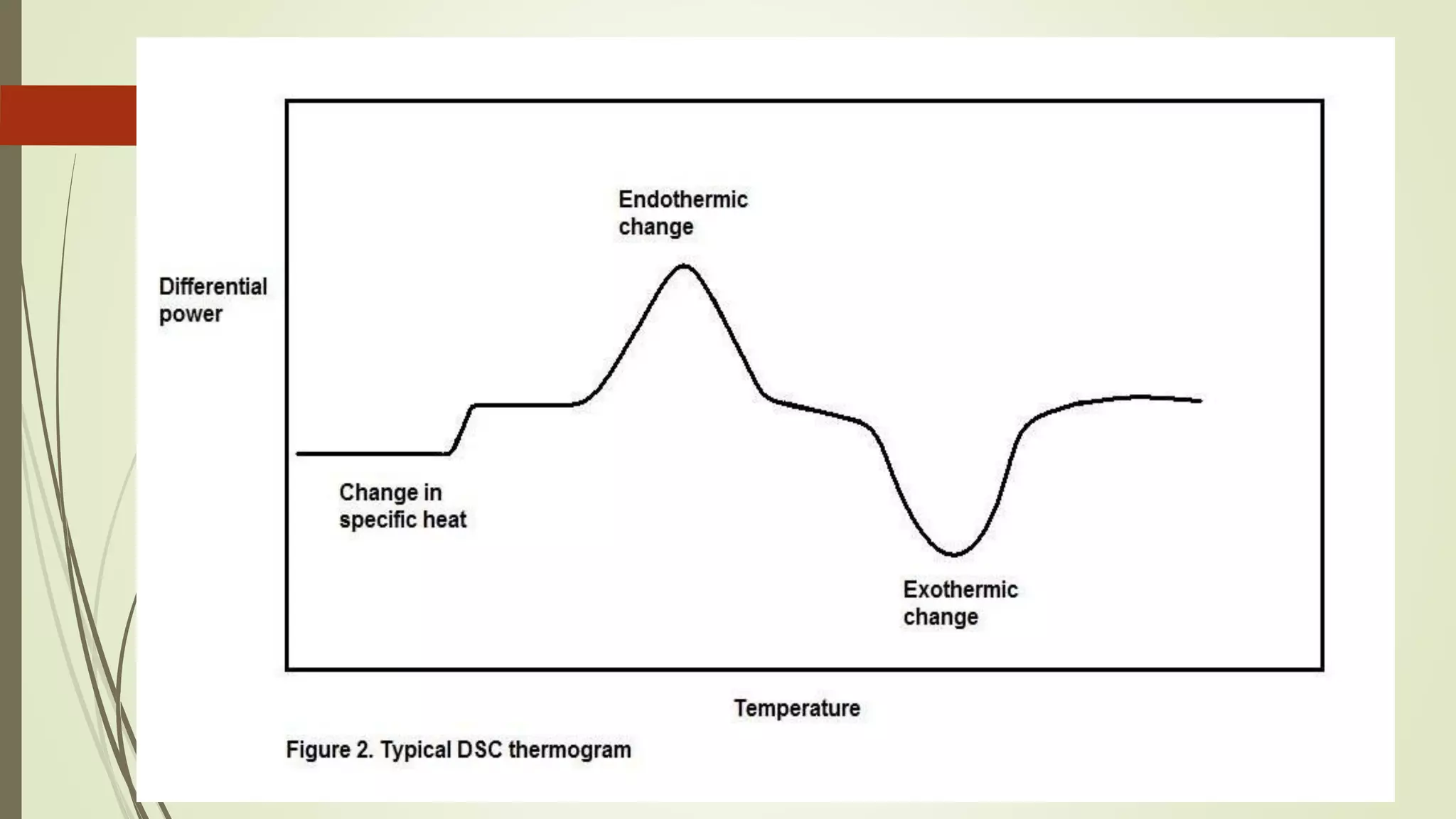
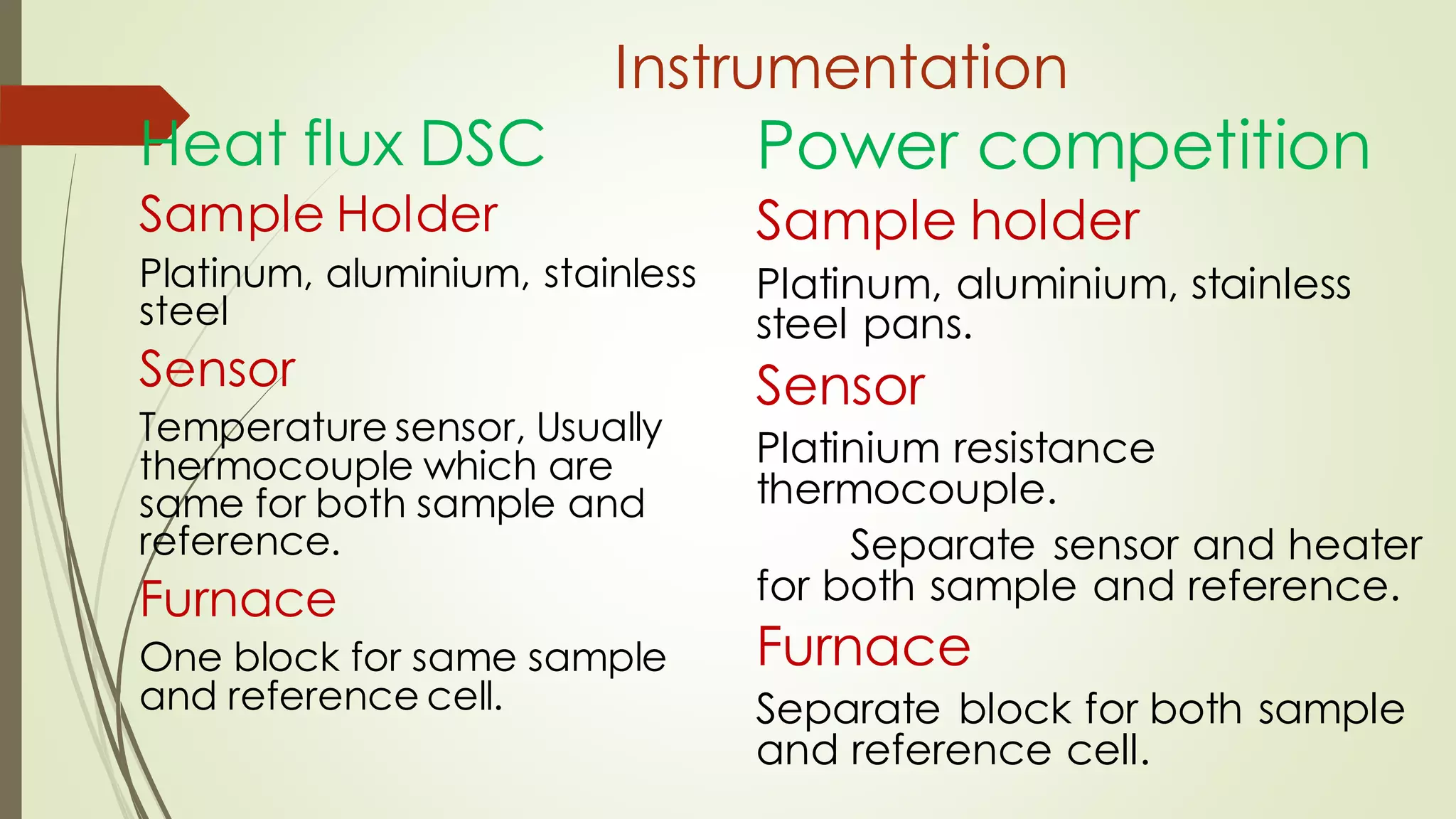
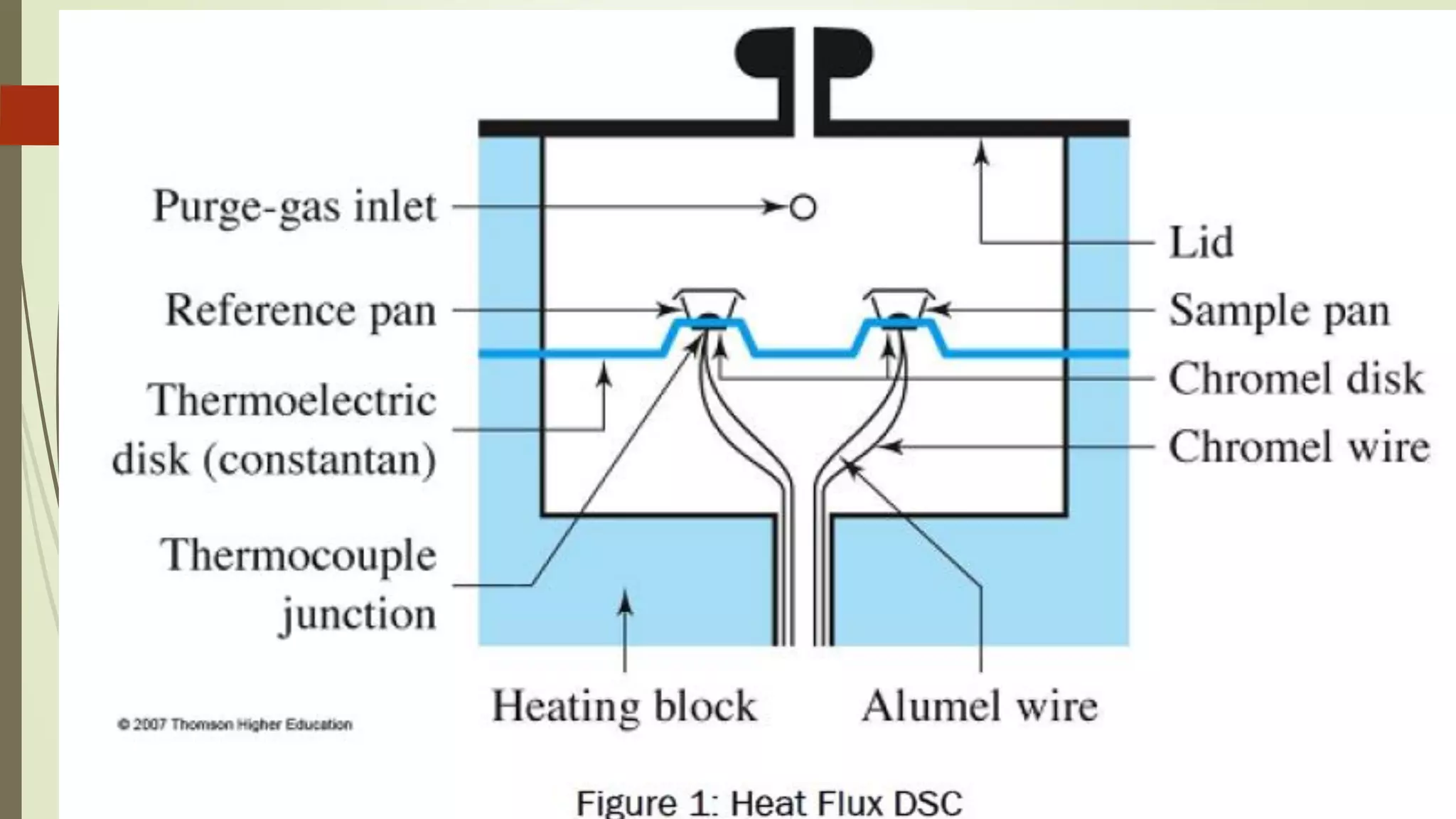
