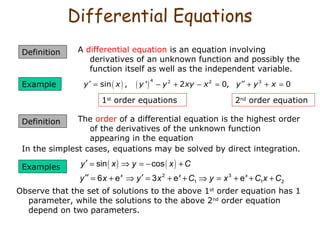
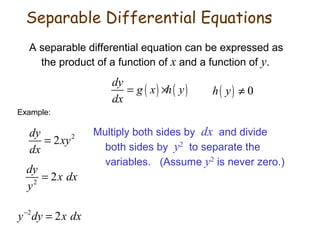
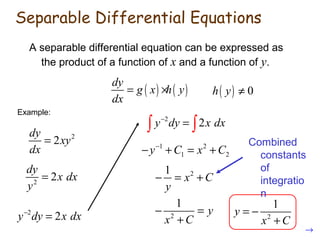
1. Differential equations are equations involving derivatives of an unknown function and can be of different orders. Separable differential equations can be expressed as the product of a function of x and a function of y.
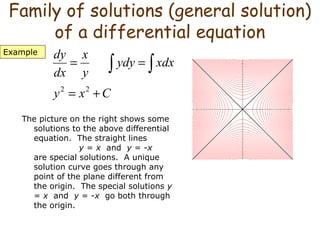
2. The general solution or family of solutions to a differential equation represents all possible solutions. Specific solutions satisfy initial conditions.
3. Models of natural growth and decay can be represented by differential equations where the rate of change is proportional to the amount present, following an exponential solution. The logistic growth model includes limitations on growth.
4. Mixing problems can be modeled using differential equations to determine properties of mixtures over time as different substances enter and exit a container.