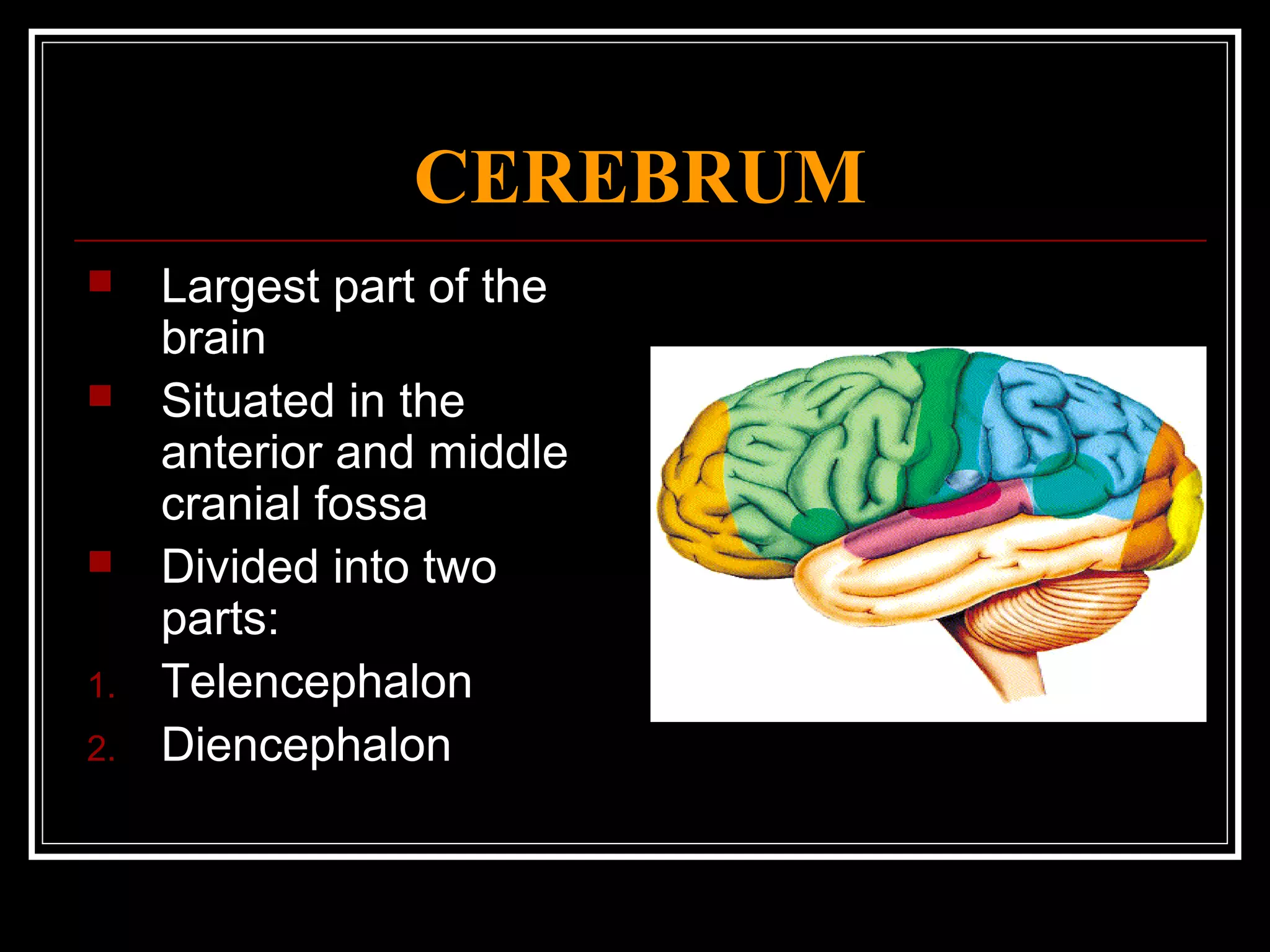
