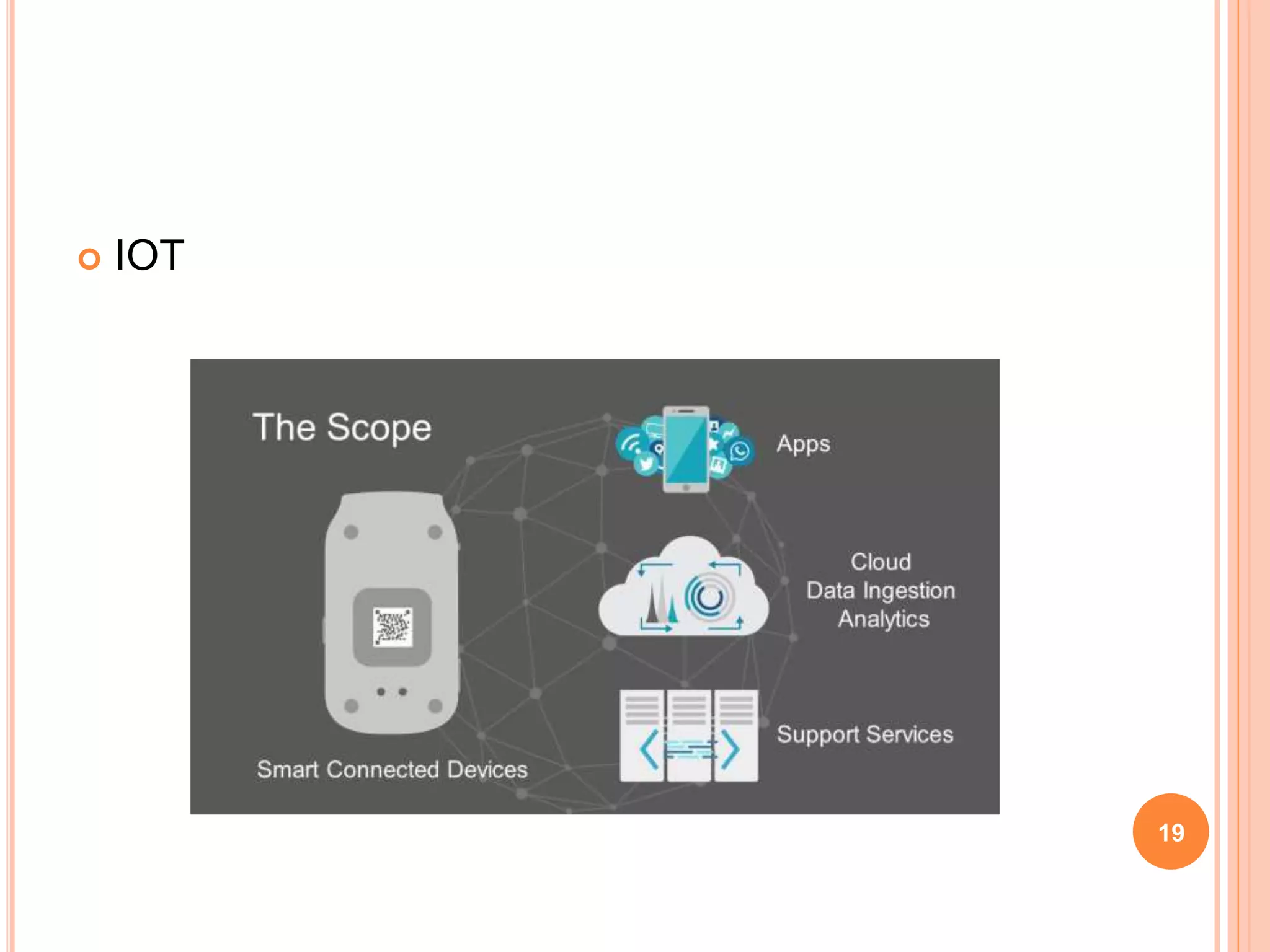
Big data refers to large volumes of data that are difficult to process using traditional data processing applications. The volume of data generated every day is massive, including 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created daily and over 40,000 Google searches per second. Big data comes from a wide variety of sources, including social media, websites, sensors, and other devices. It has five key characteristics known as the 5Vs: volume, velocity, variety, veracity and value. Technologies like Hadoop, NoSQL, Hive and Sqoop help store, analyze and transfer both structured and unstructured big data across clusters of computers. Big data has many applications in industries such as government, healthcare, transportation and more to gain insights and improve