1) Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration until uniform distribution is reached. It occurs more quickly in gases than liquids due to particles moving more rapidly and having more space between them in gases.
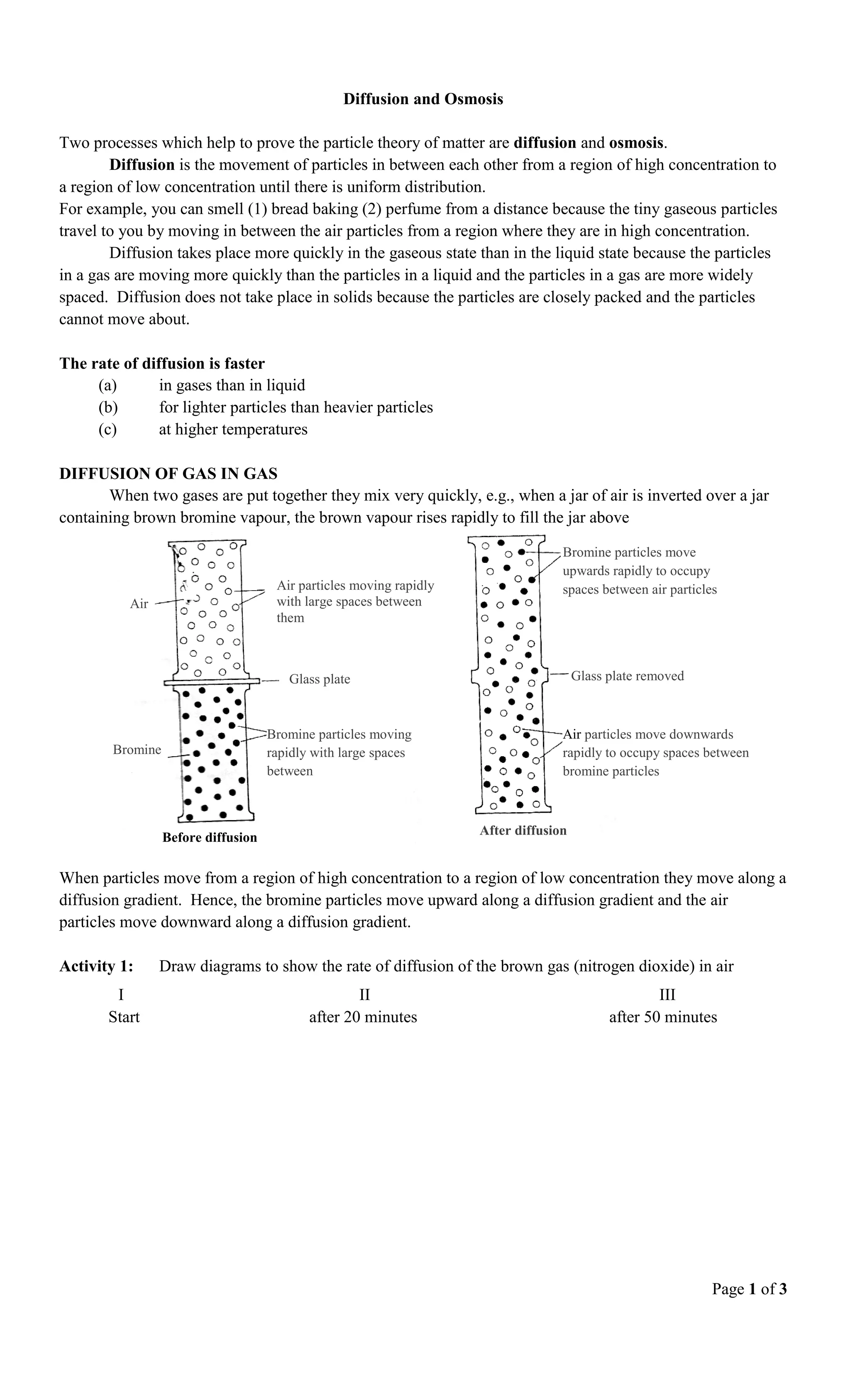
2) When two gases are combined, they mix rapidly through diffusion as particles move along concentration gradients. Bromine vapor rises into an air-filled jar through diffusion.
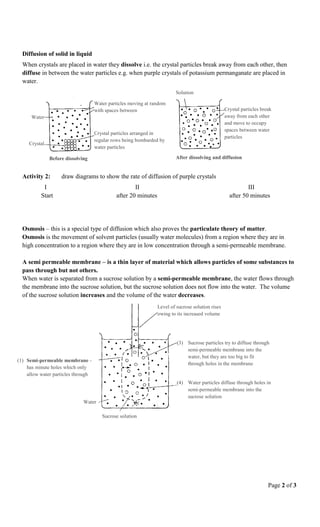
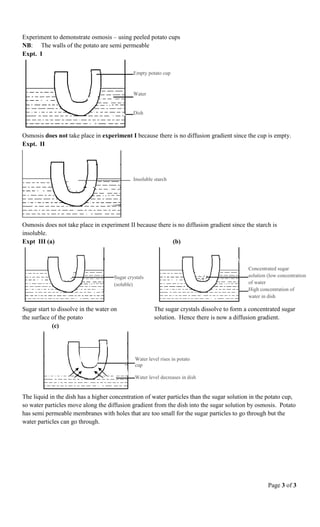
3) In osmosis, water molecules diffuse through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration into a solution with low water concentration, such as sucrose solution. The sucrose solution increases in volume while the water decreases.