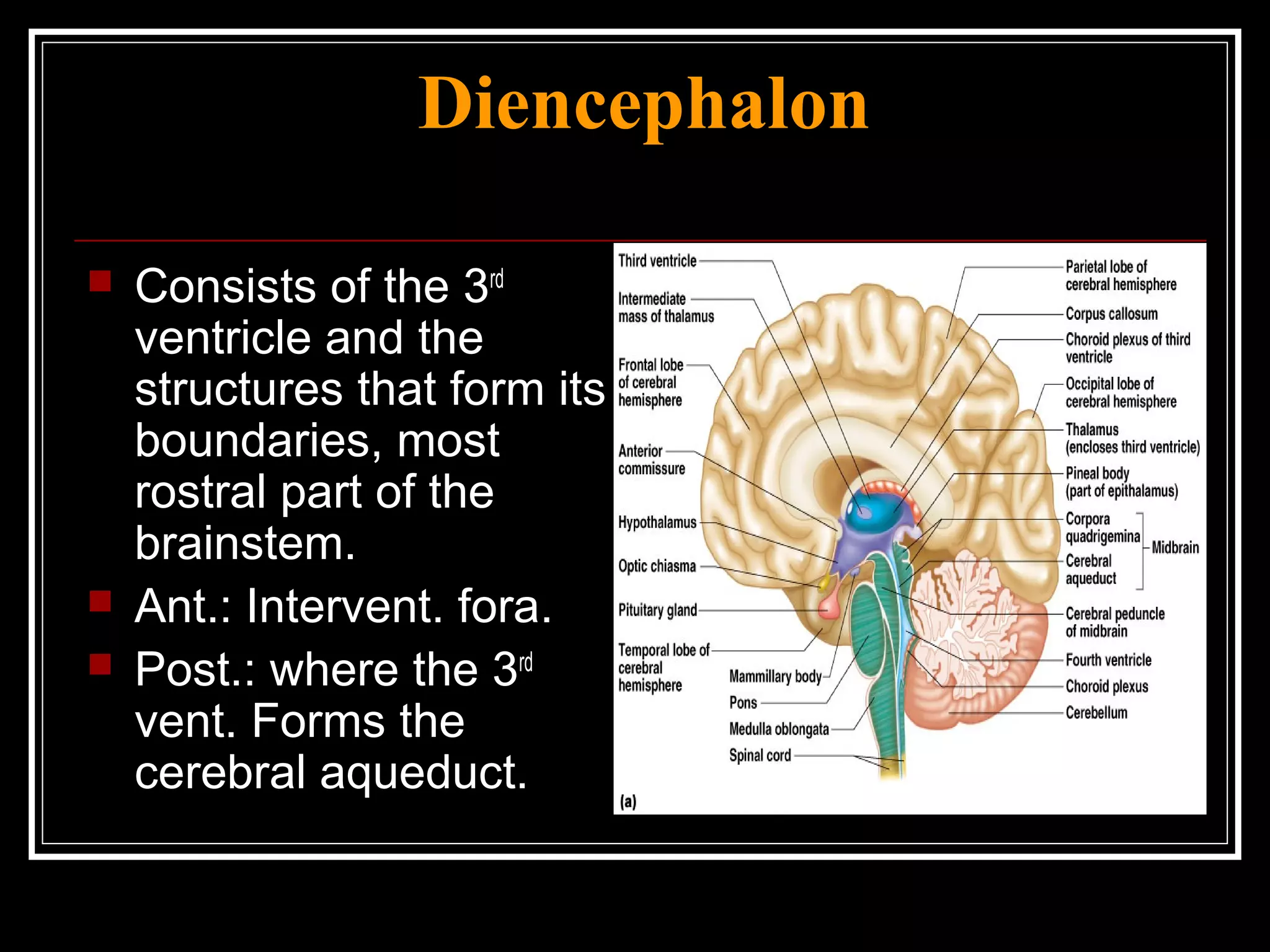
