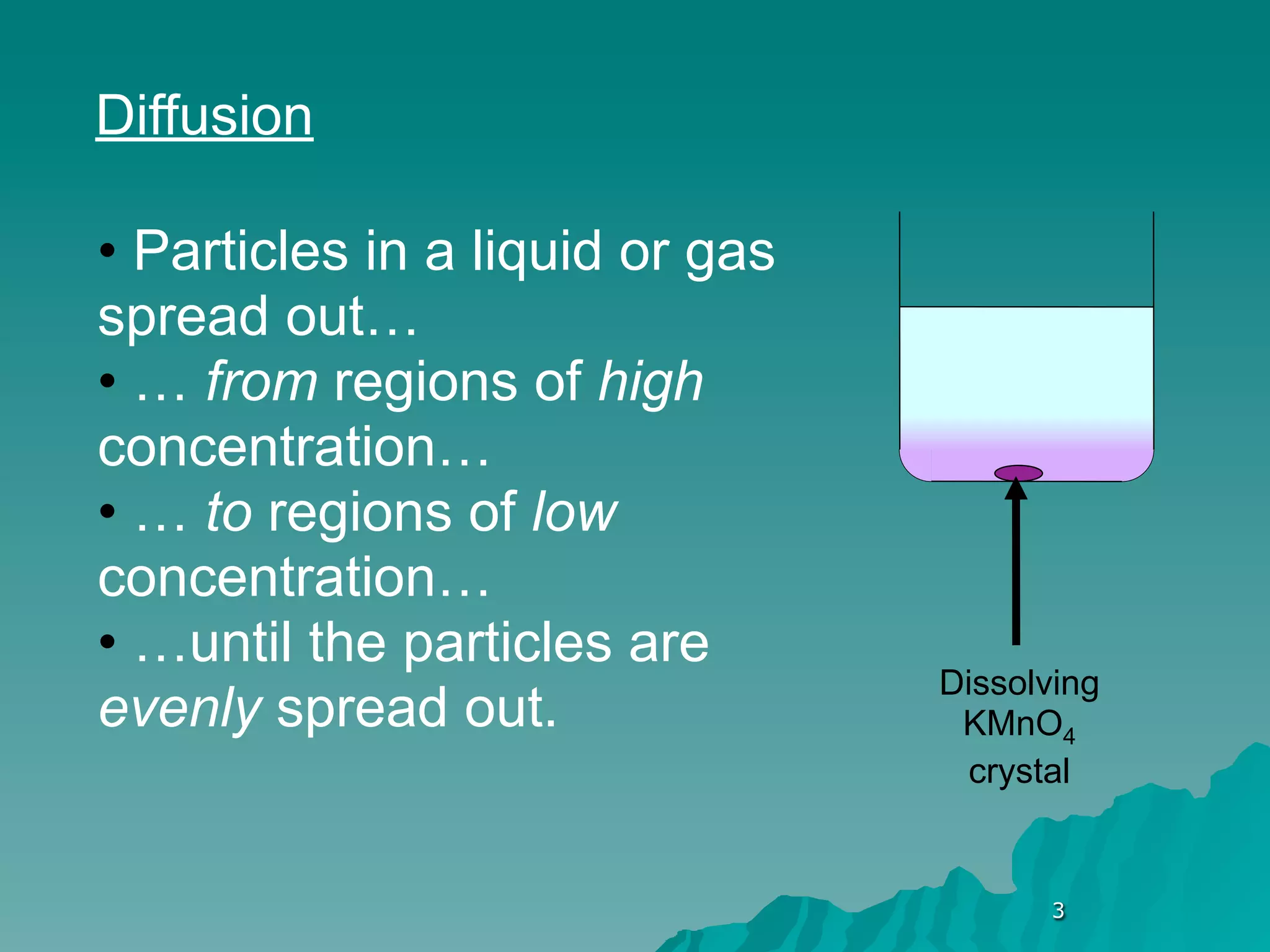
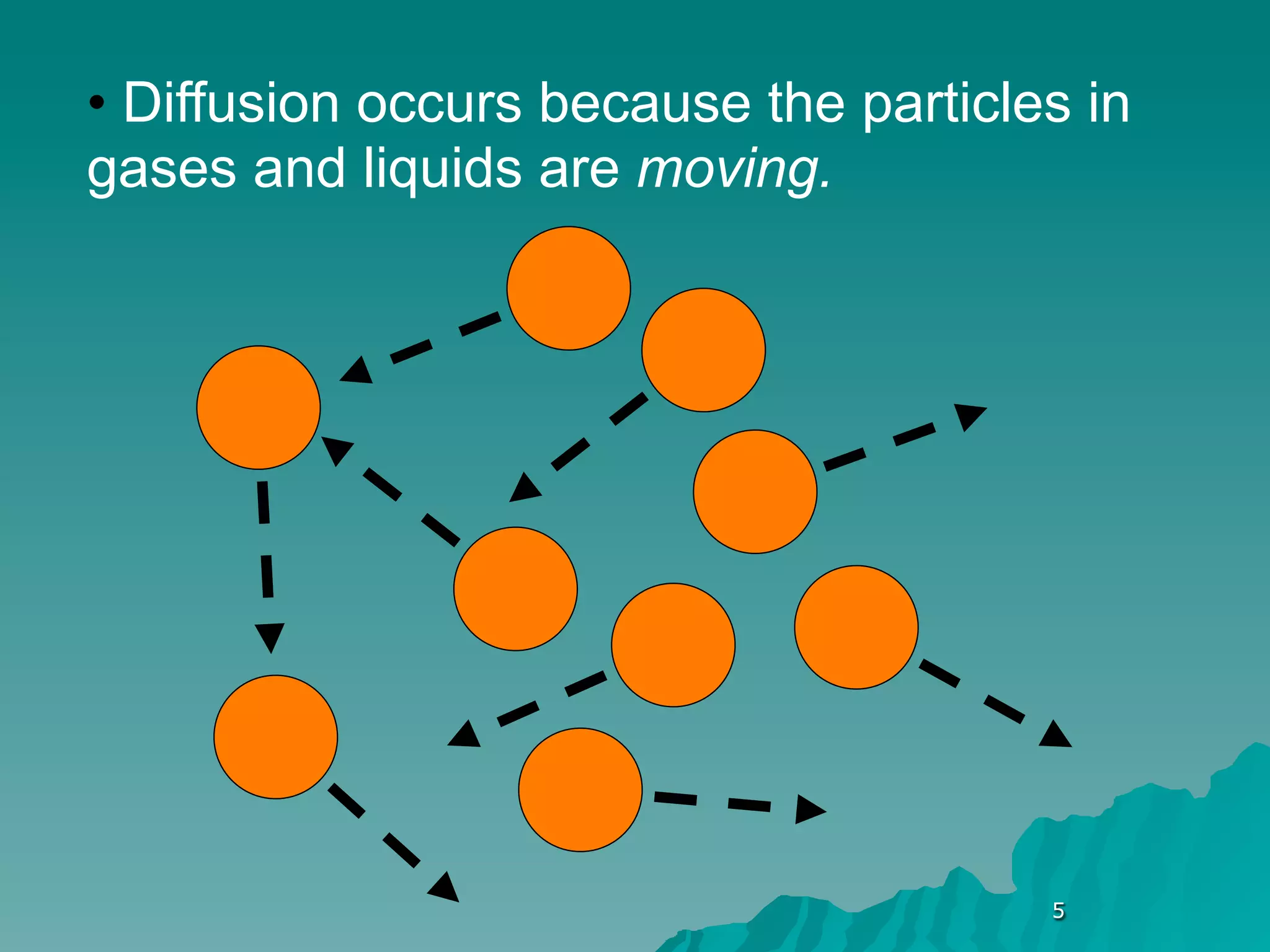
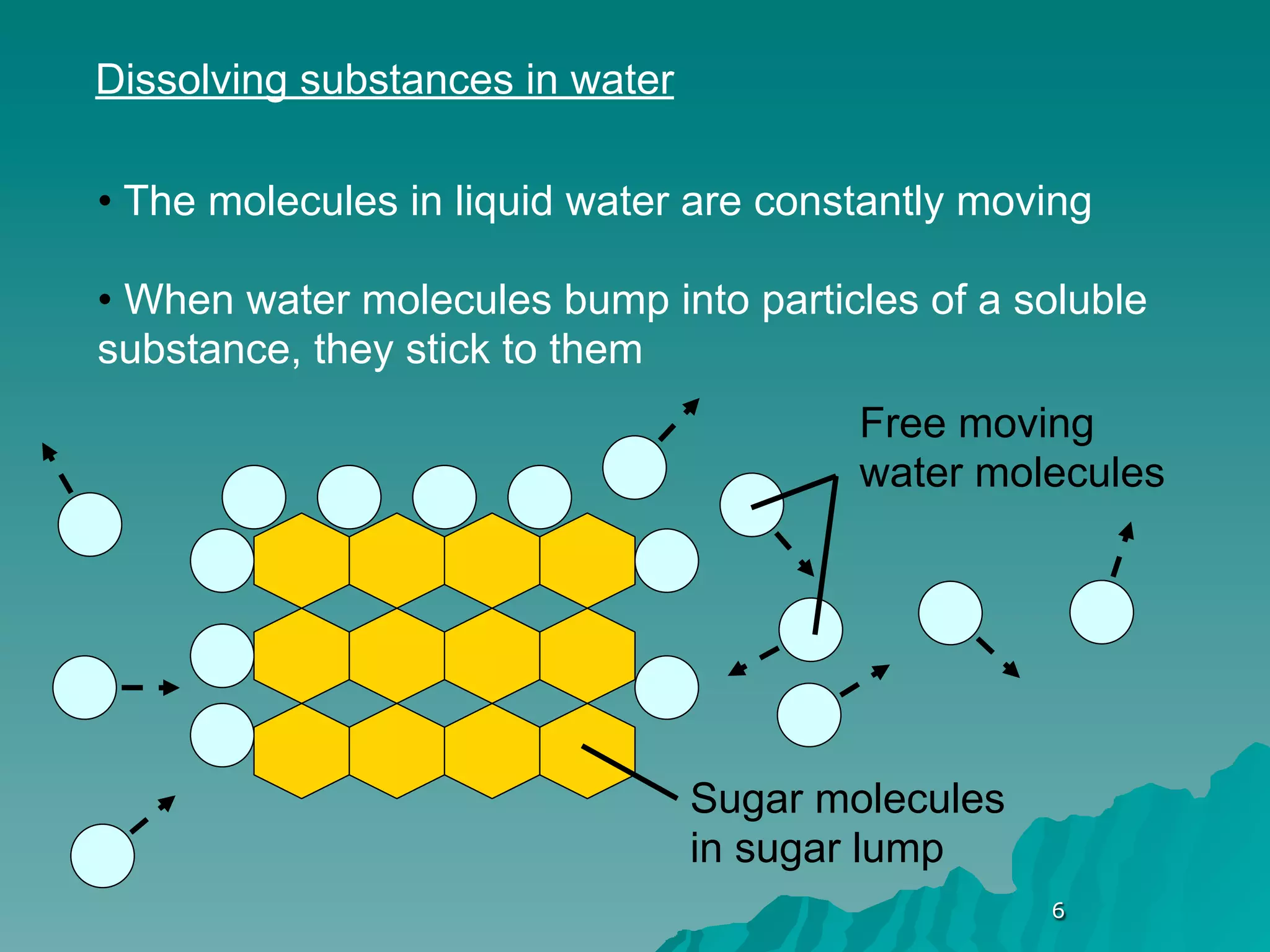