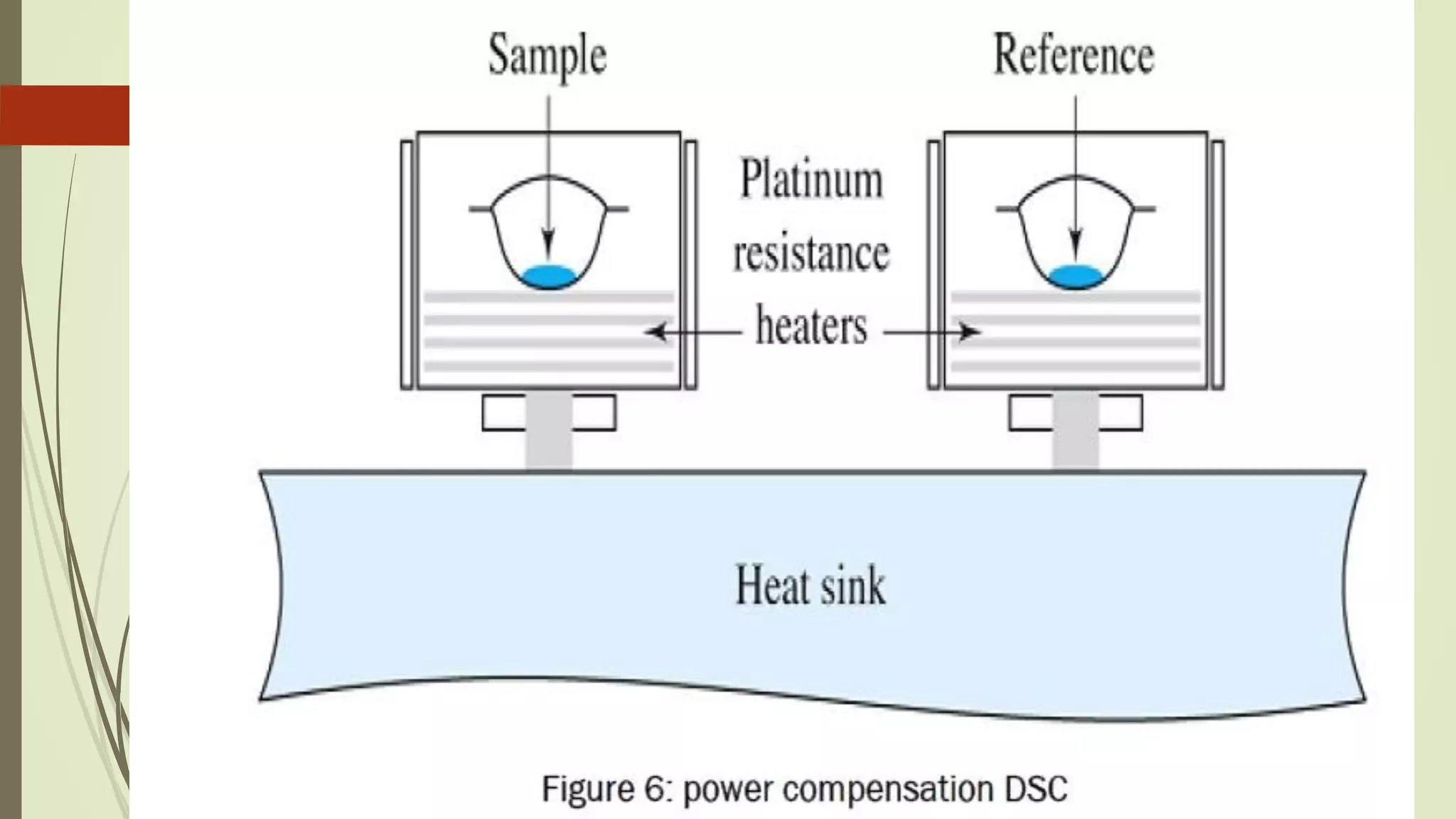
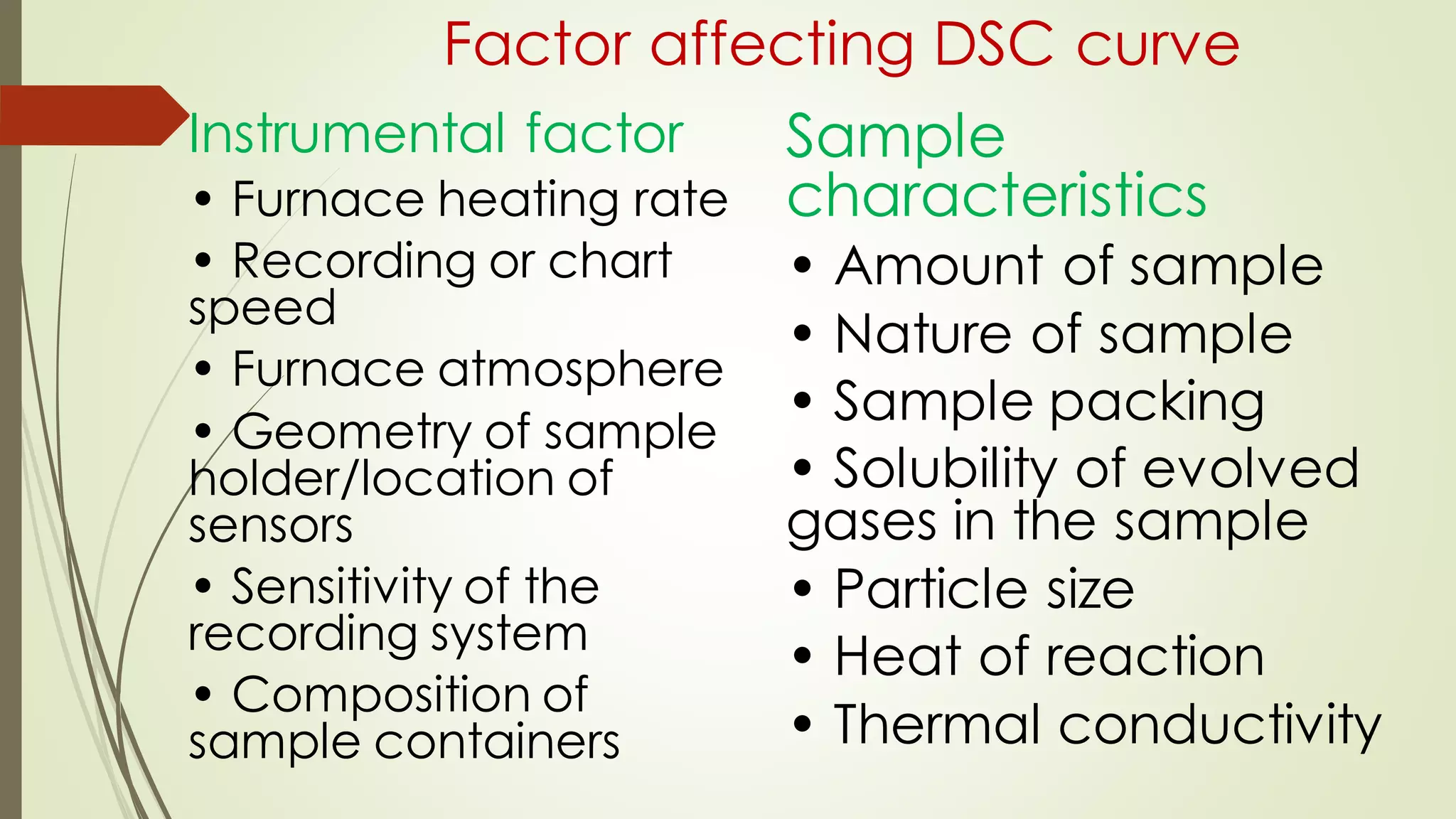
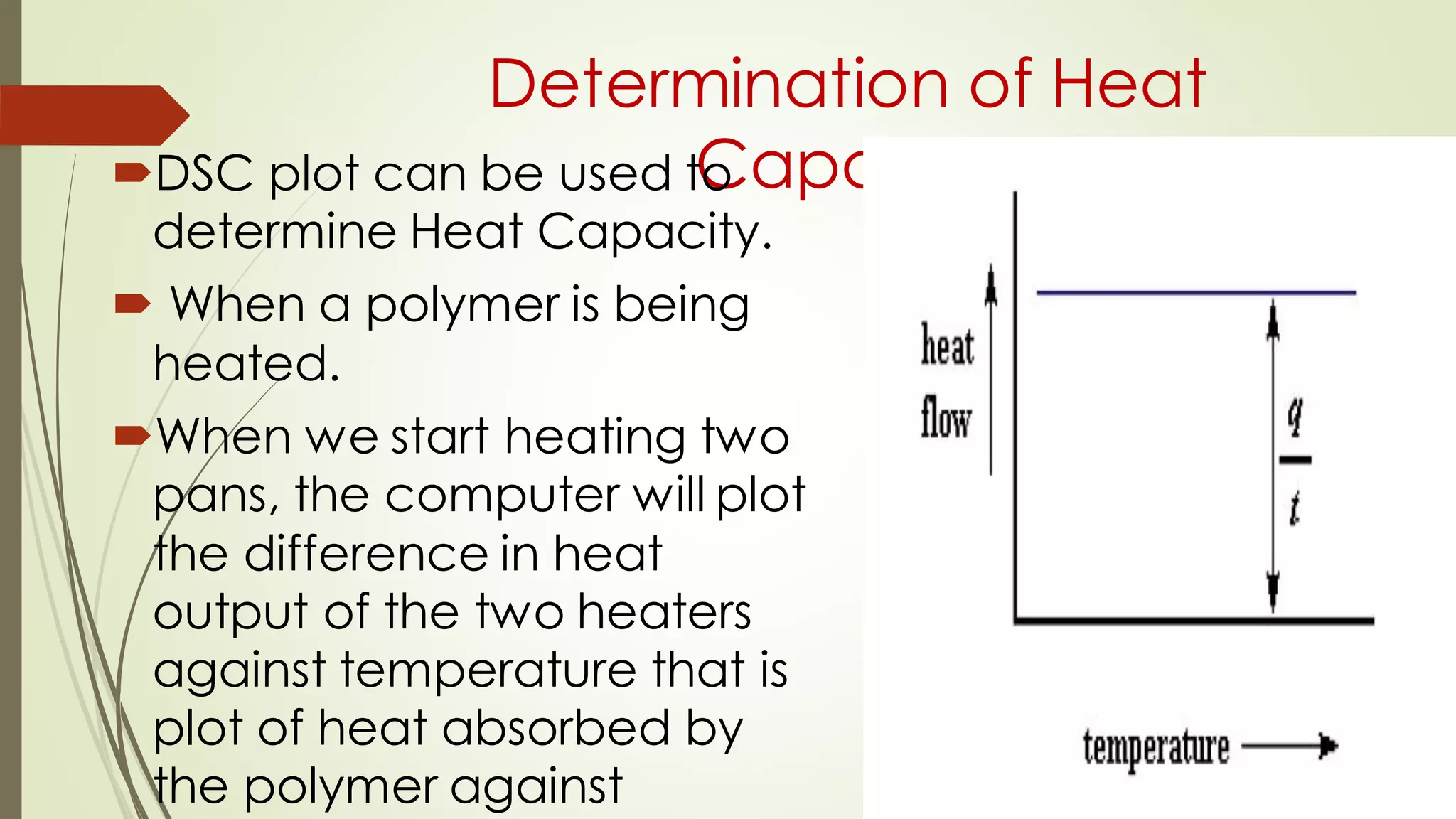