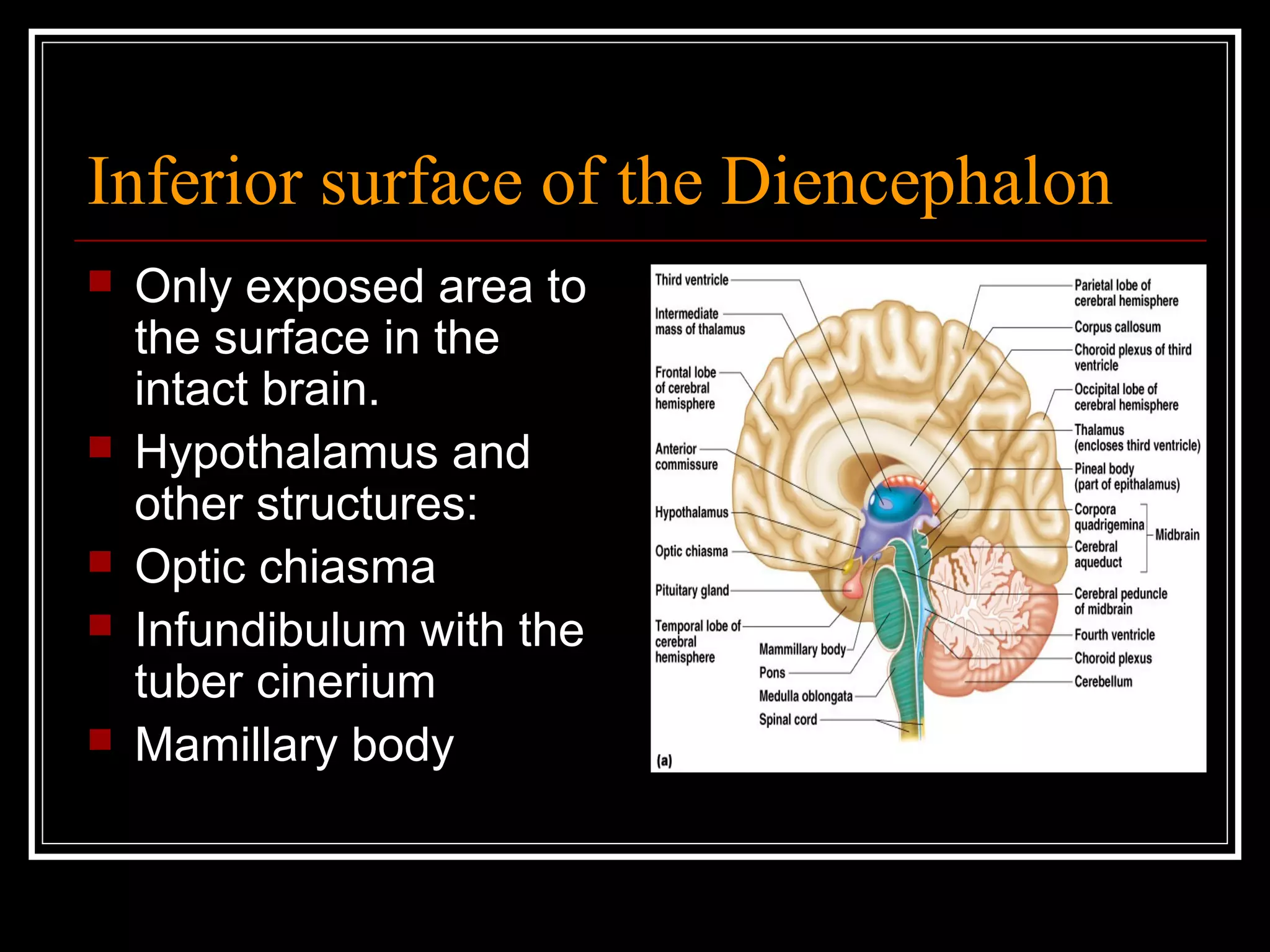
