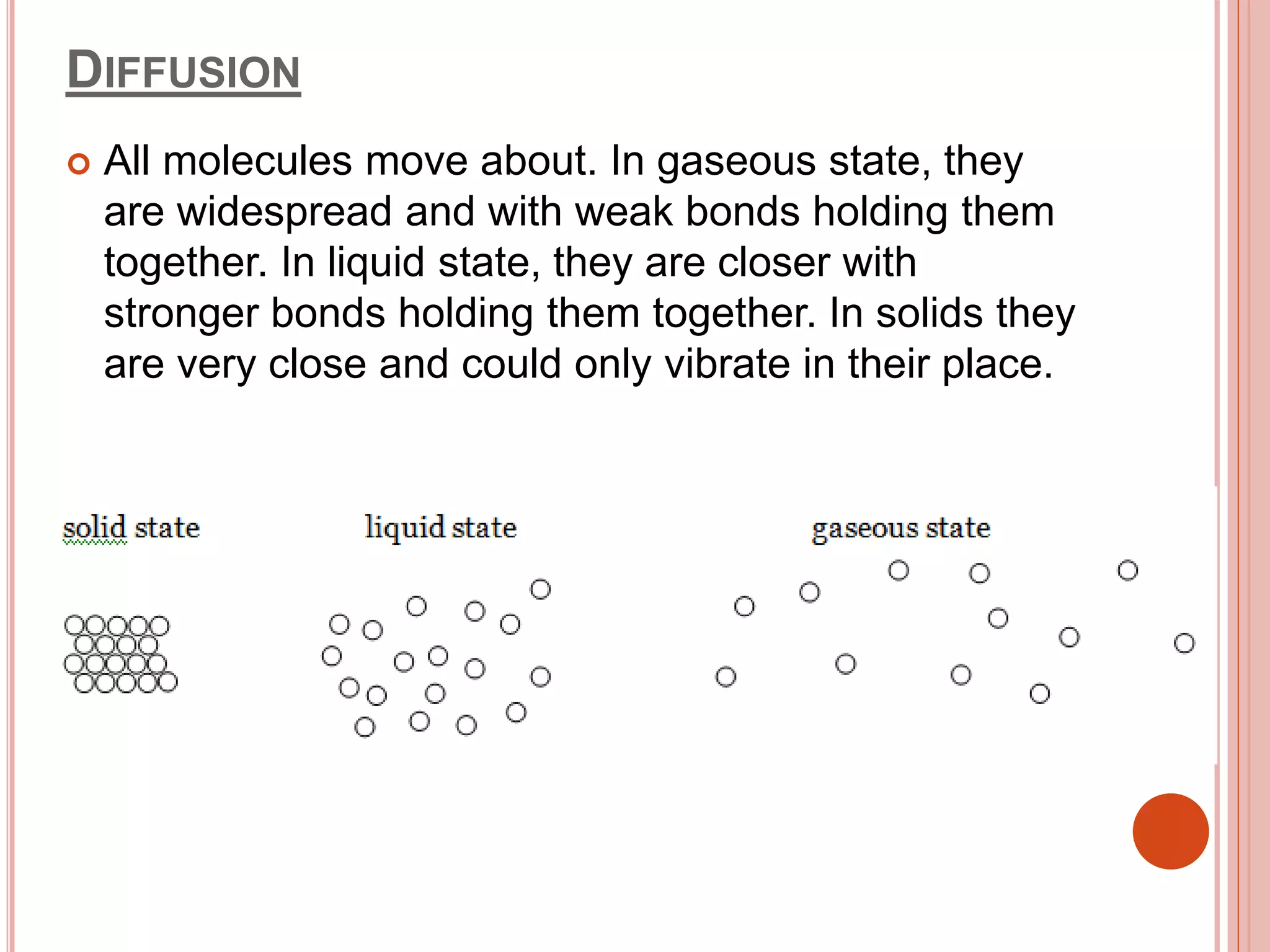
The document discusses different types of molecular movement including diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It explains that diffusion is the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration. Osmosis specifically refers to the diffusion of water molecules through a partially permeable membrane from an area of high water potential to low water potential. Active transport differs in that it moves molecules against their concentration gradient, from low to high concentration areas, and requires energy in the form of ATP.