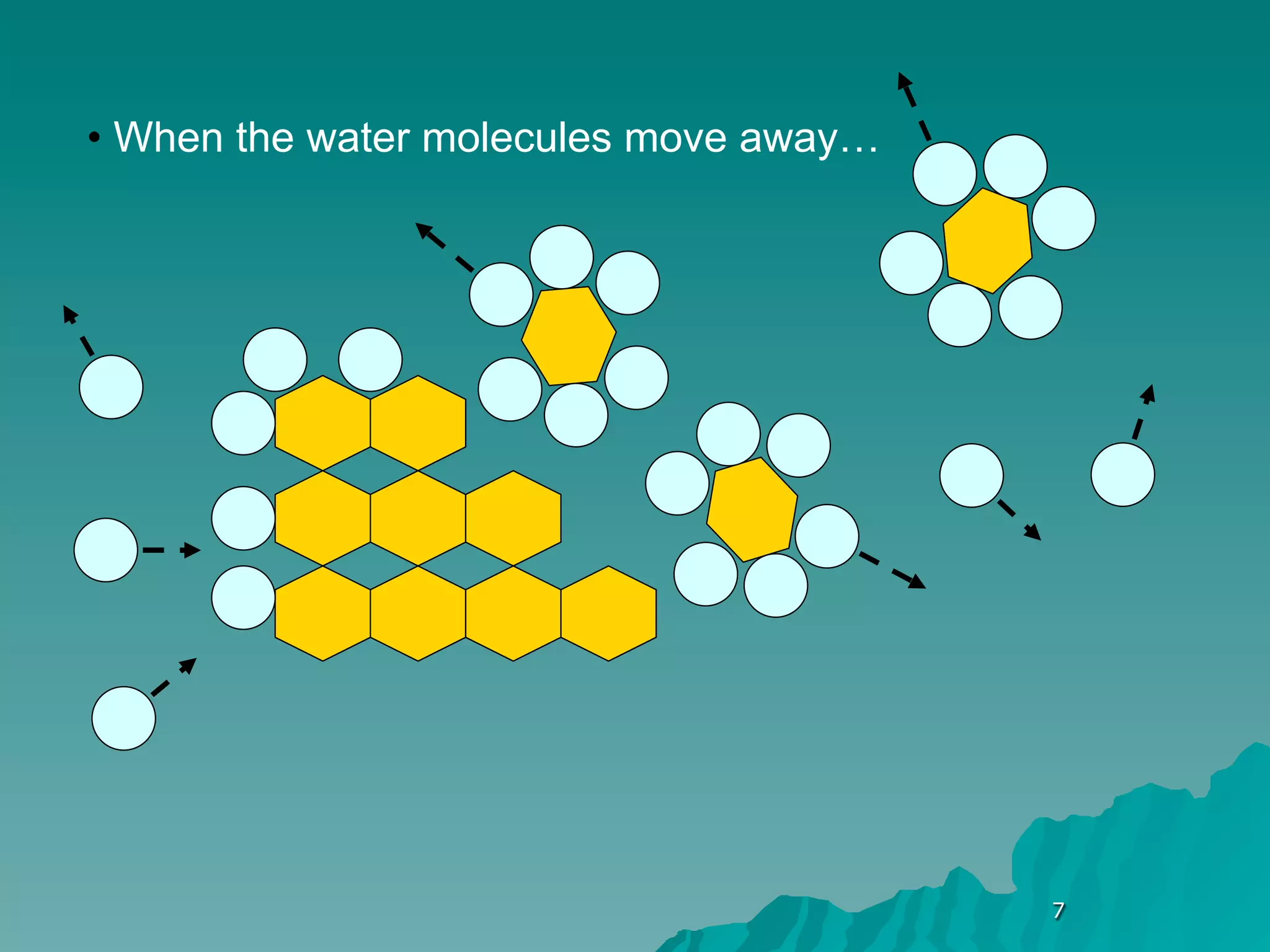
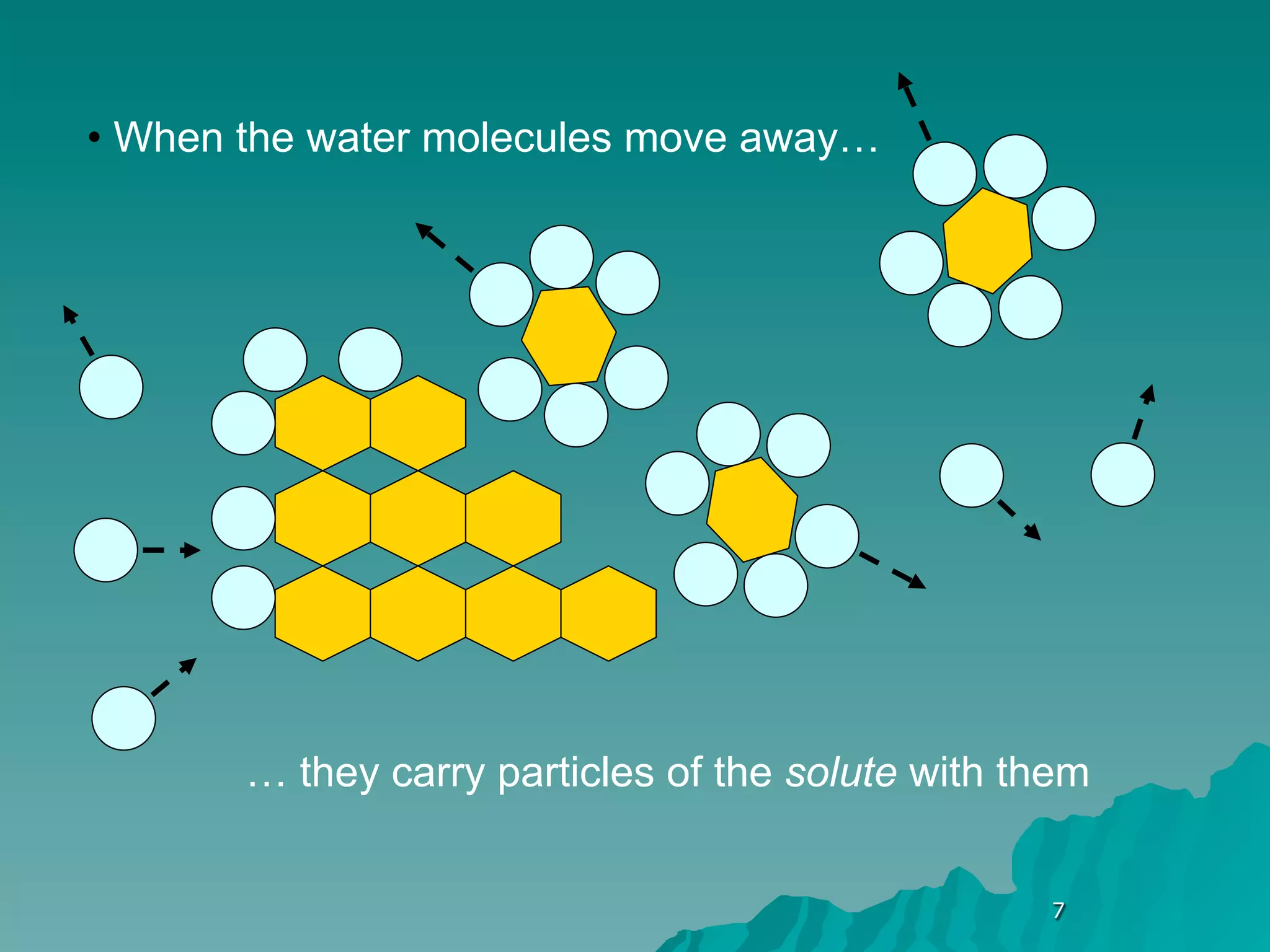