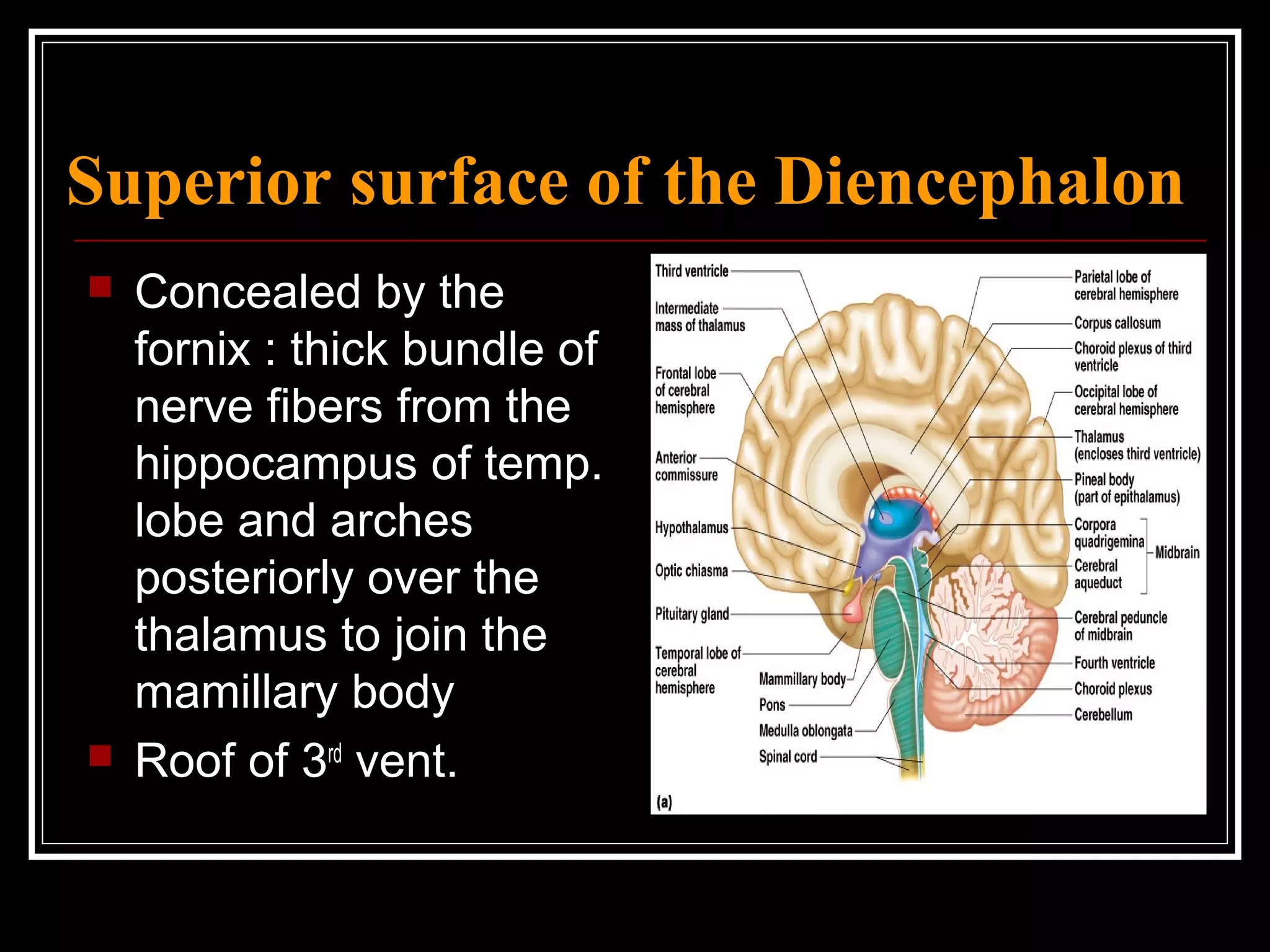
