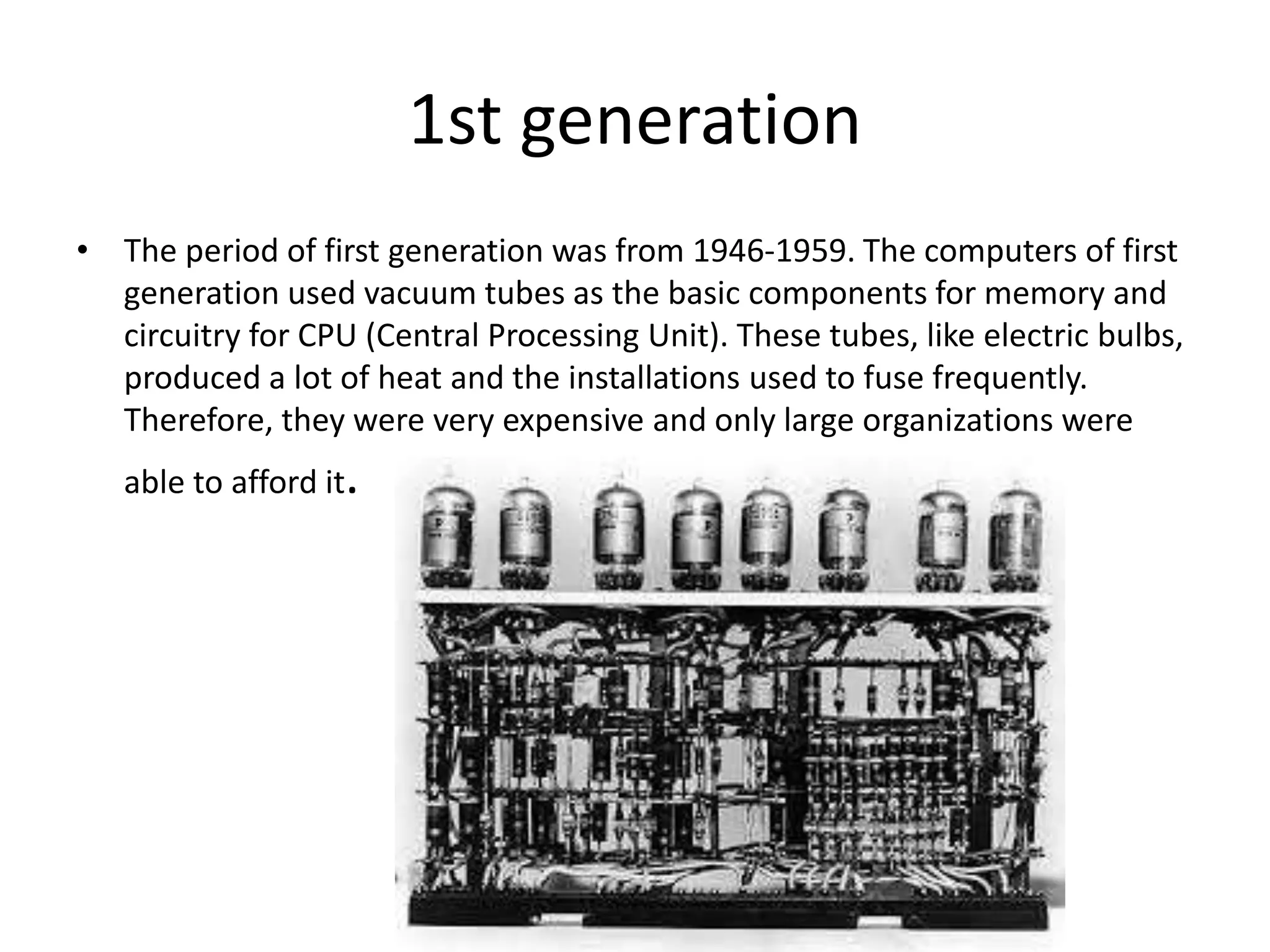
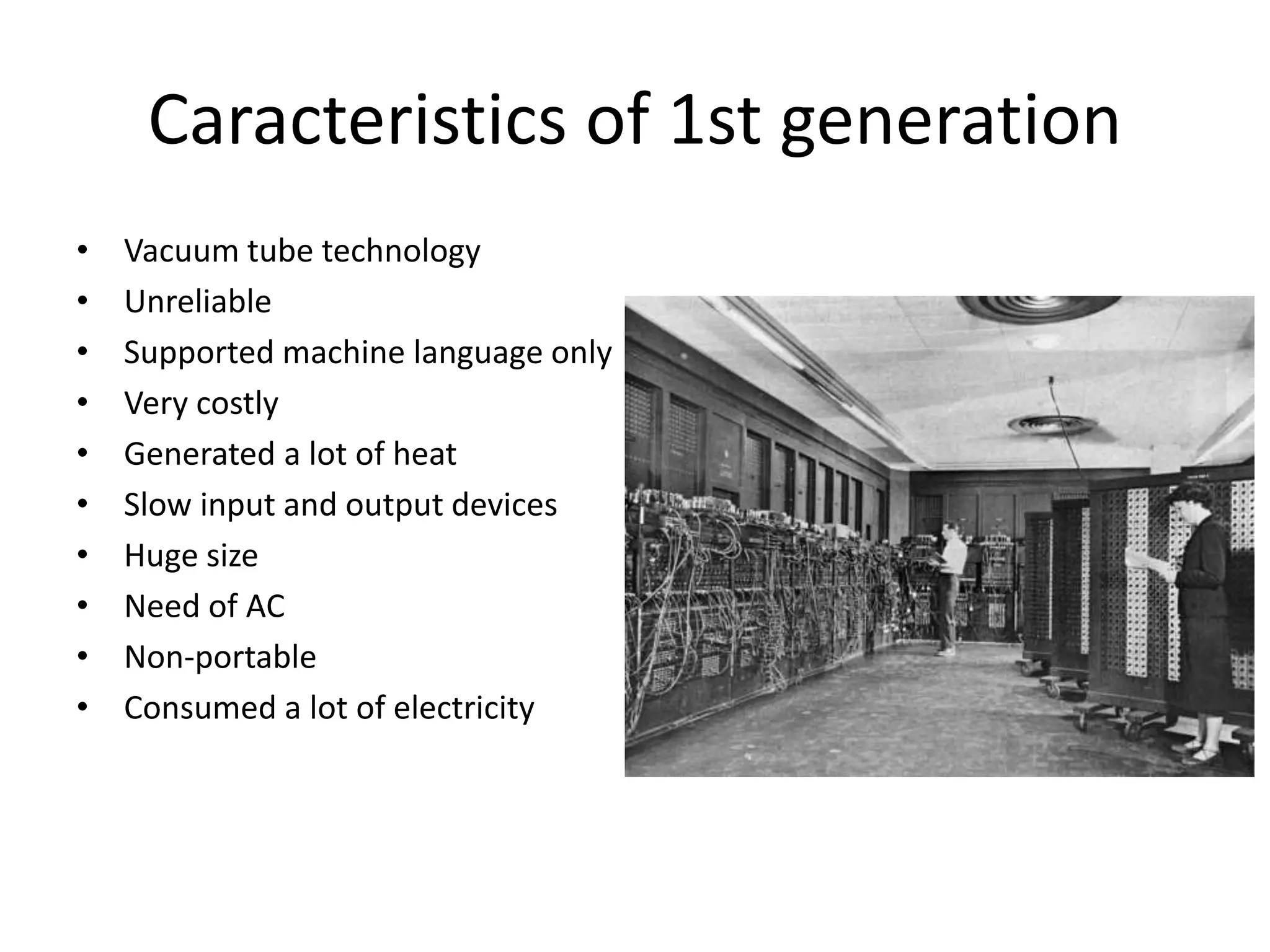
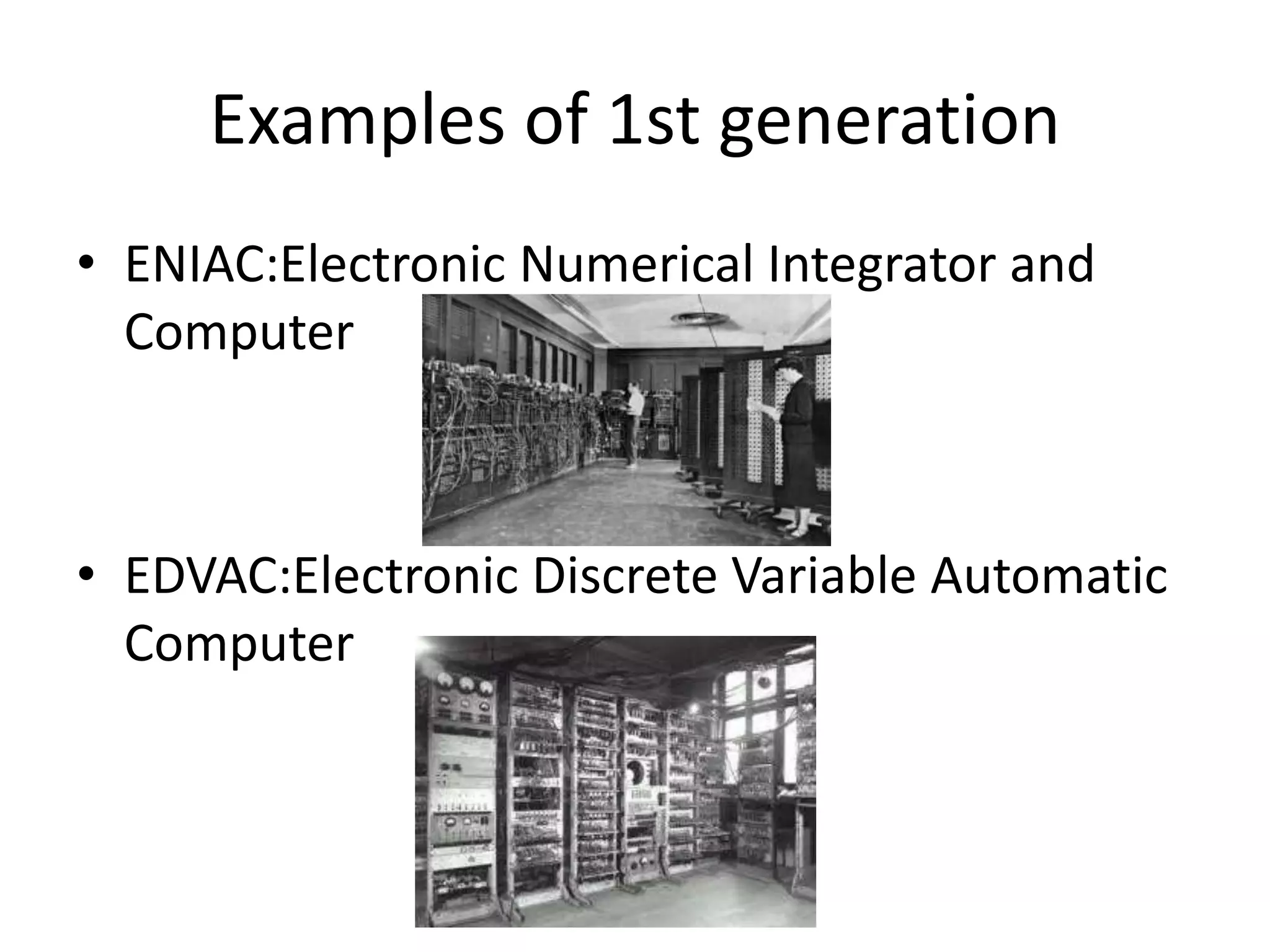
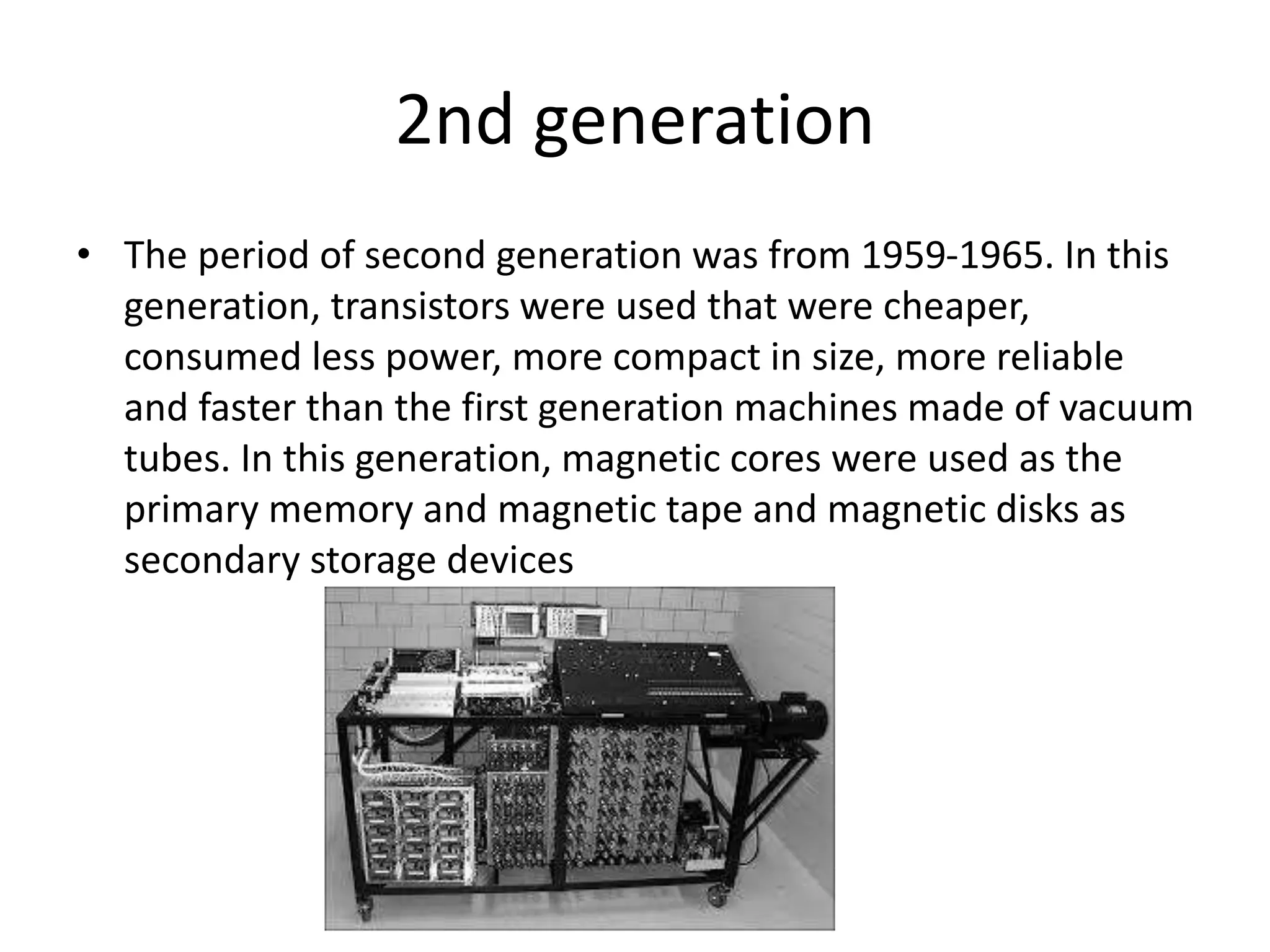
This document discusses the five generations of computers from 1946 to the present. Each generation is defined by the technology used in processors and circuits. The 1st generation used vacuum tubes, the 2nd used transistors, the 3rd used integrated circuits, the 4th used VLSI circuits, and the 5th uses ULSI technology. Each generation brought improvements in size, cost, speed, reliability and capabilities. Examples of computers from each generation are provided. The conclusion states that computer technology continues to advance positively for humanity.