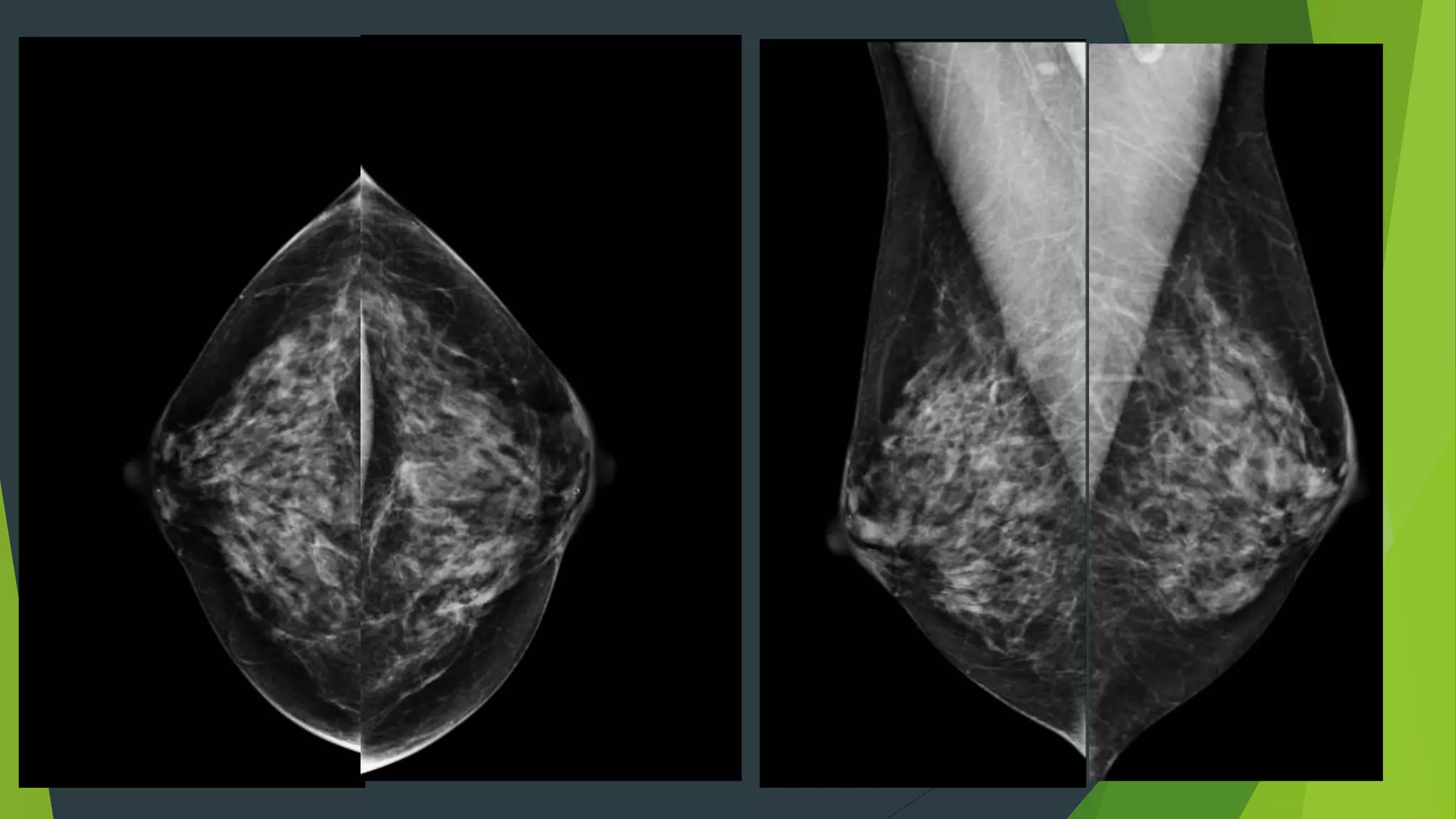
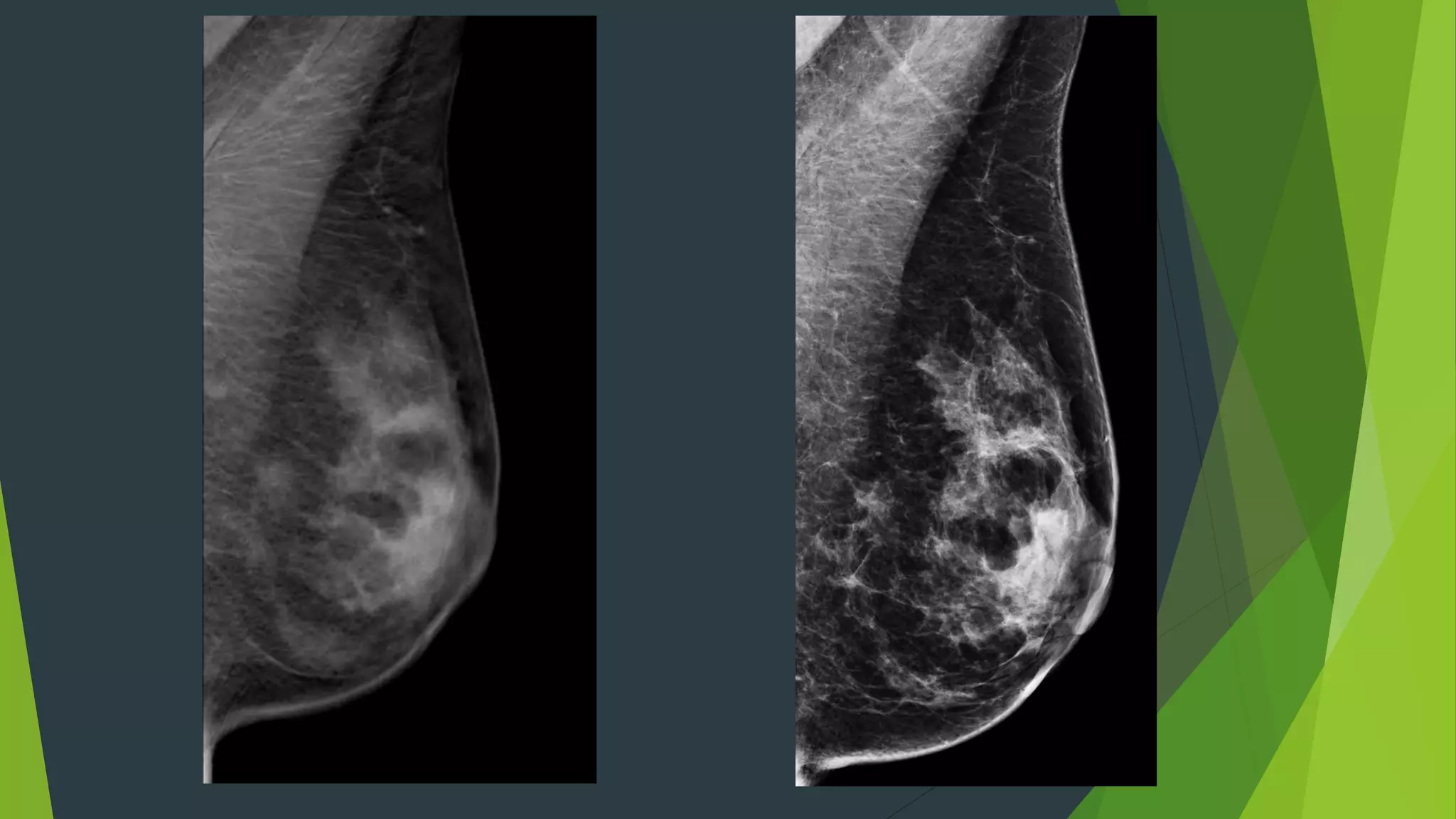
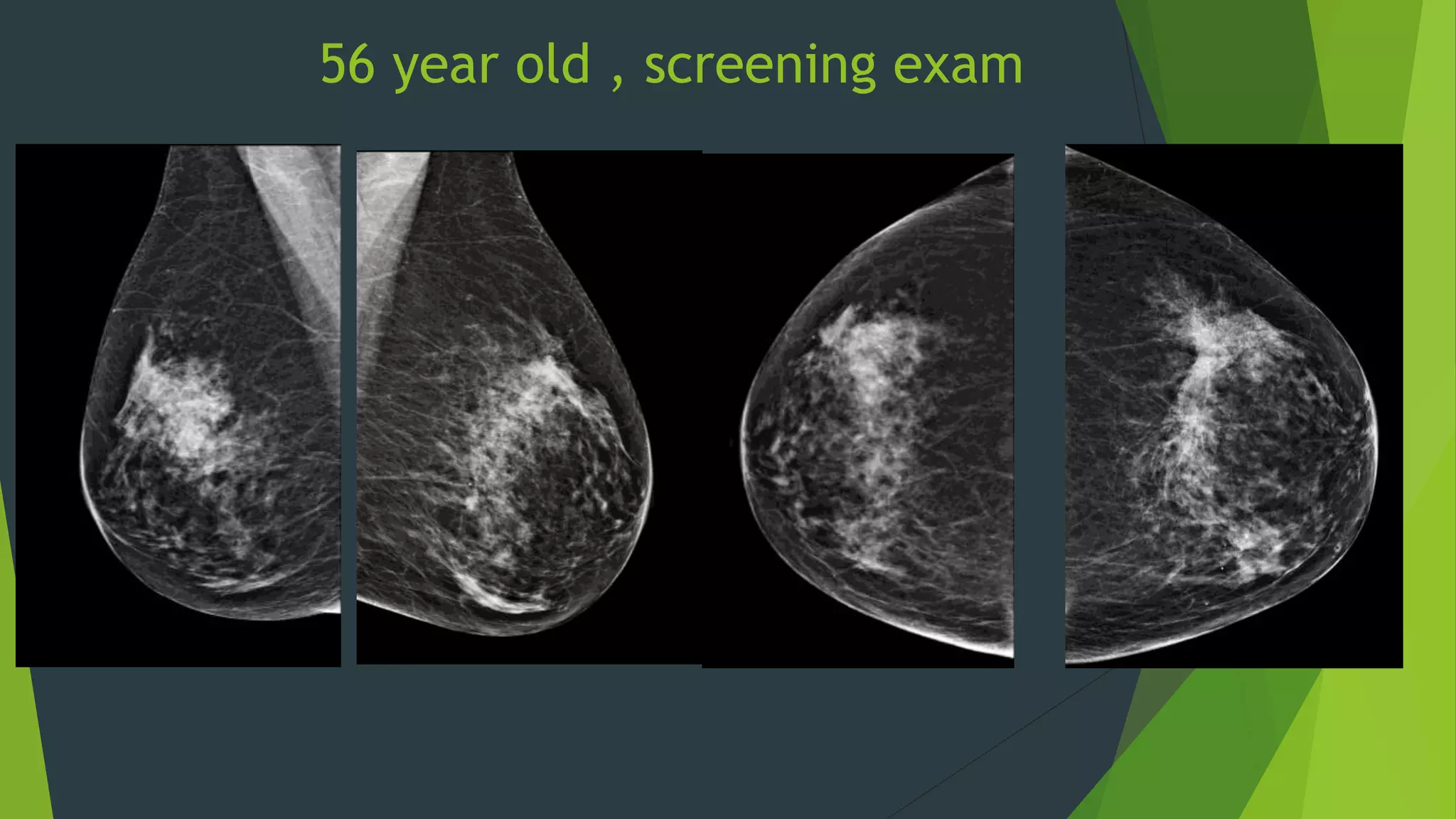
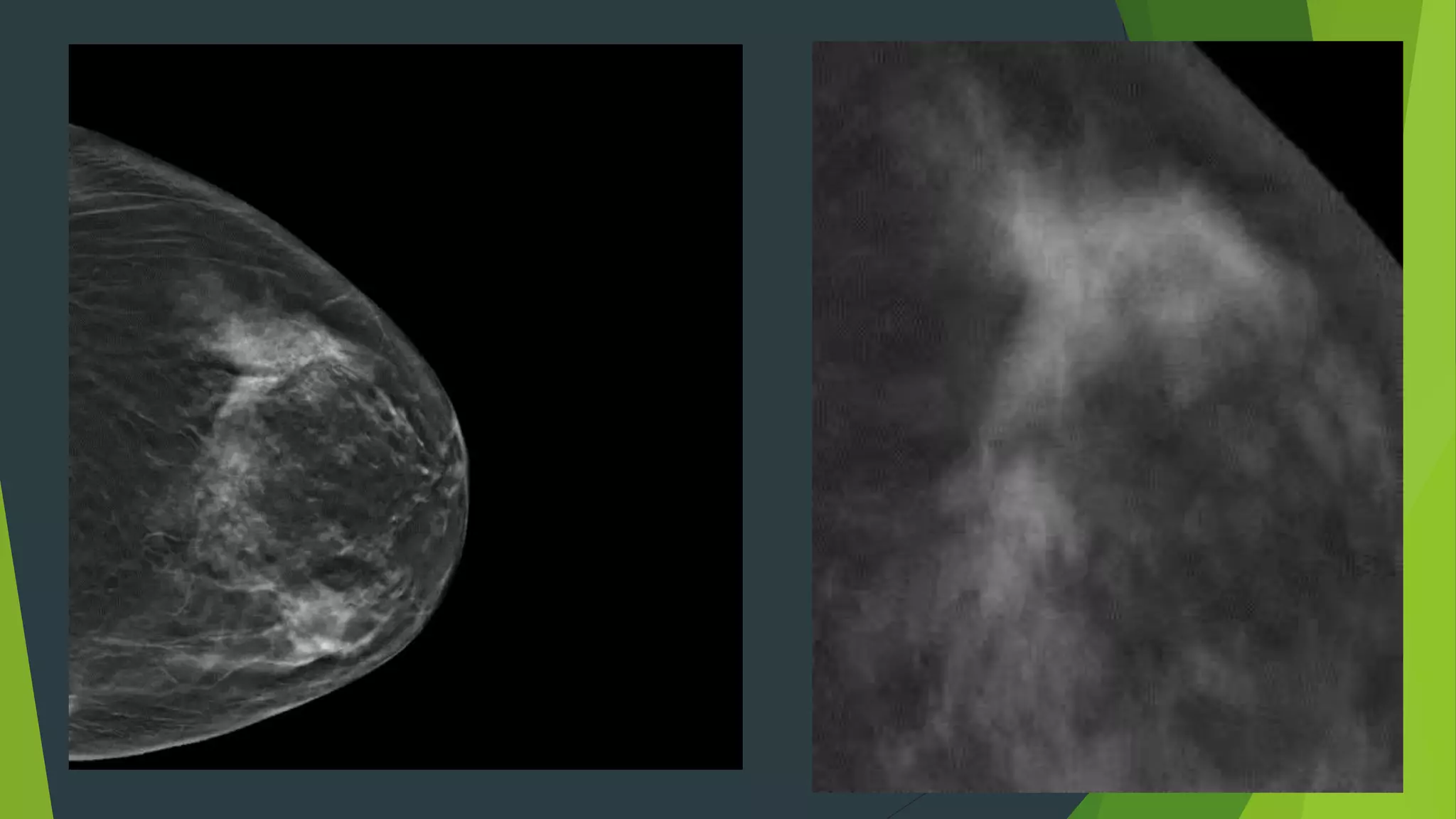
Digital breast tomosynthesis (3D mammography) significantly improves breast cancer detection rates and reduces false positive recalls compared to traditional 2D mammography. While it has limitations such as longer reading times and increased storage requirements, its enhanced sensitivity, especially for dense breasts, makes it a valuable tool in breast cancer screening. Legislative changes now require mammography facilities to report breast density, reflecting its impact on cancer detection and patient awareness.