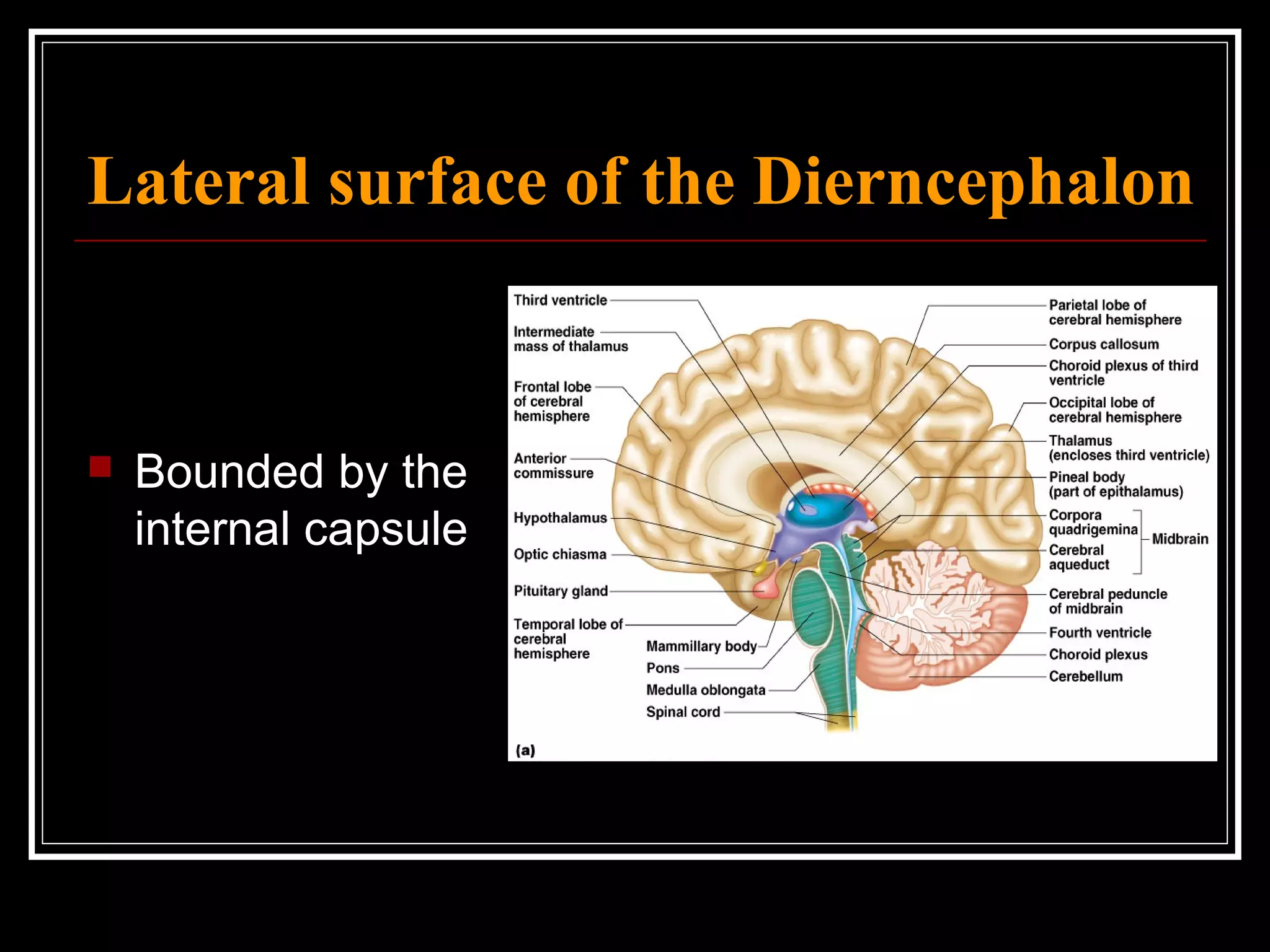