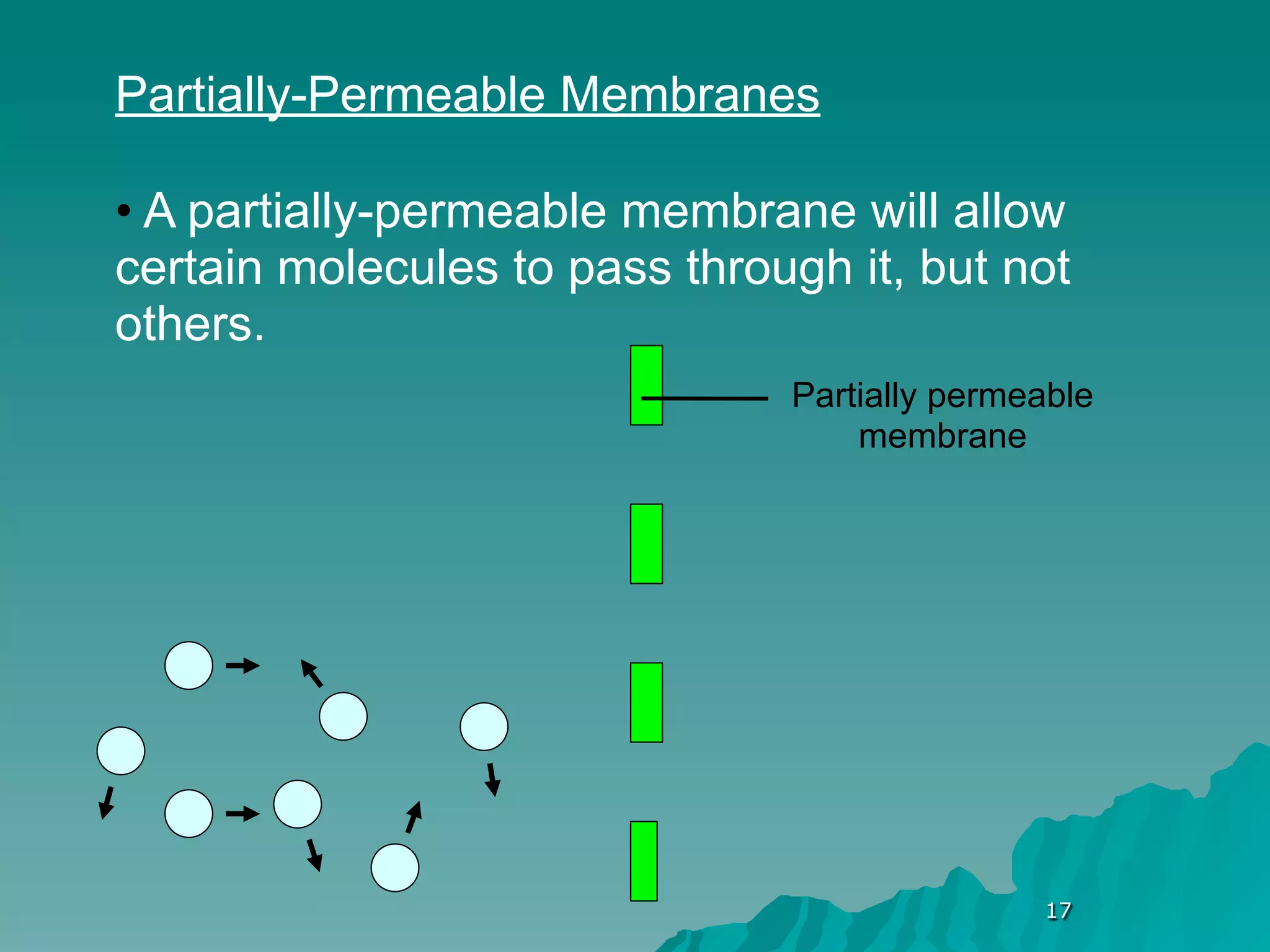
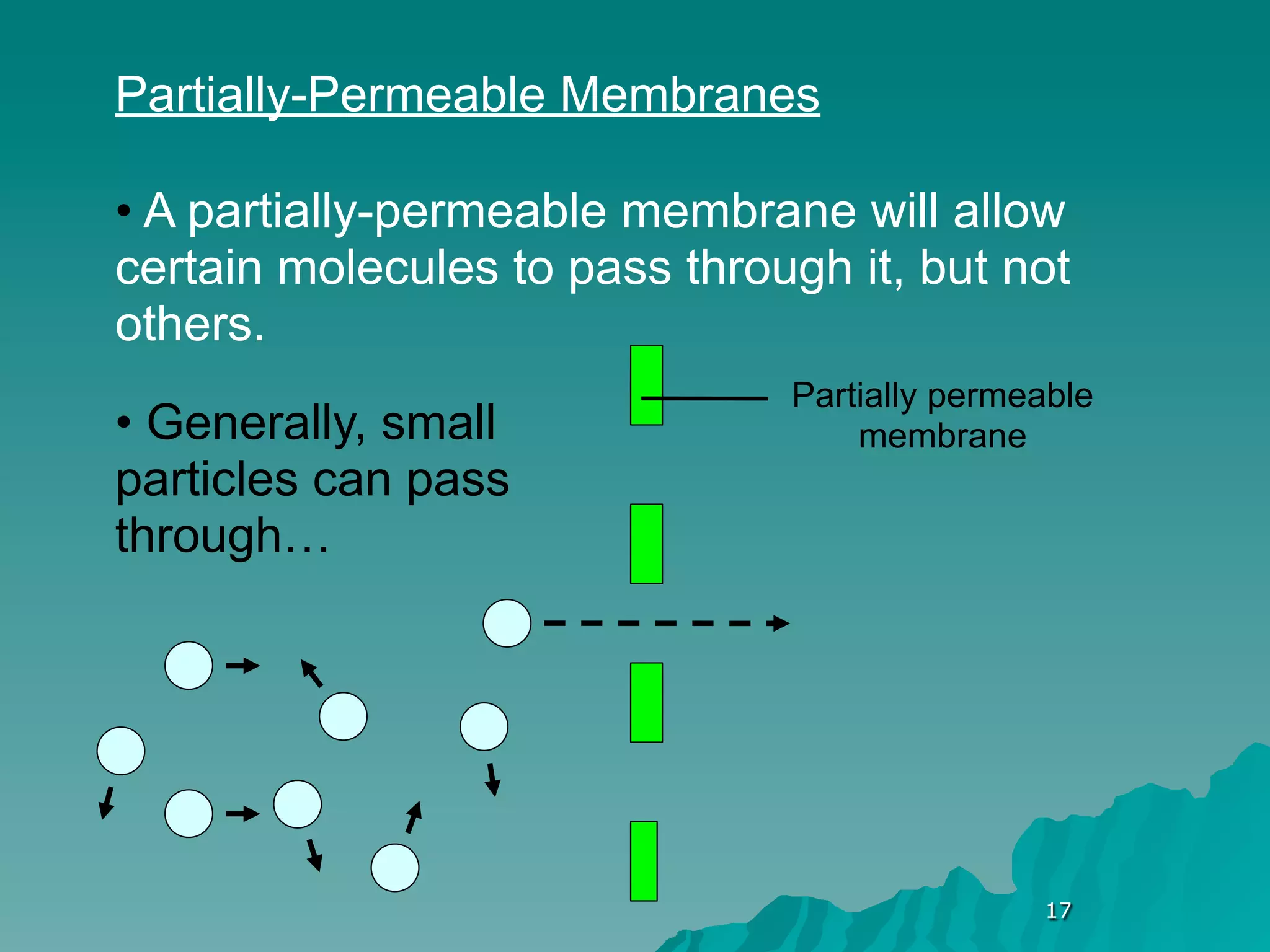
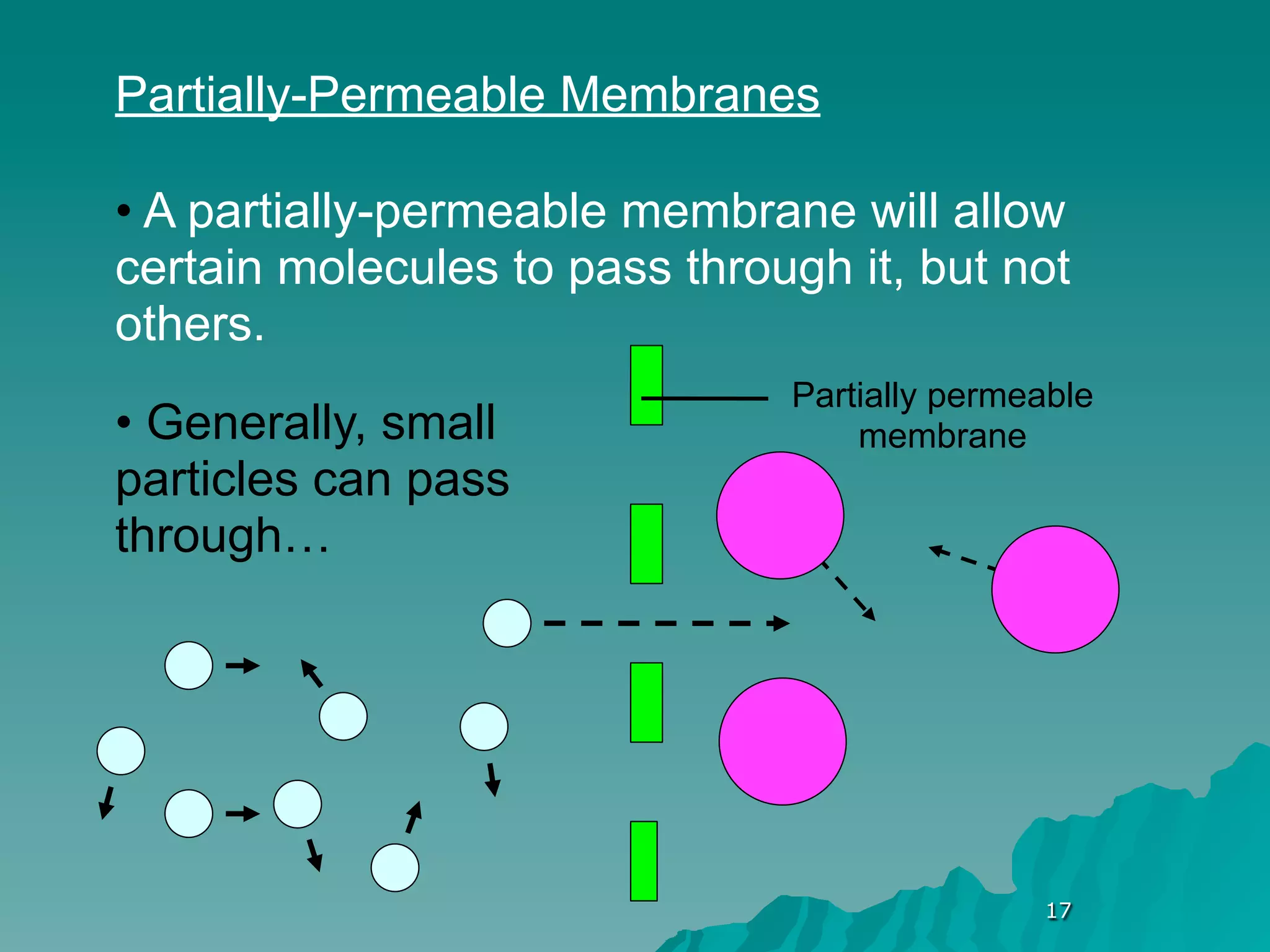
