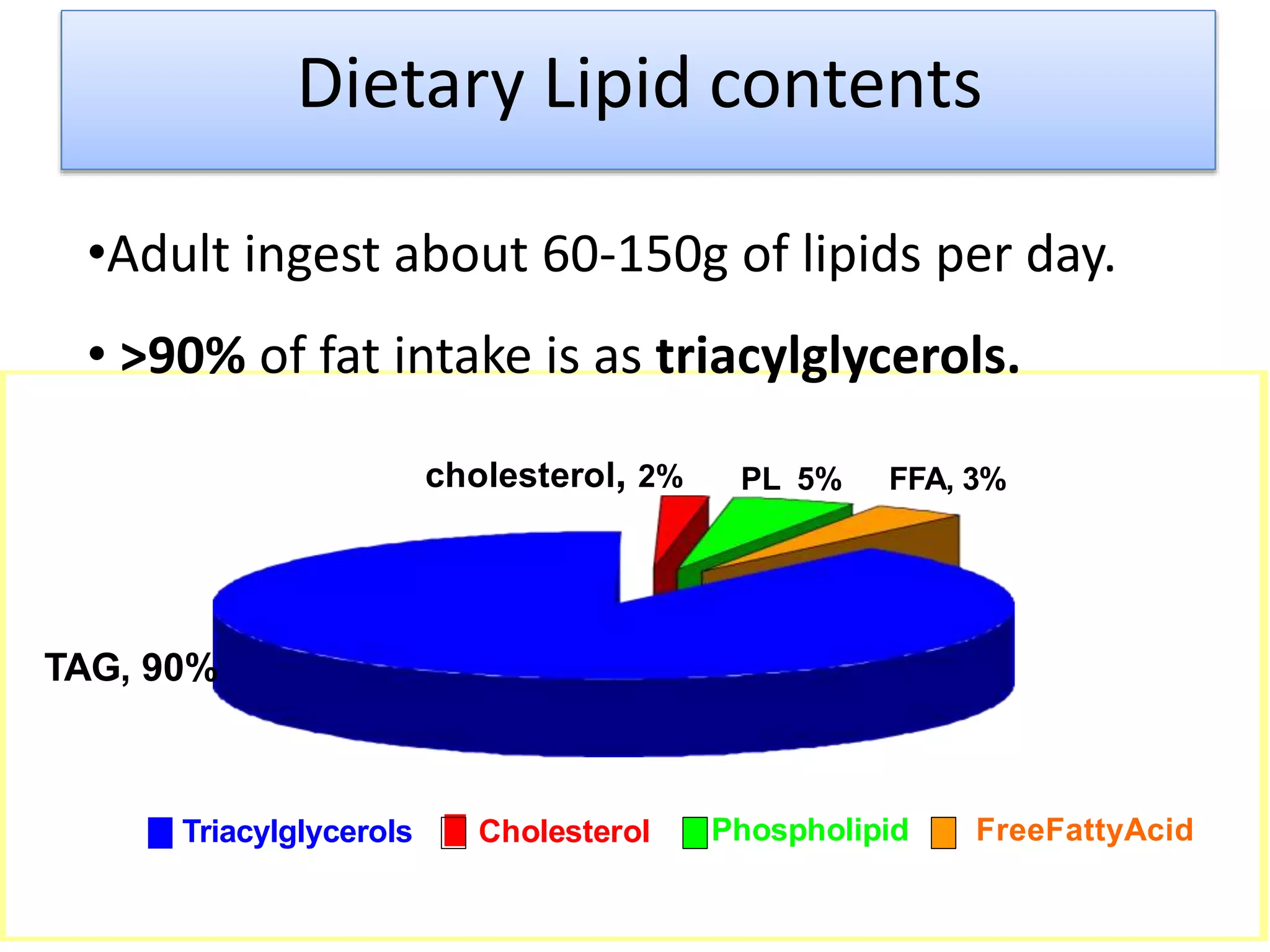
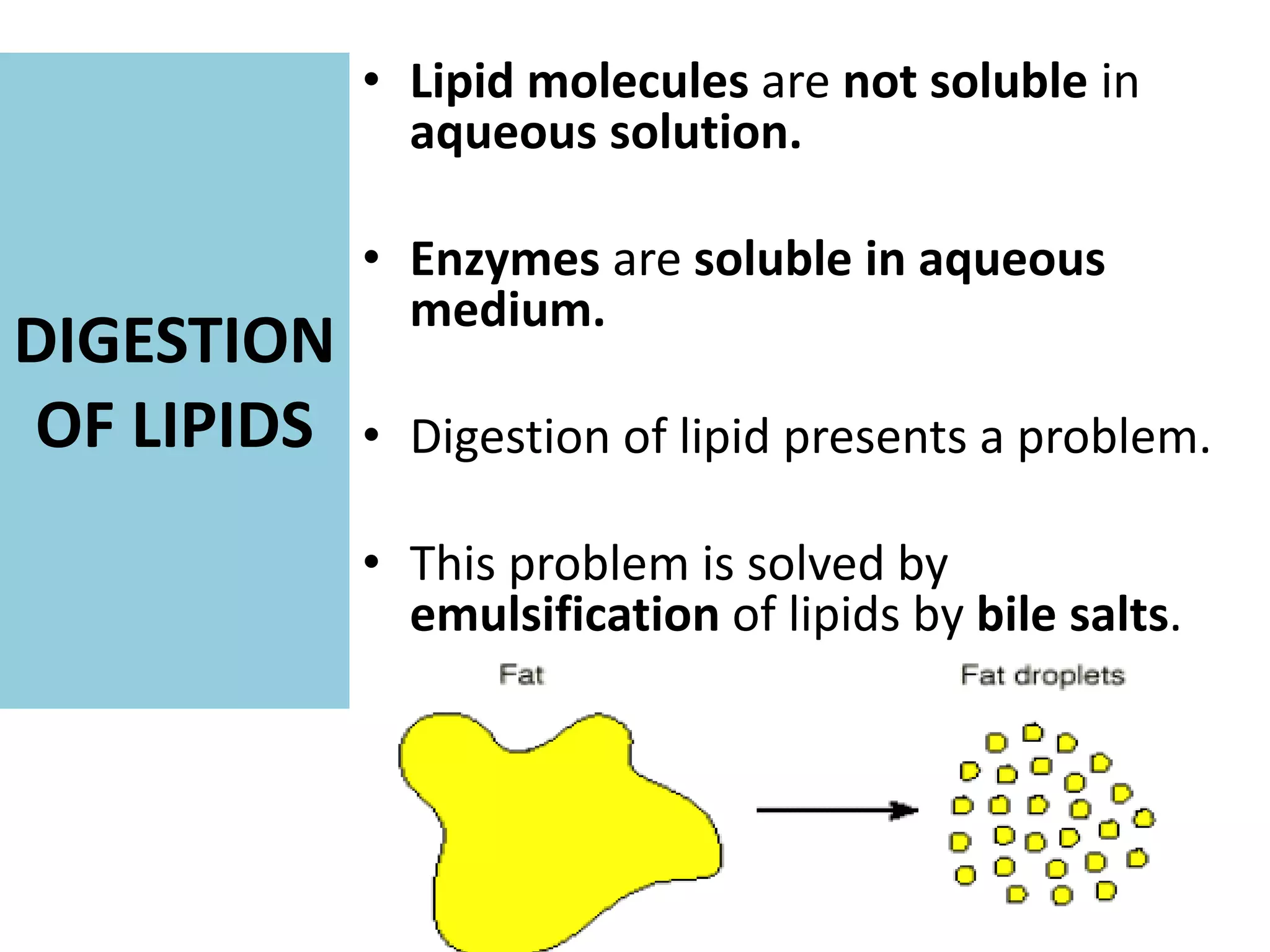
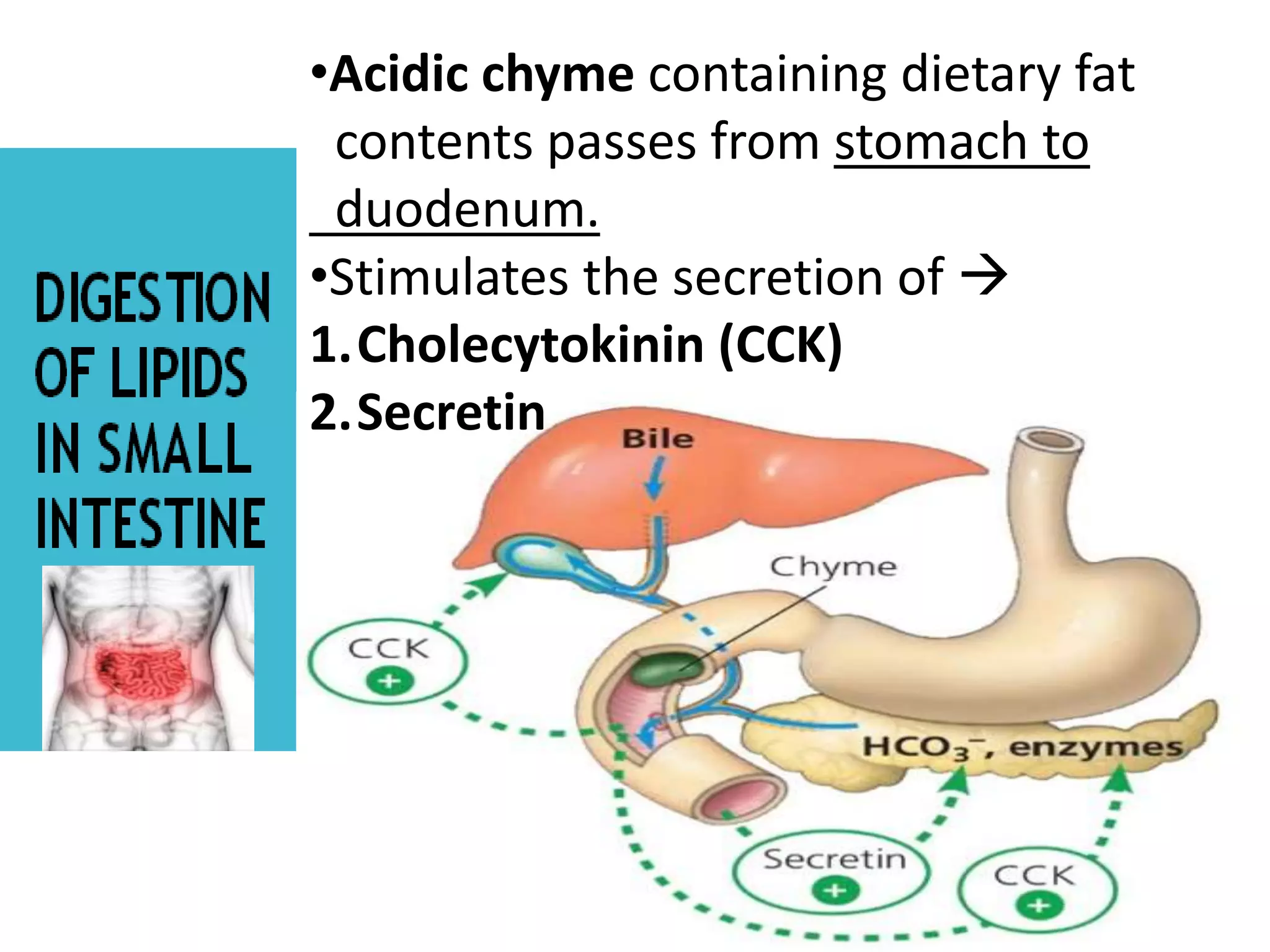
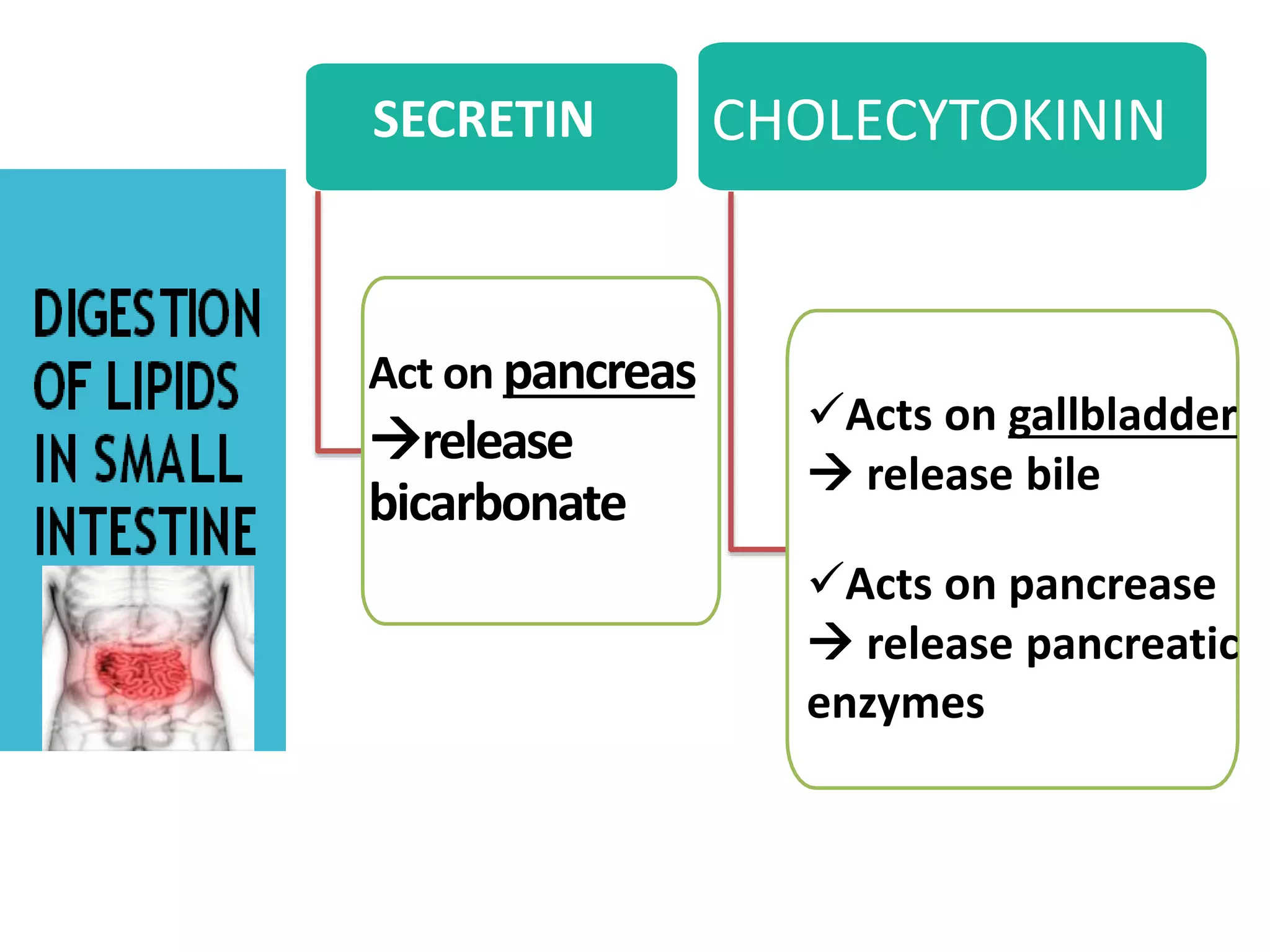
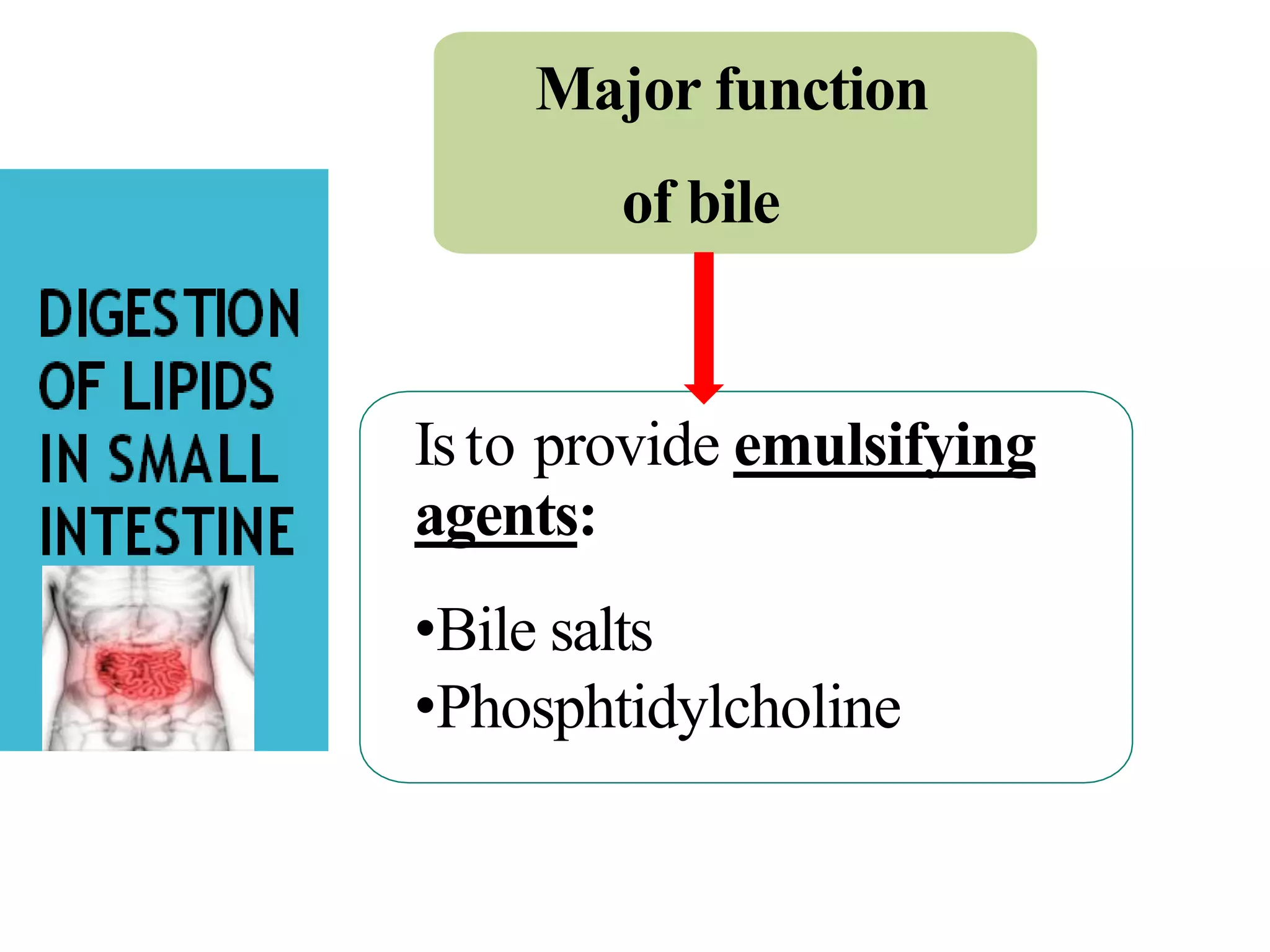