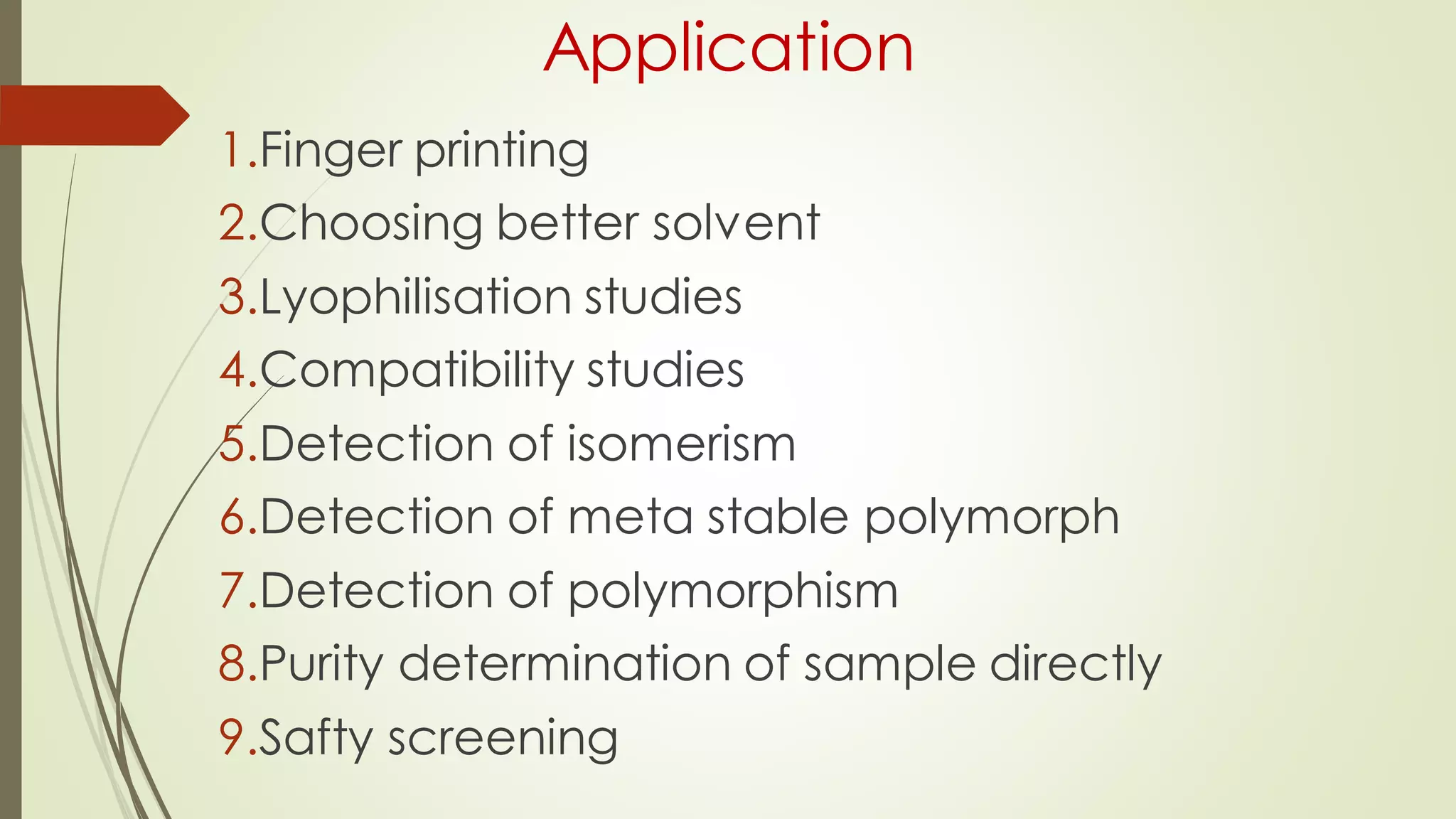
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermoanalytical technique used to analyze thermal transitions in materials. It works by measuring the difference in heat flow between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. DSC can detect phase transitions like melting, crystallization, and glass transitions that require or release energy. The document discusses the history, principles, instrumentation, types, advantages, disadvantages and applications of DSC for analyzing materials.