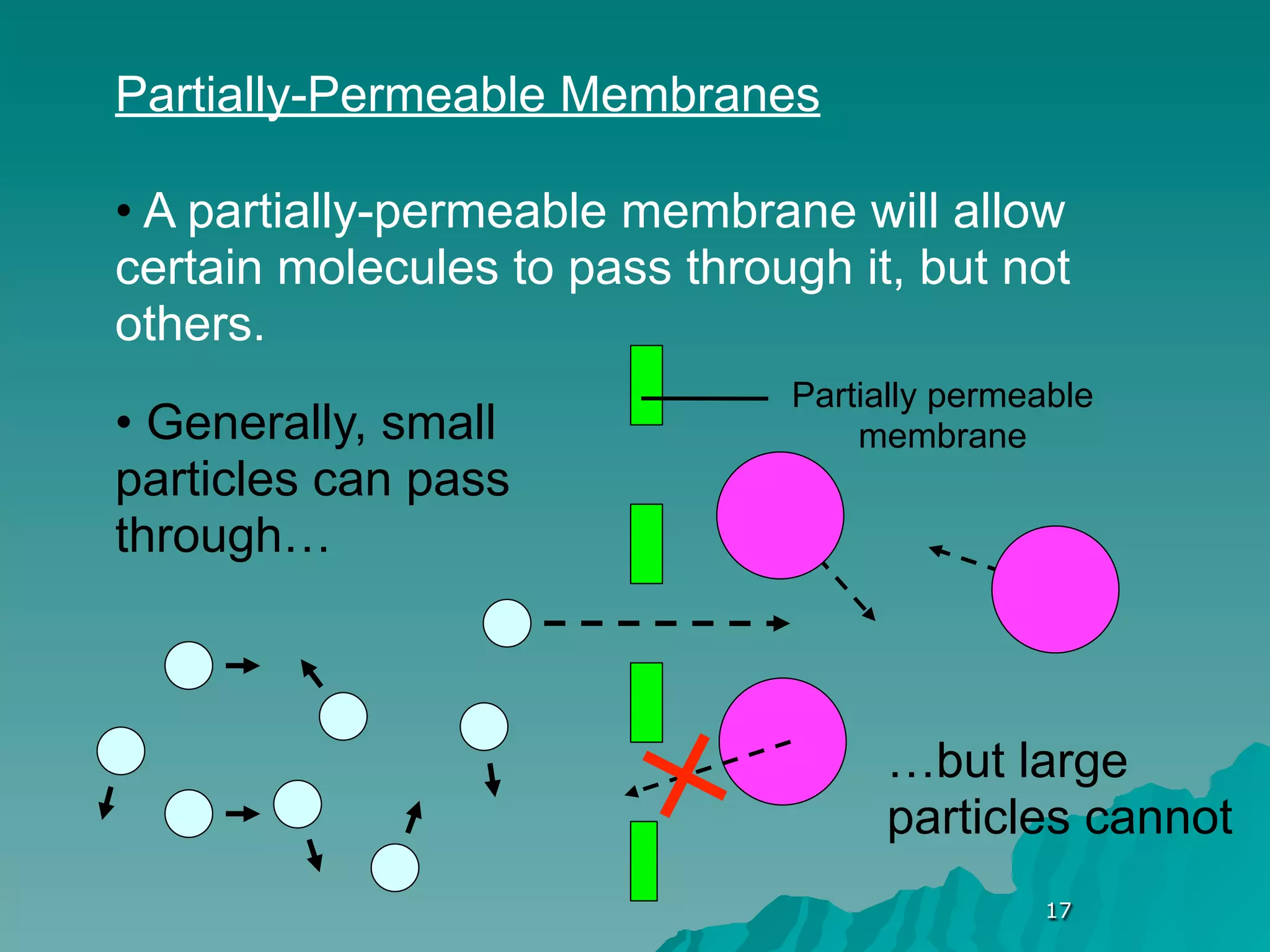
The document discusses diffusion and osmosis. It defines diffusion as the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration. It defines osmosis as the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, from an area of high water concentration to low. The document explains that diffusion and osmosis are important processes for the exchange of gases, water, minerals and waste at the cellular level, which is necessary for homeostasis and survival of living things.