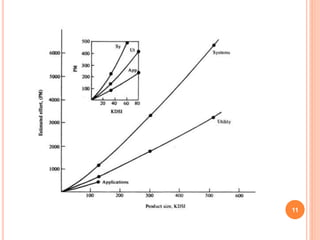
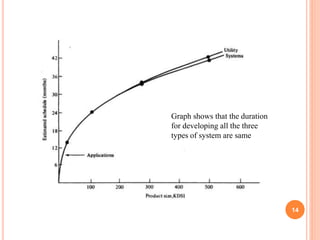
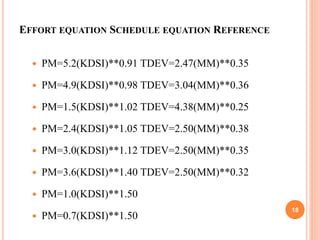
This document discusses major factors that influence software cost estimation. It identifies programmer ability, product complexity, product size, available time, required reliability, and level of technology as key factors. It provides details on how each factor affects software cost, including equations to estimate programming time and effort based on variables like source lines of code and developer months. Program complexity is broken into three levels: application, utility, and system software. The document also discusses how underestimating code size and inability to compress development schedules can impact cost estimates.
![SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
SOFTWARE COST FACTOR
B.Abinaya Bharathi,
II-M.Sc[Cs&IT],
Nadar Saraswathi college of Arts and Science,
Theni.
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-180801110838/85/software-cost-factor-1-320.jpg)