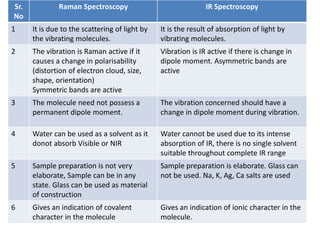
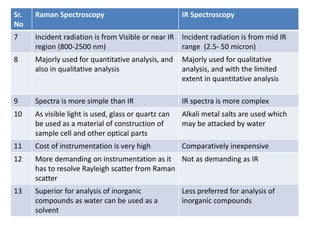
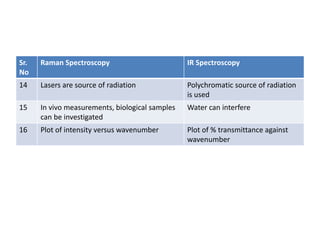
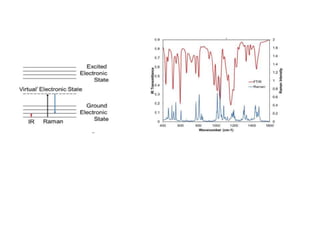
Raman spectroscopy and IR spectroscopy are techniques for analyzing vibrational modes in molecules. Raman spectroscopy involves scattering of light by vibrating molecules and can be used to analyze both organic and inorganic compounds using visible or near-IR radiation. IR spectroscopy involves absorption of light by vibrating molecules that change dipole moment and is better suited for qualitative analysis using mid-IR radiation, though water can interfere with samples. The two techniques provide complementary information about molecular structure and bonding.