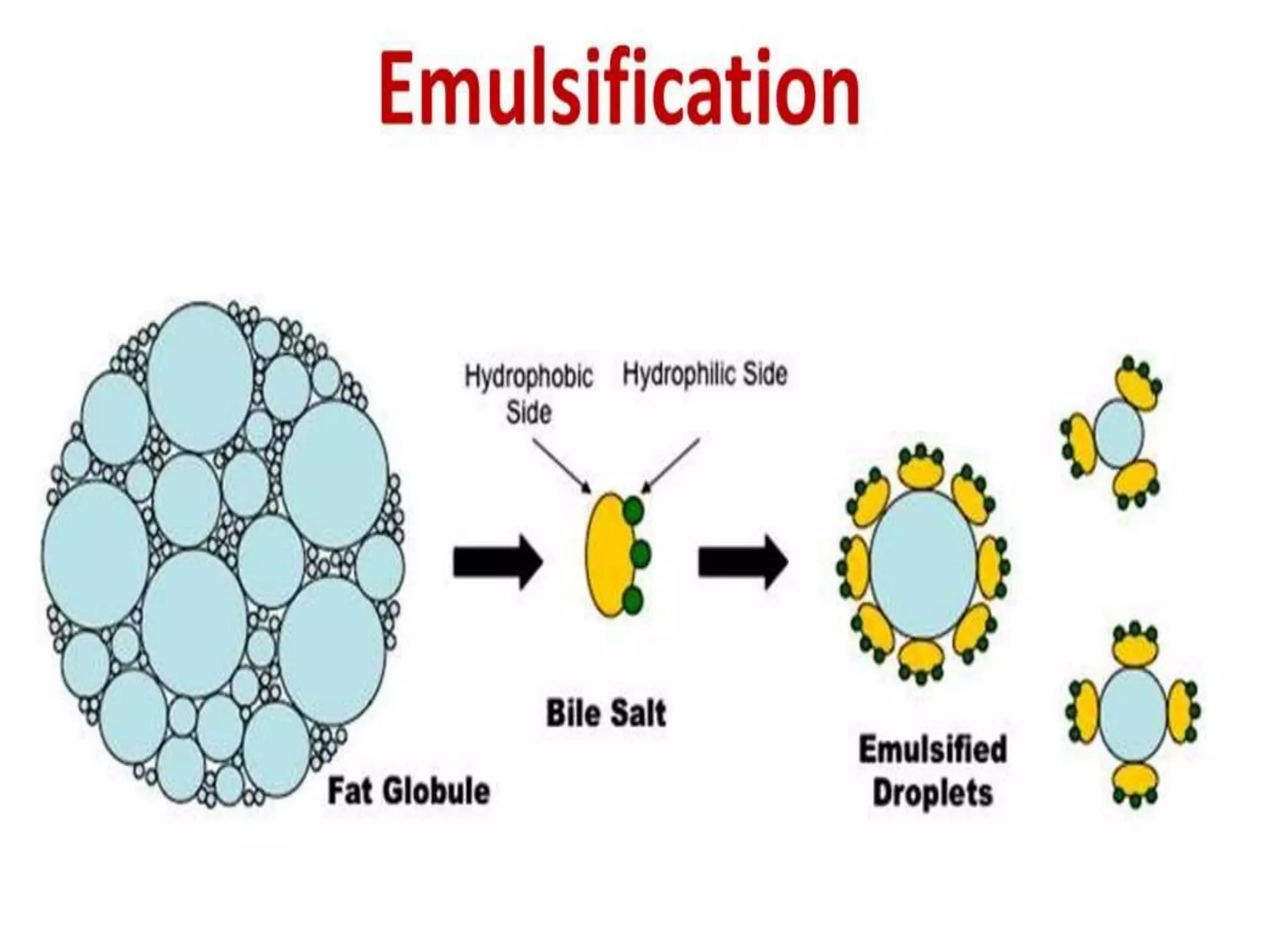
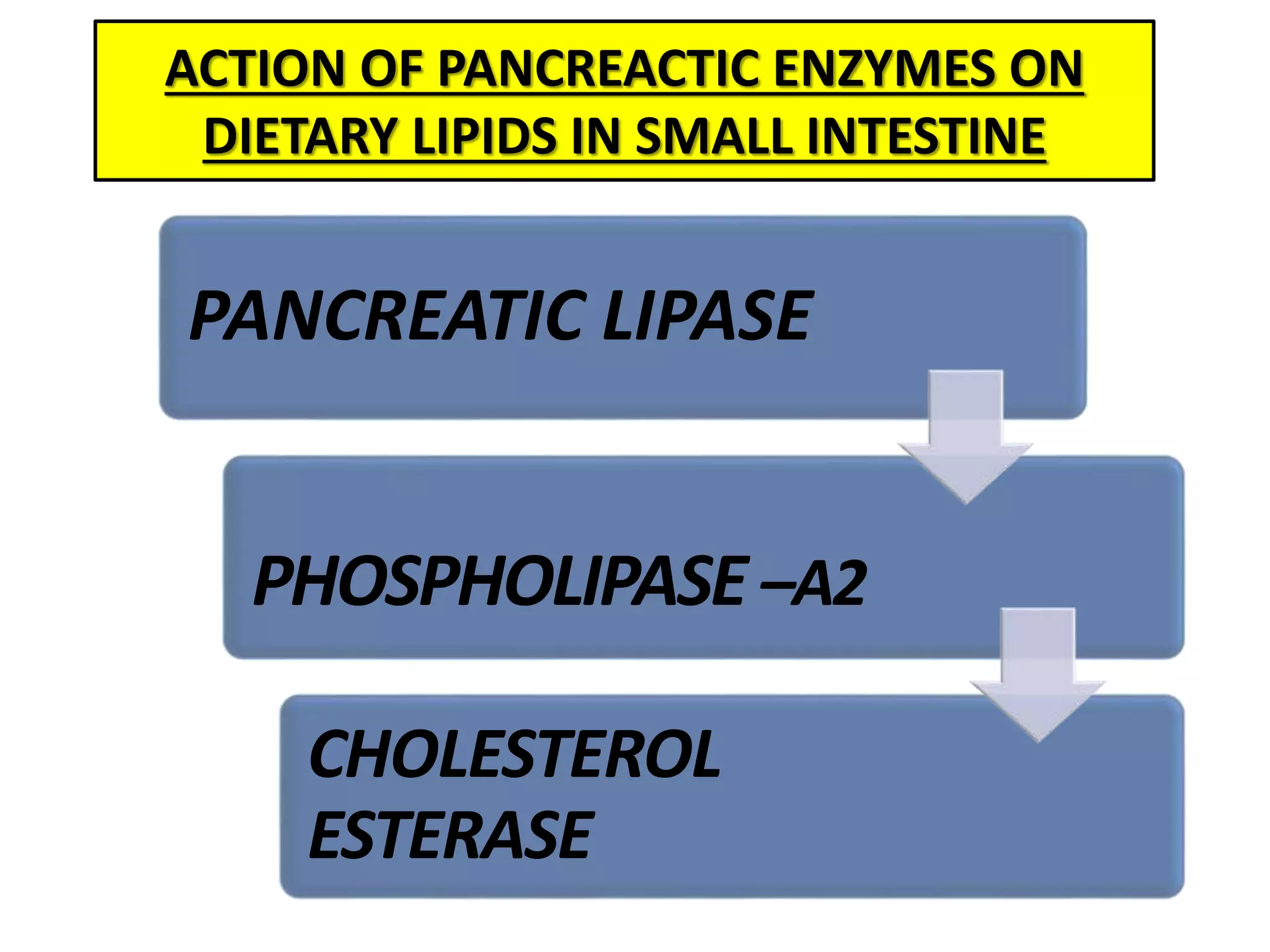
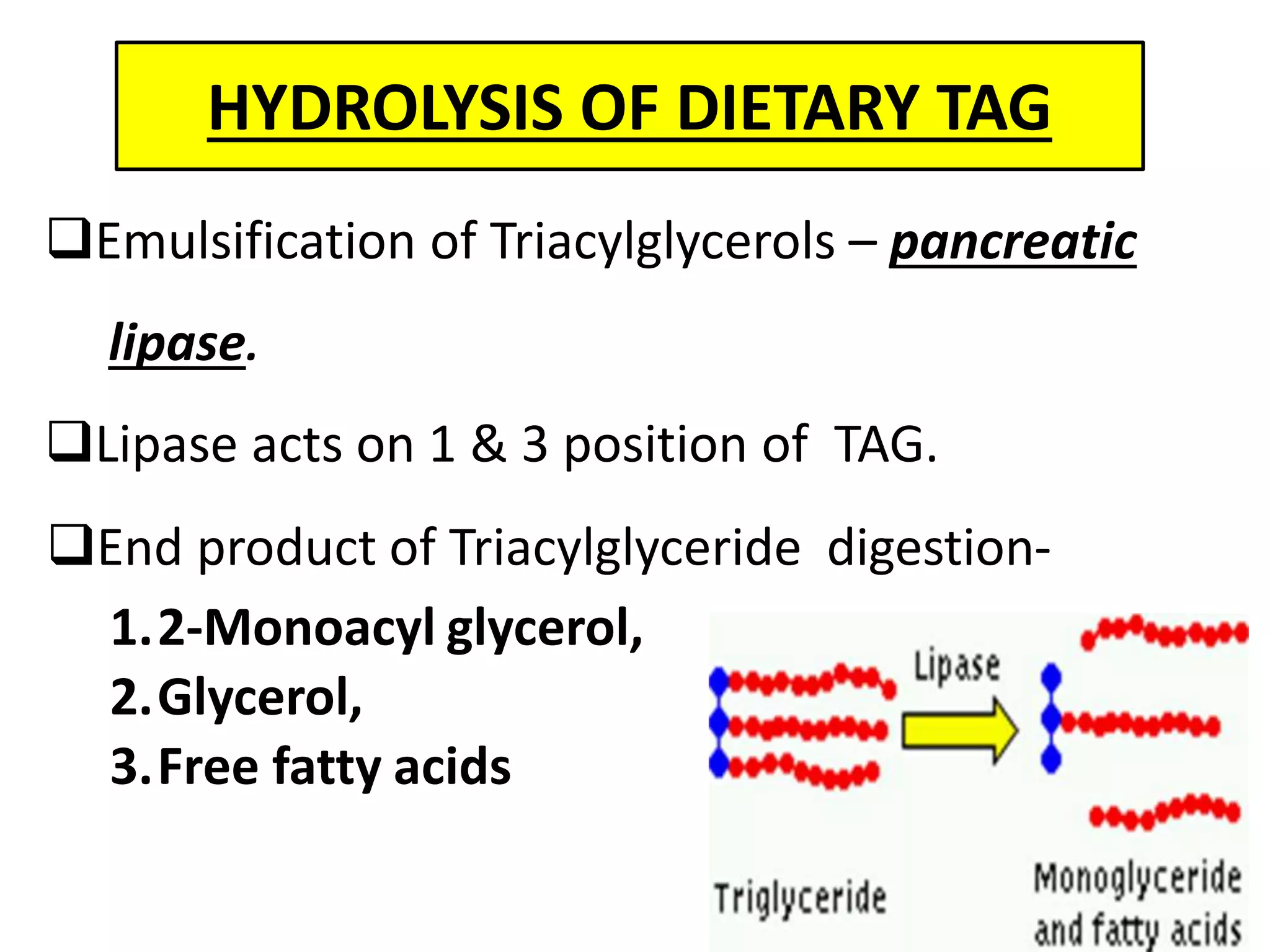
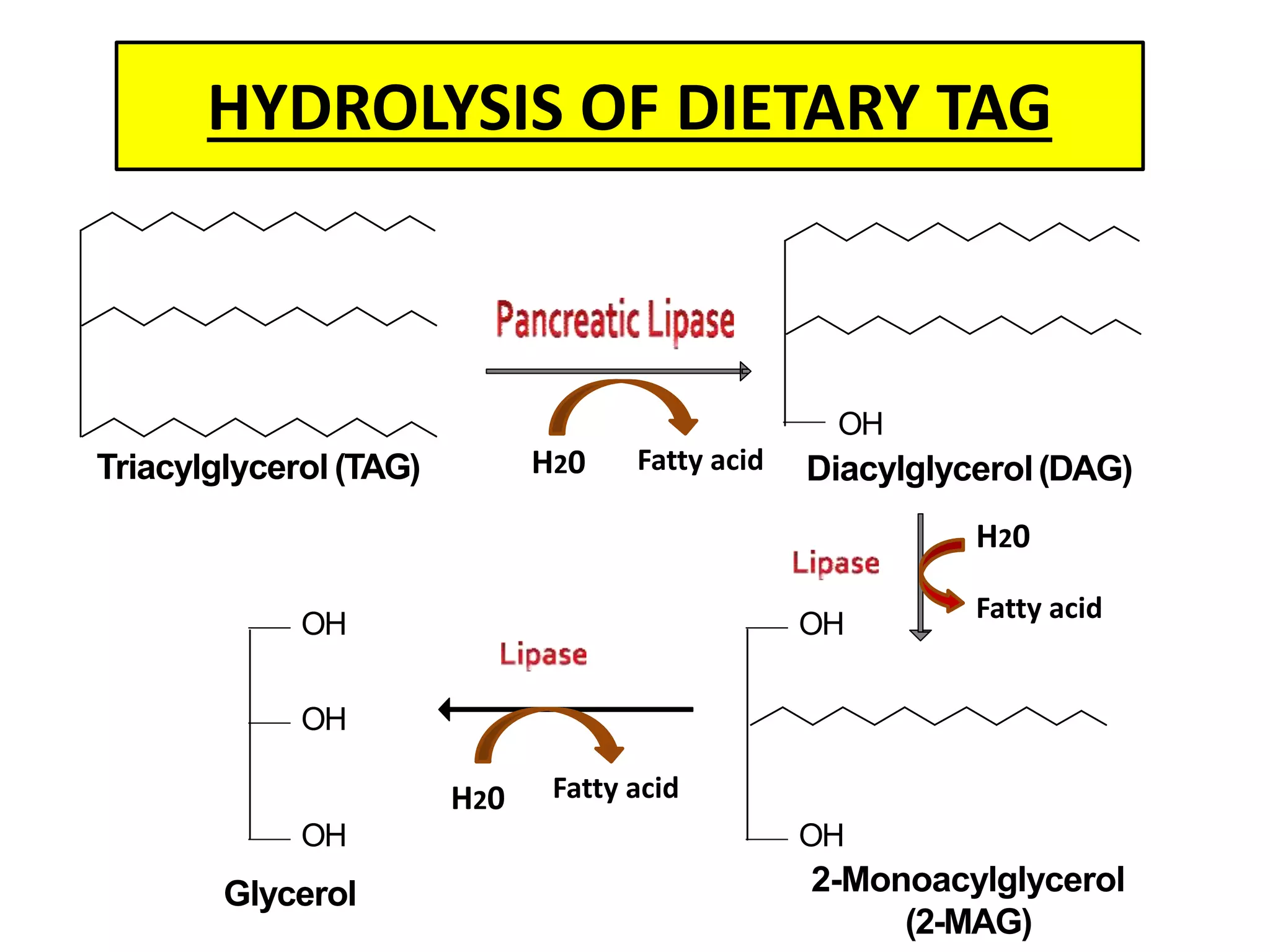
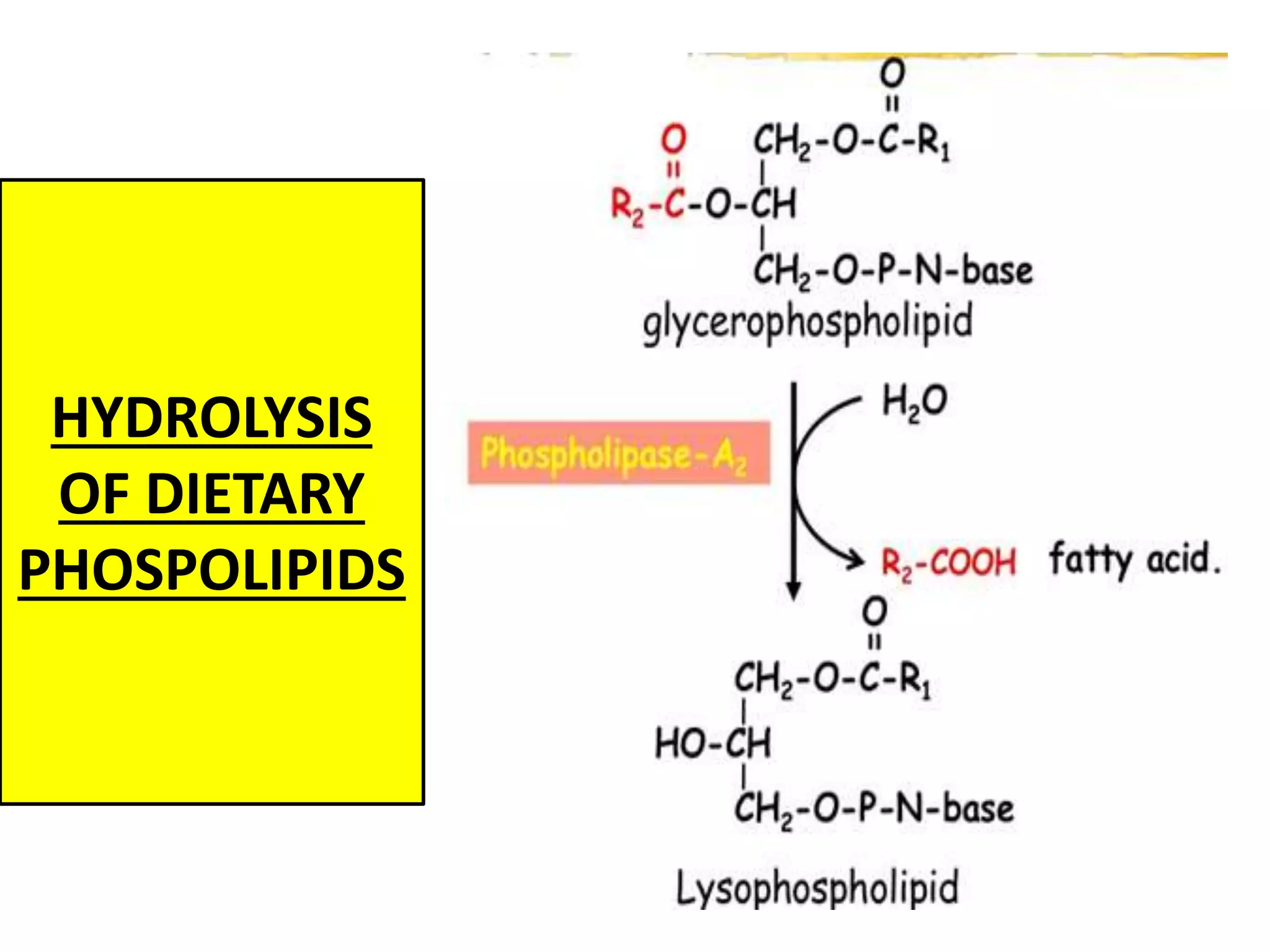
