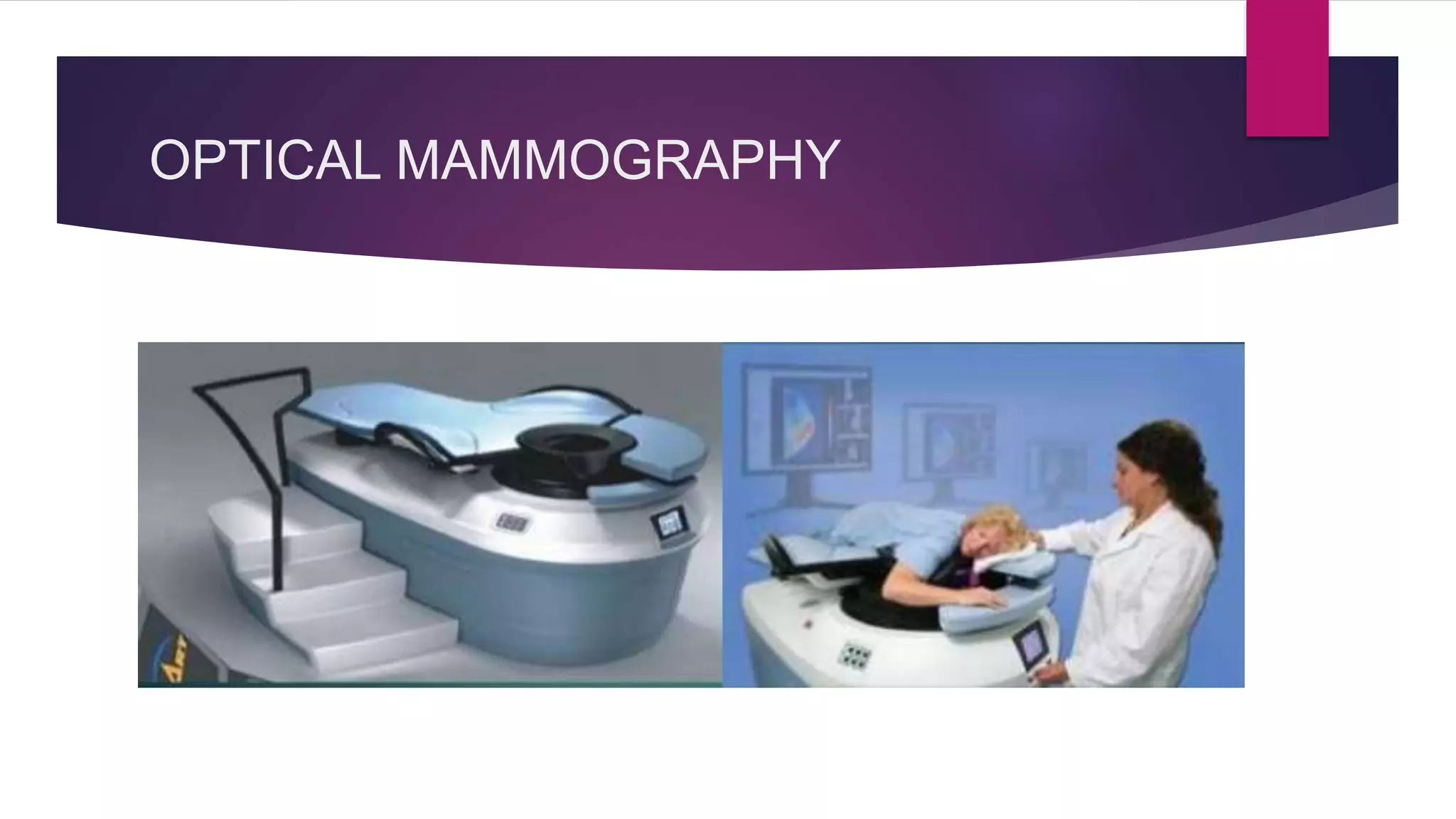
The document discusses mammography as a primary imaging modality for breast cancer detection, detailing its equipment, techniques, and indications. It emphasizes the importance of high-quality images and the recent advances in digital mammography, including various new technologies aimed at improving detection rates. Additionally, it outlines guidelines for patient selection and preparation for mammography along with recommendations for complementary techniques such as ultrasound.