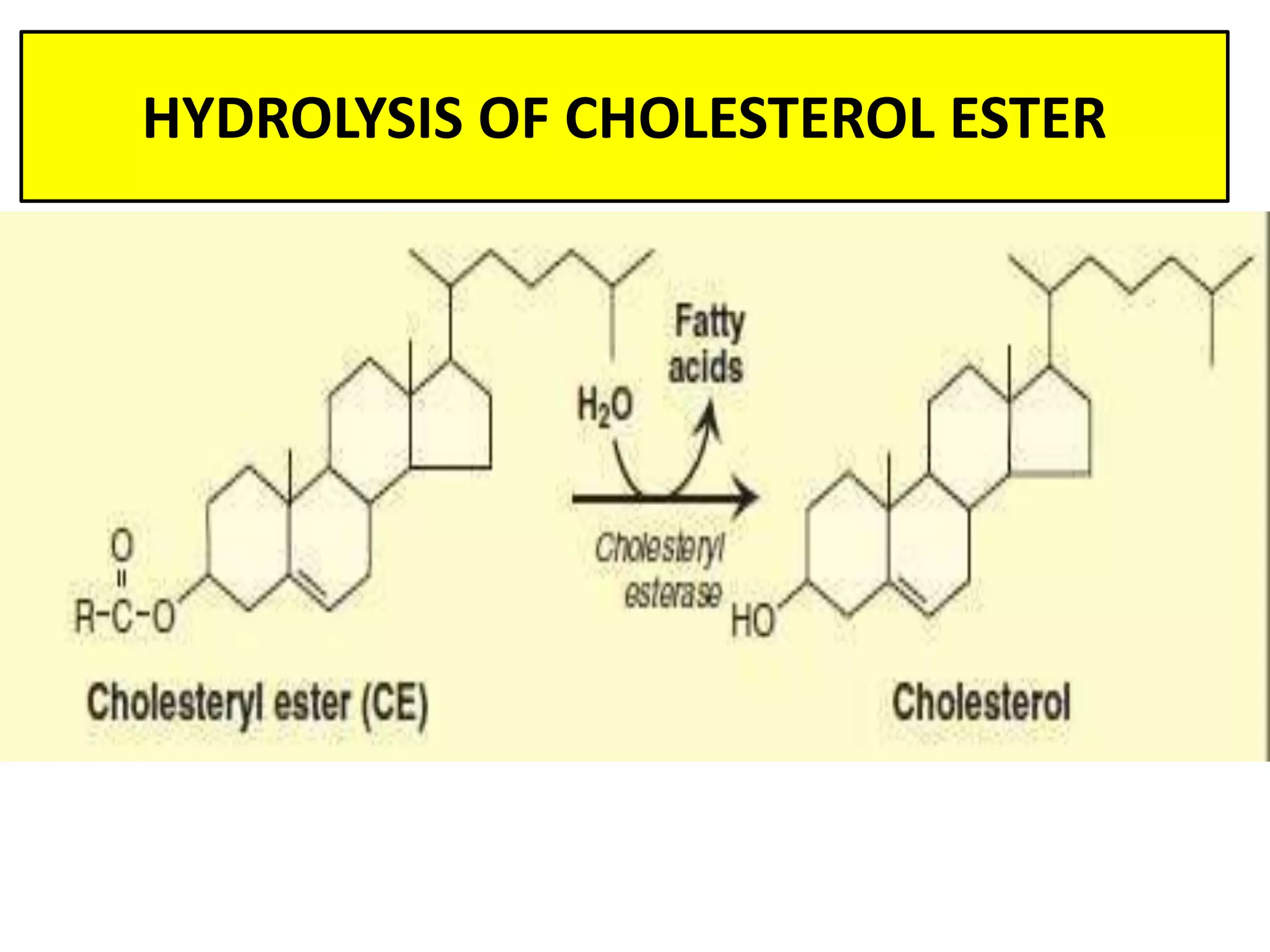
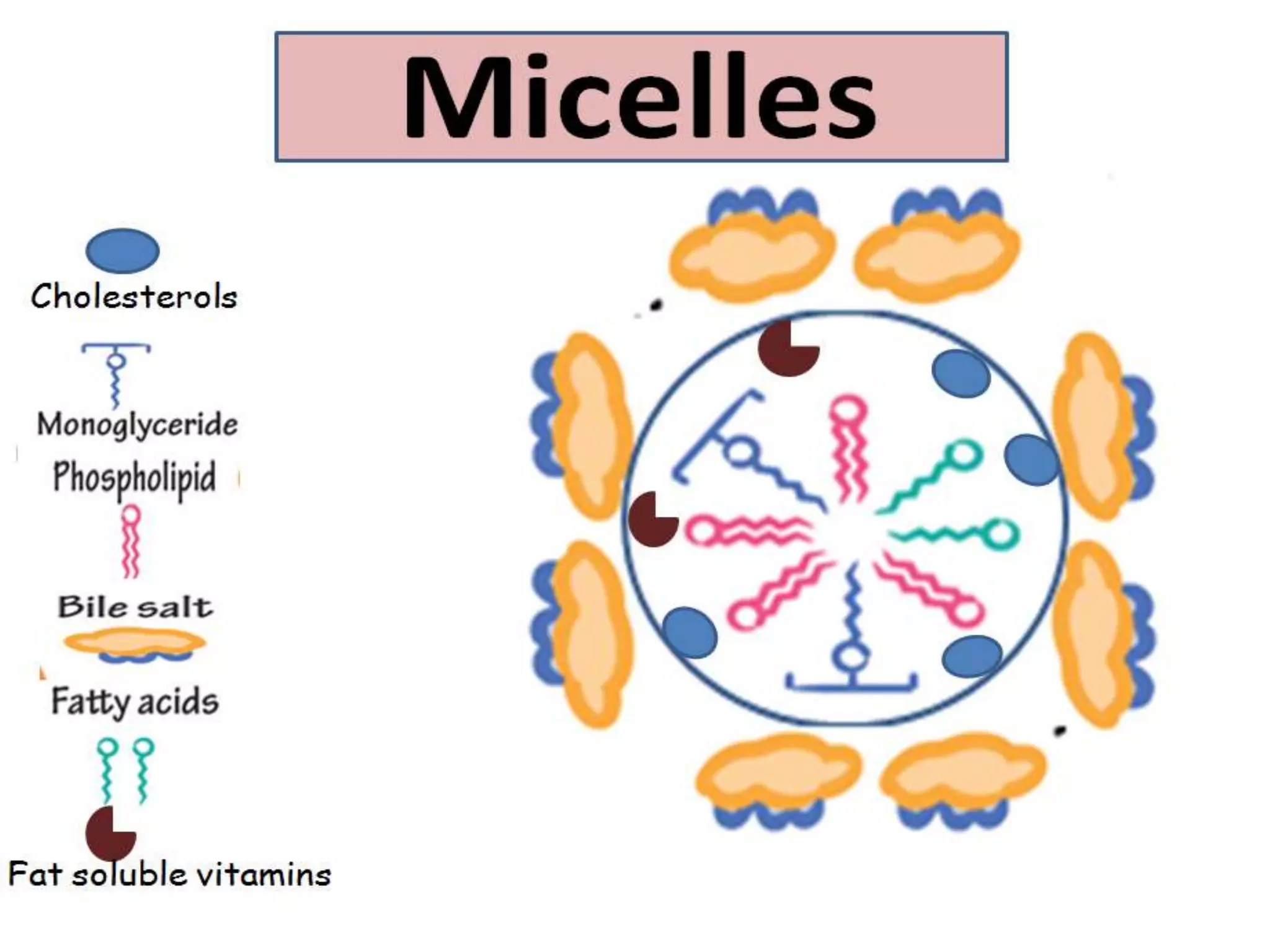
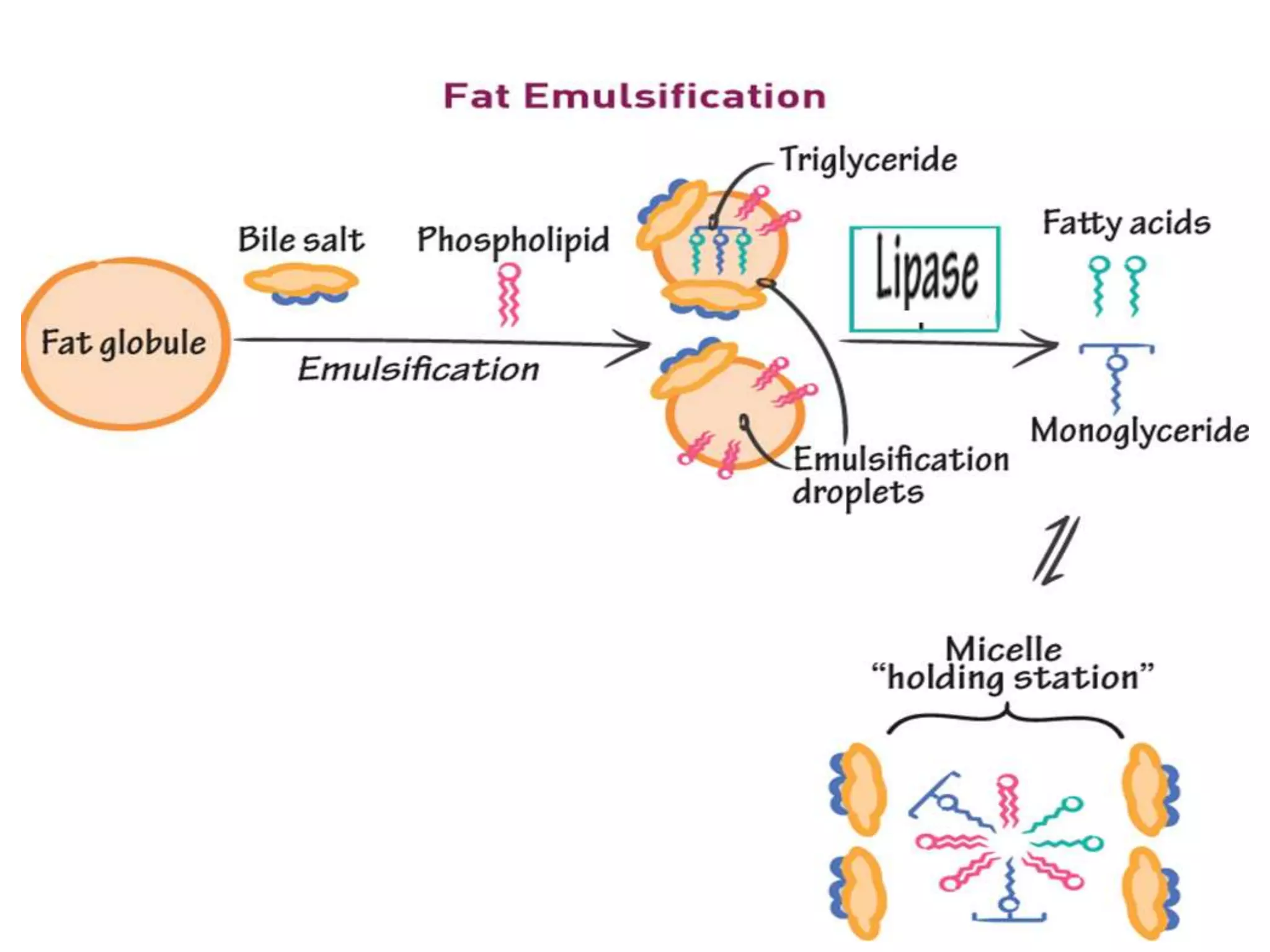
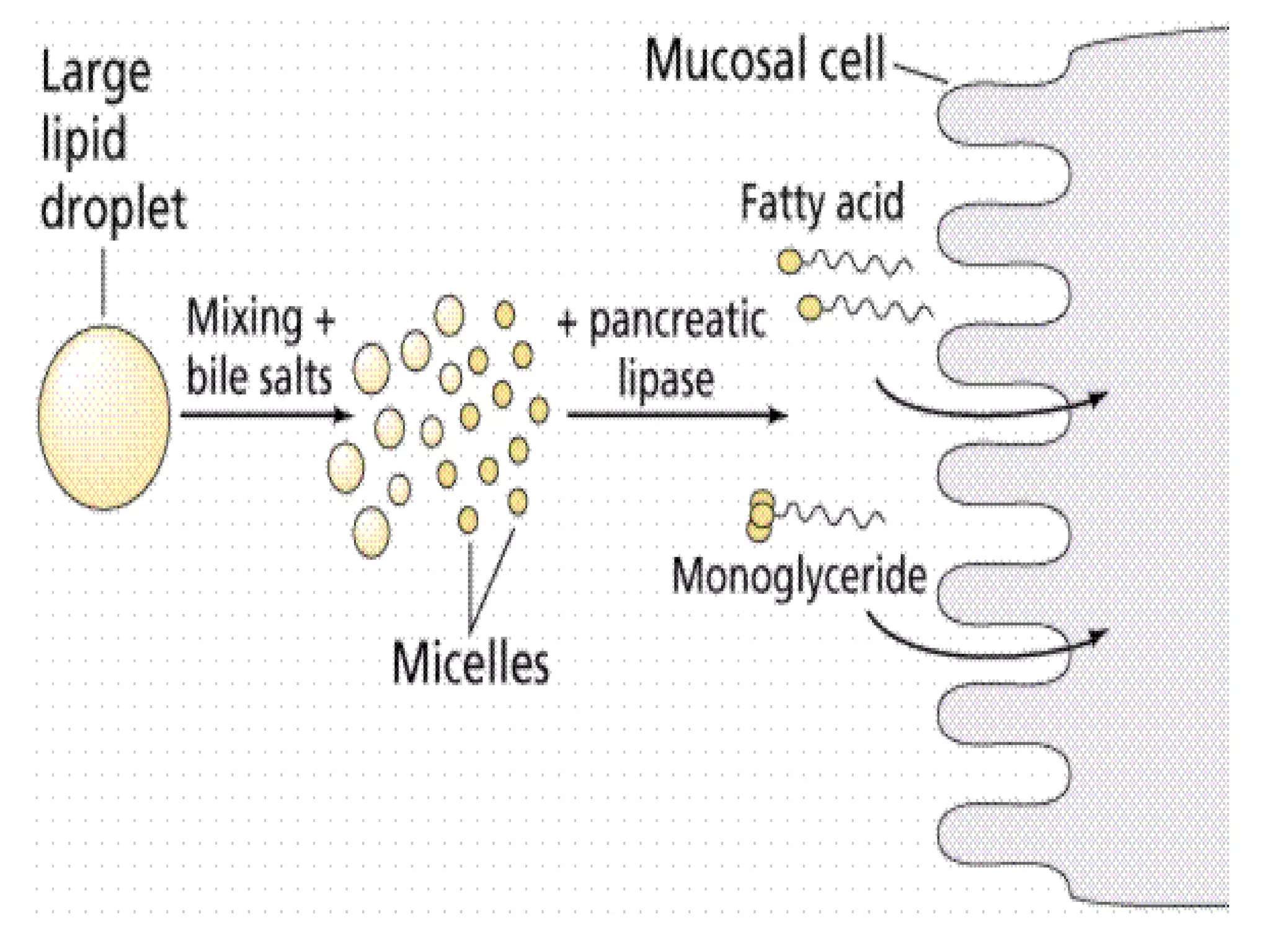
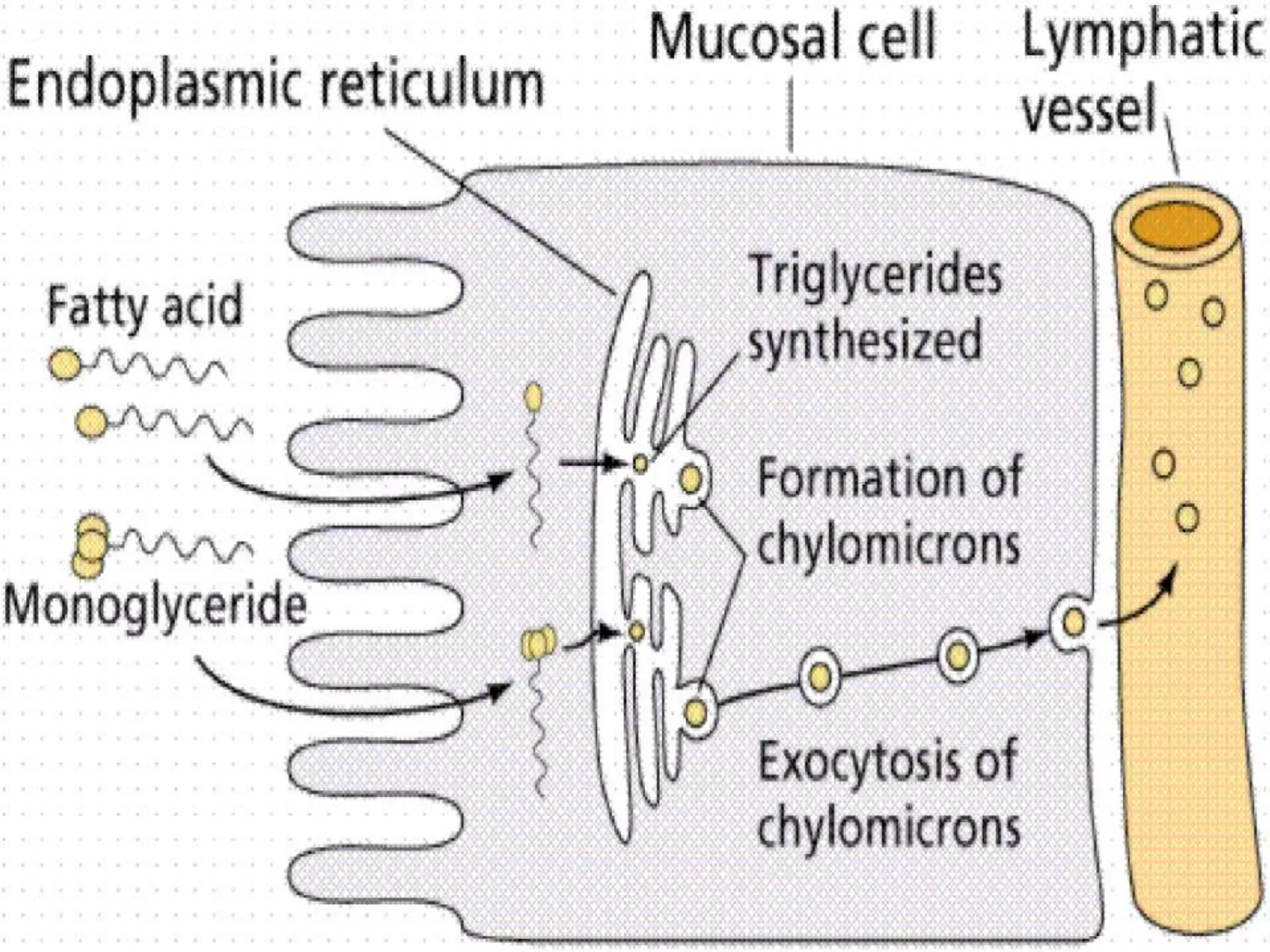
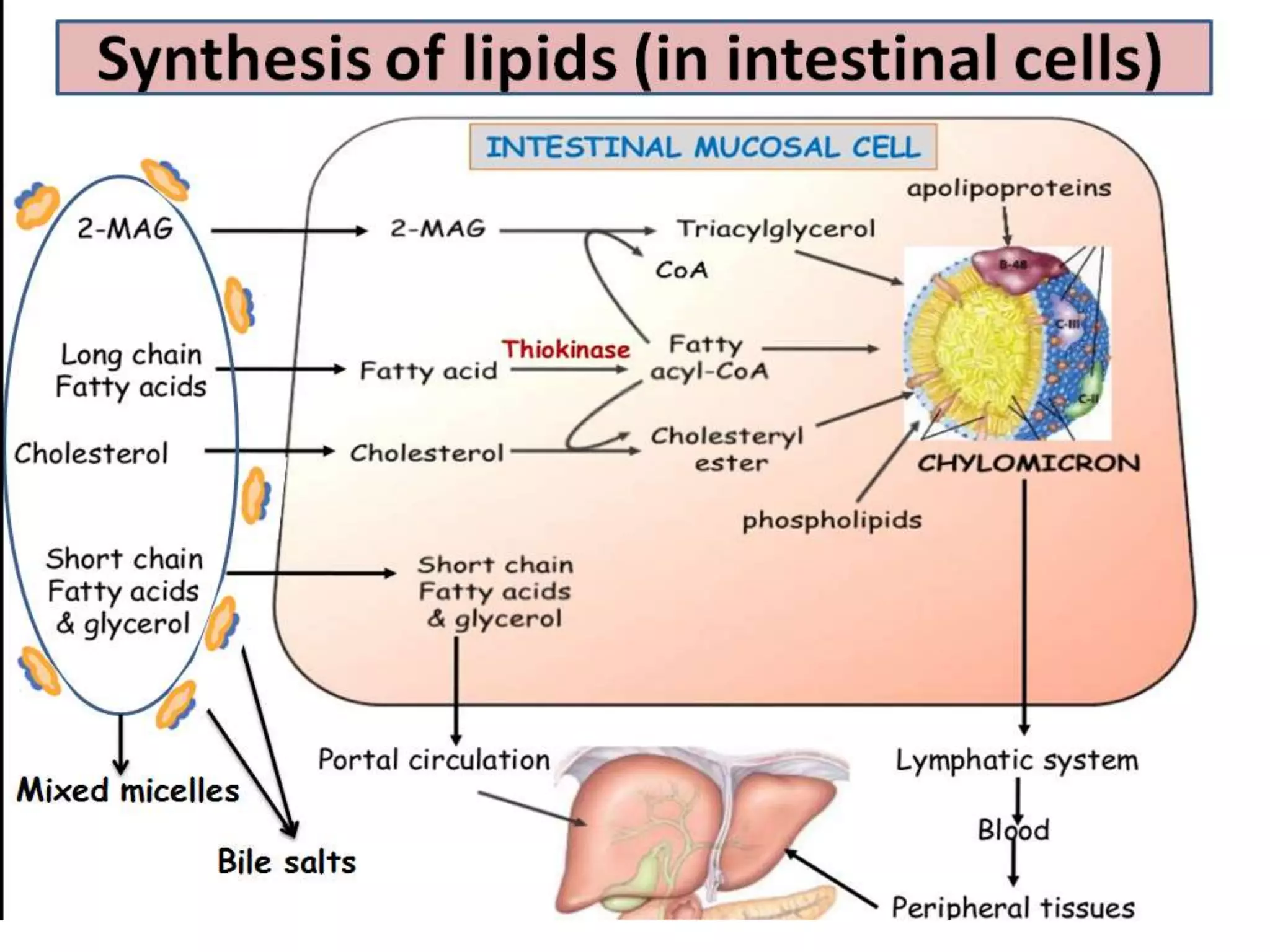
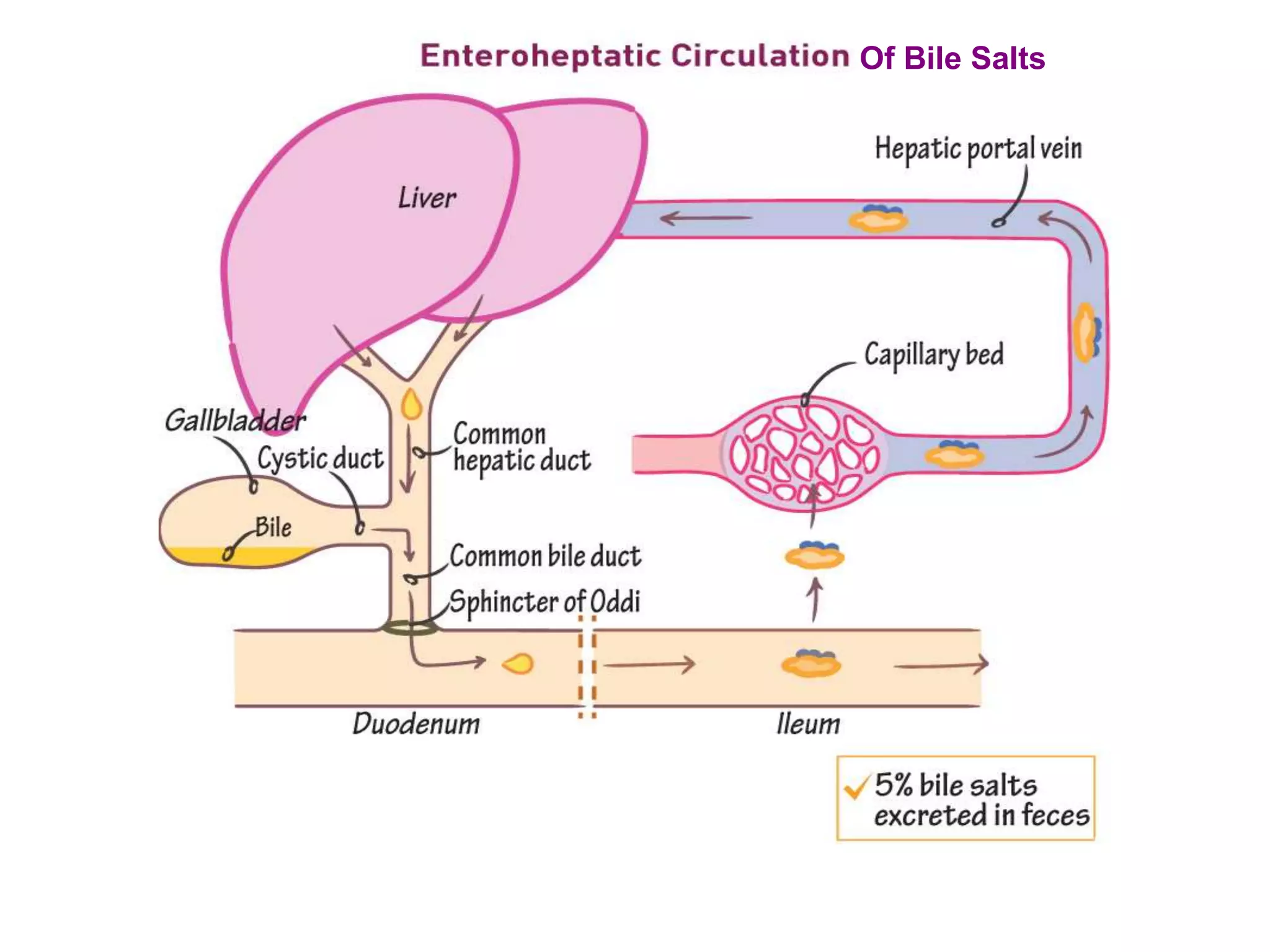
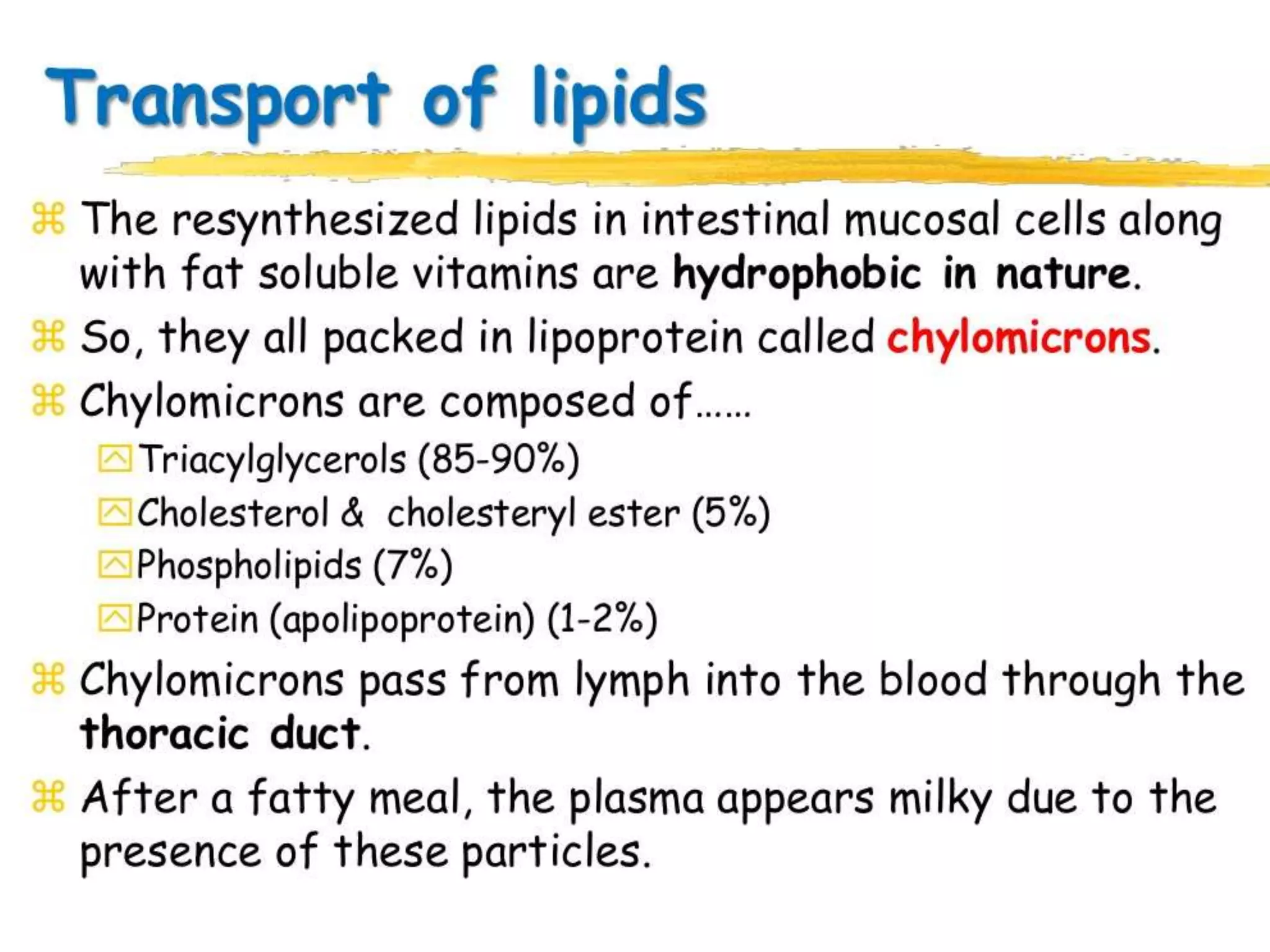
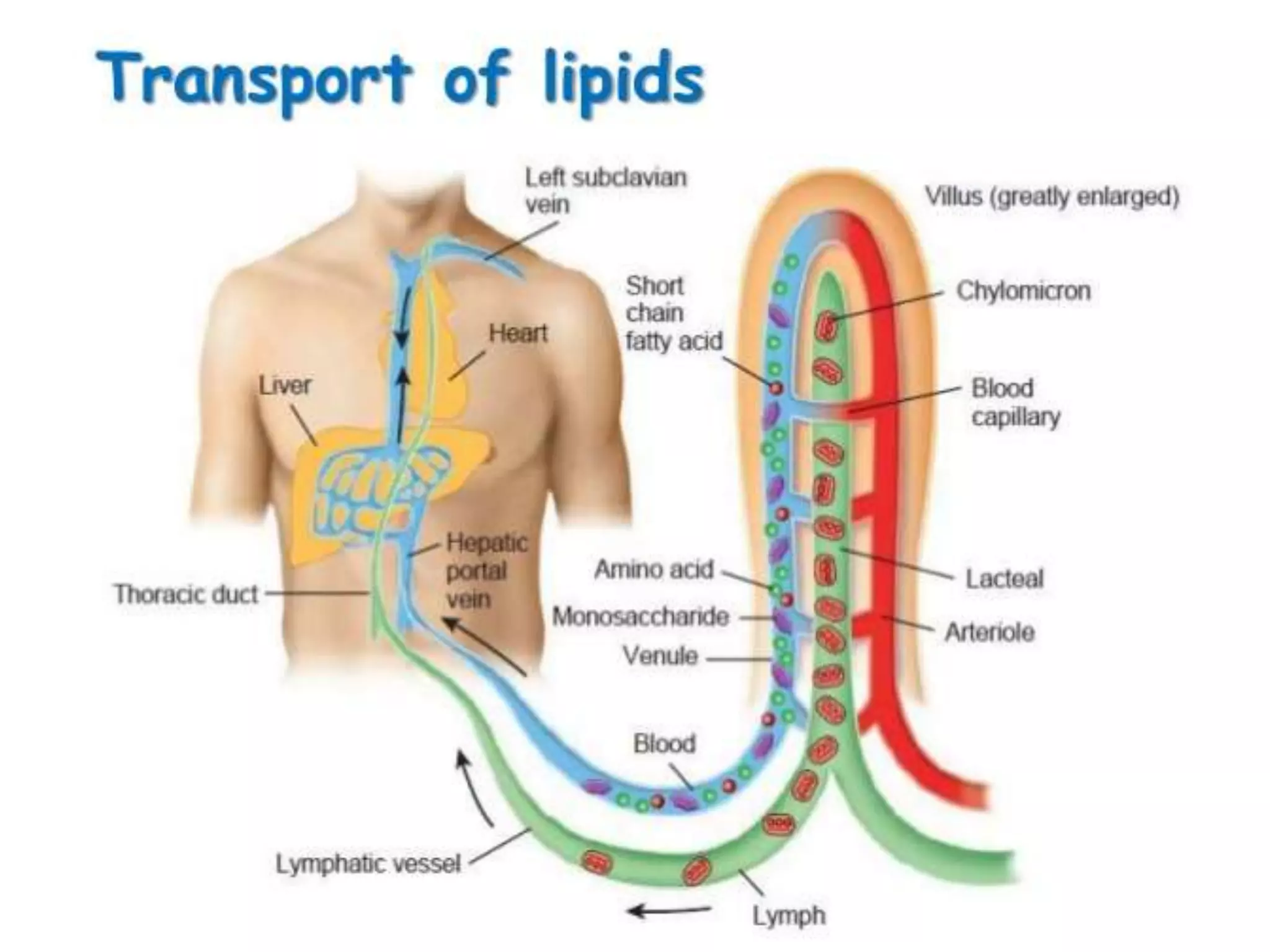
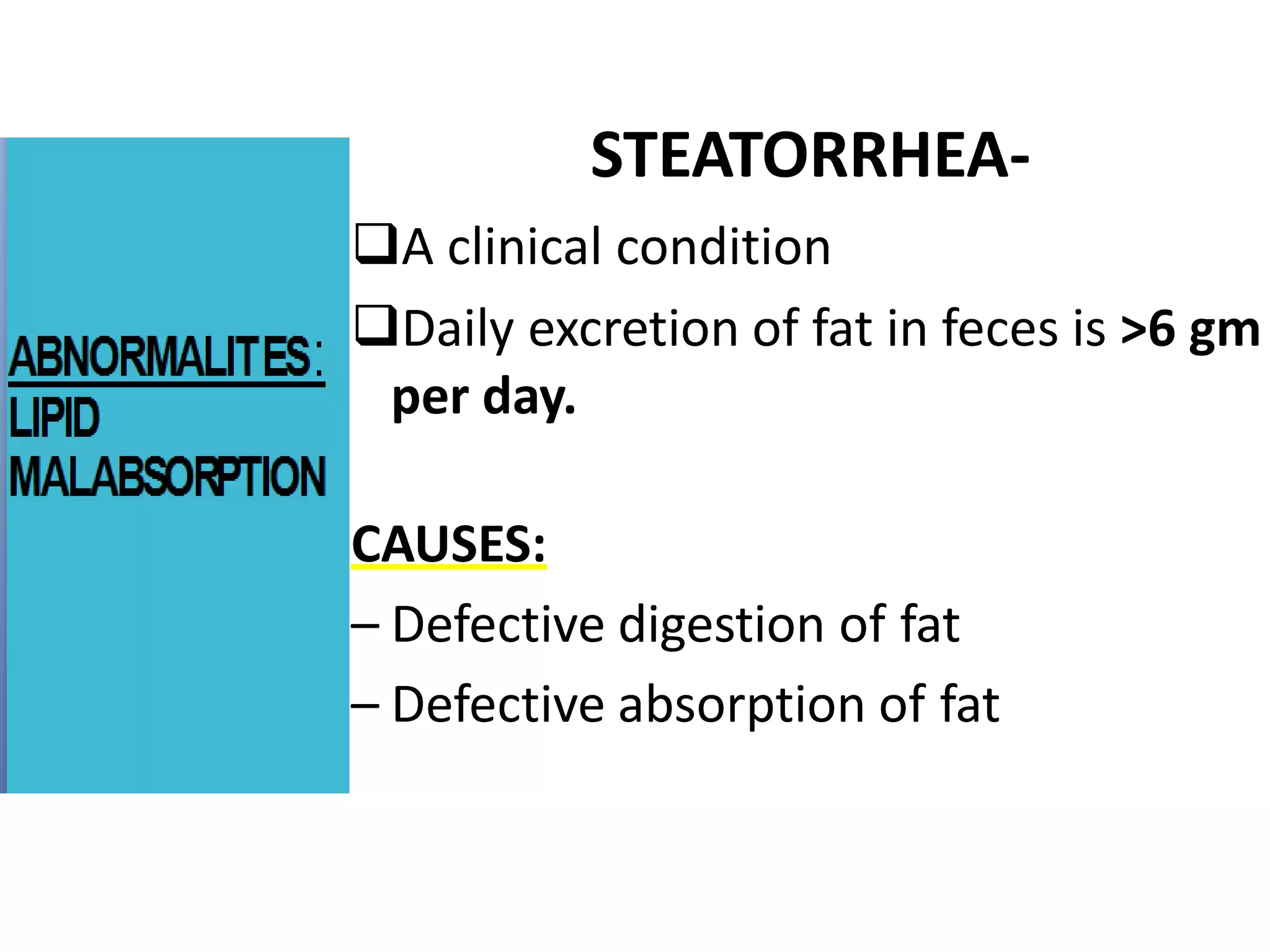
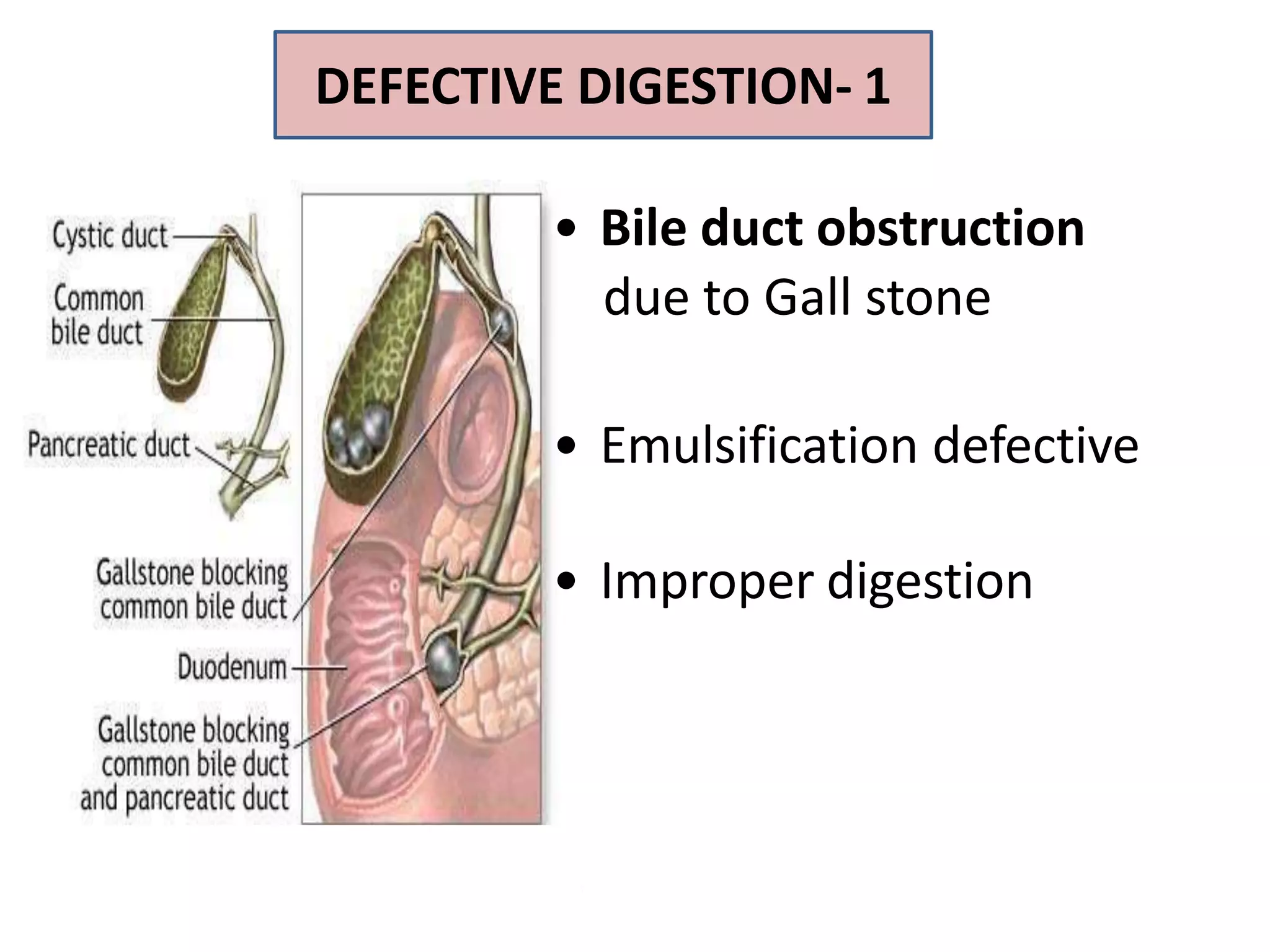
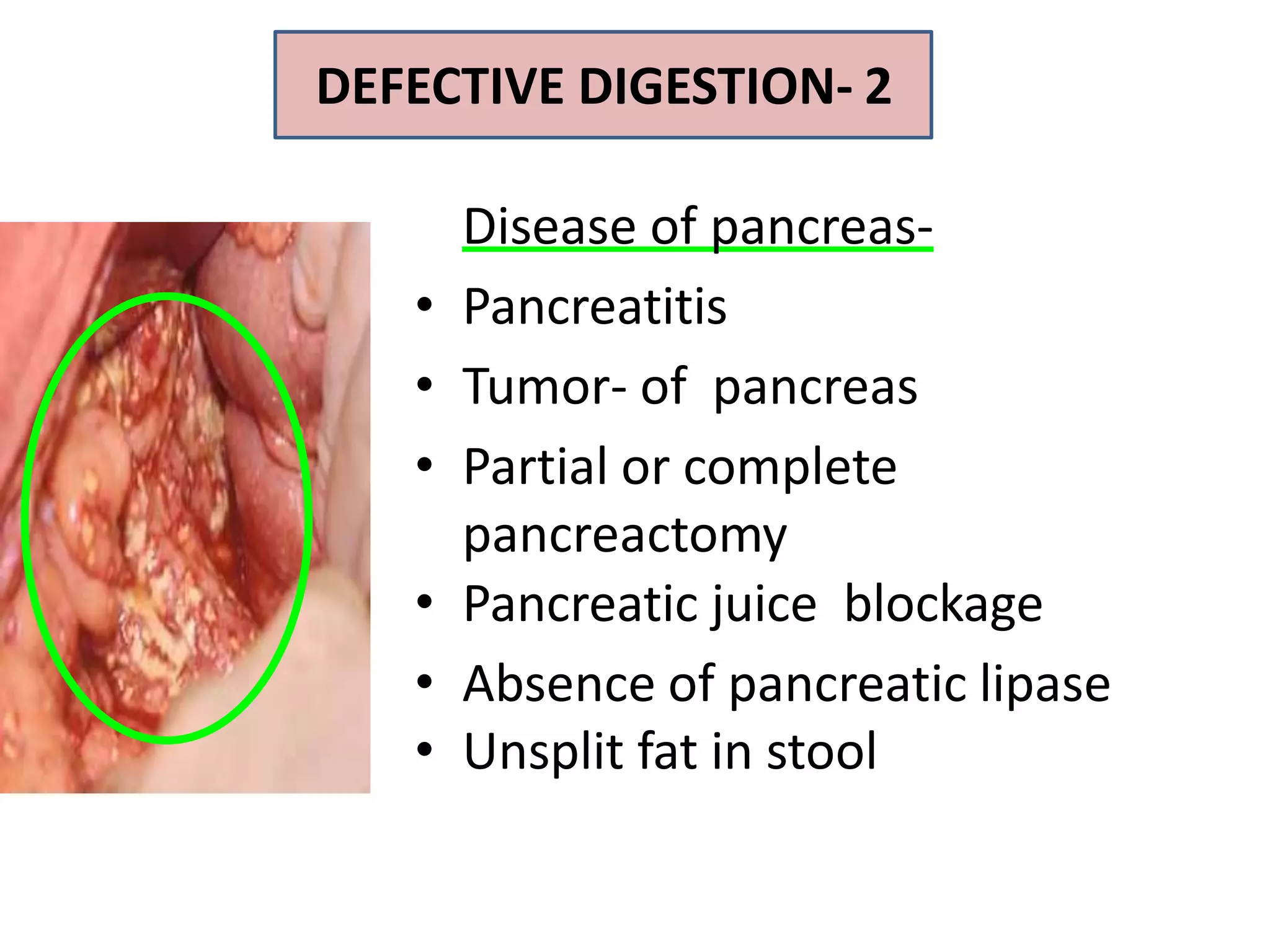
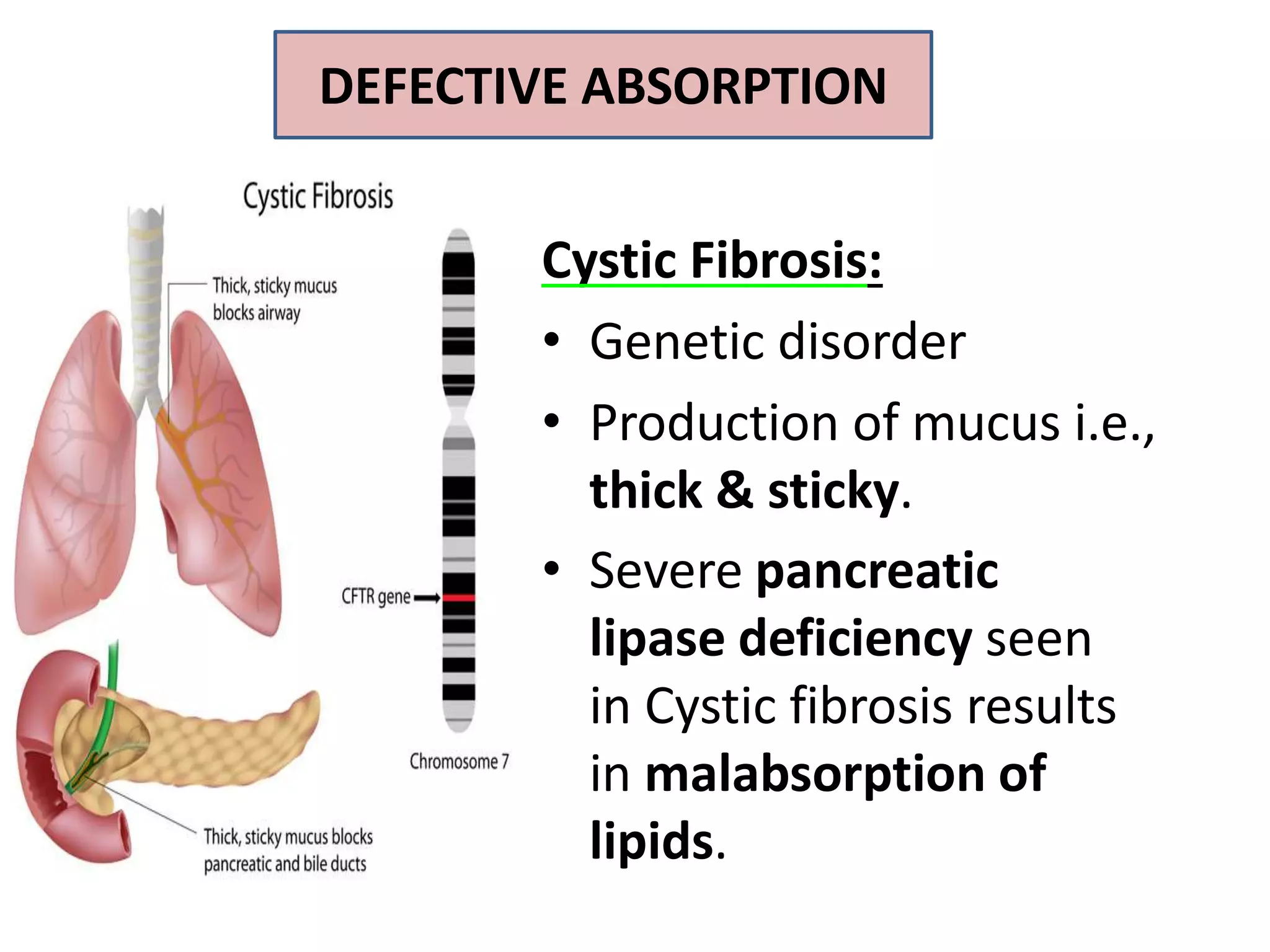
Dietary lipids are primarily triglycerides ingested from plants and animals. They provide energy and material for cell growth. Lipids cannot be absorbed in their original form due to their insolubility in water. Digestion and absorption of lipids involves emulsification by bile salts and hydrolysis by pancreatic lipases. In the small intestine, pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoacylglycerols. Bile salts form micelles to solubilize the breakdown products allowing absorption across the intestinal walls. Defects in emulsification, digestion, or absorption can result in excess fat in stool known as steatorrhea.