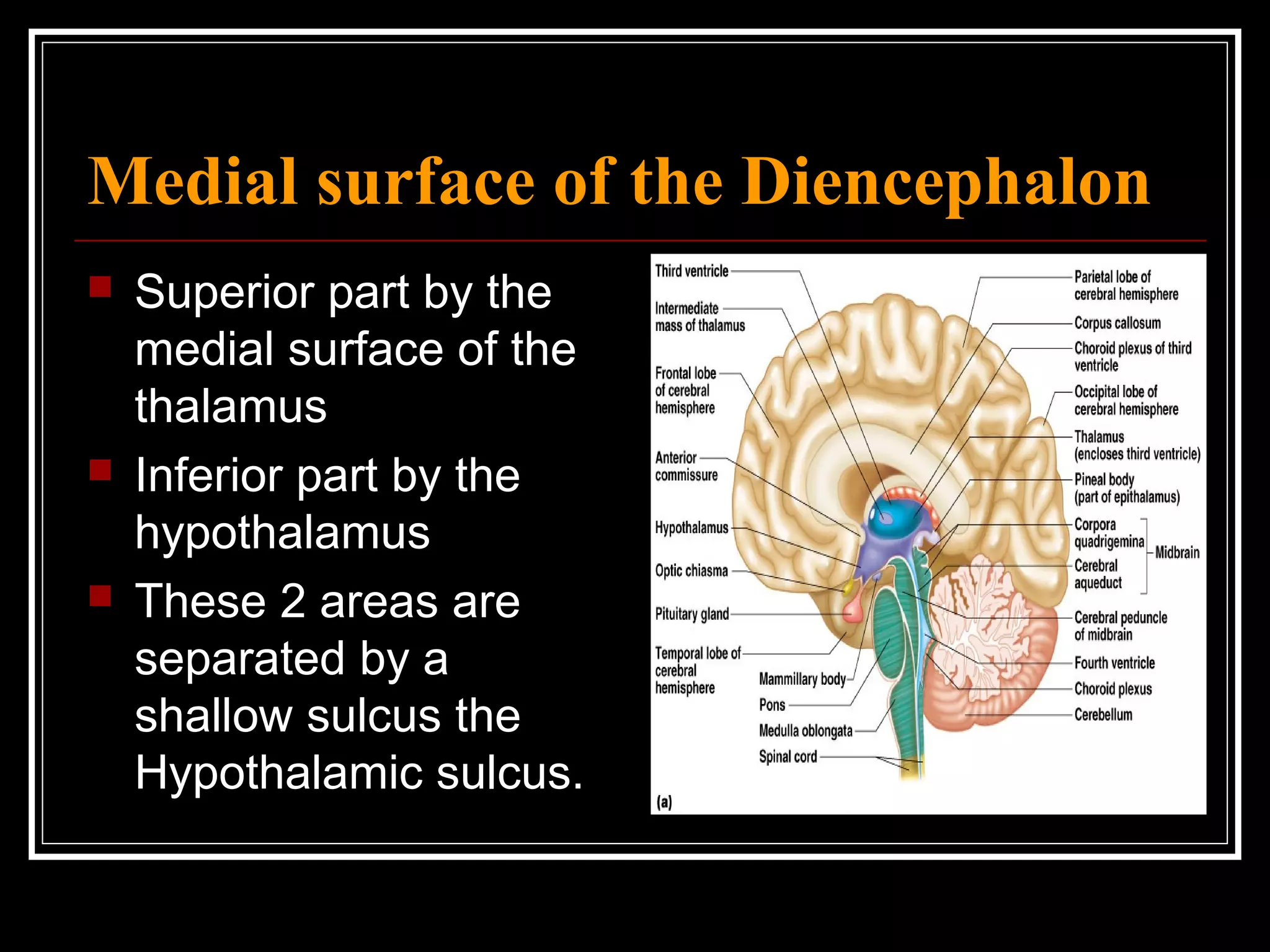
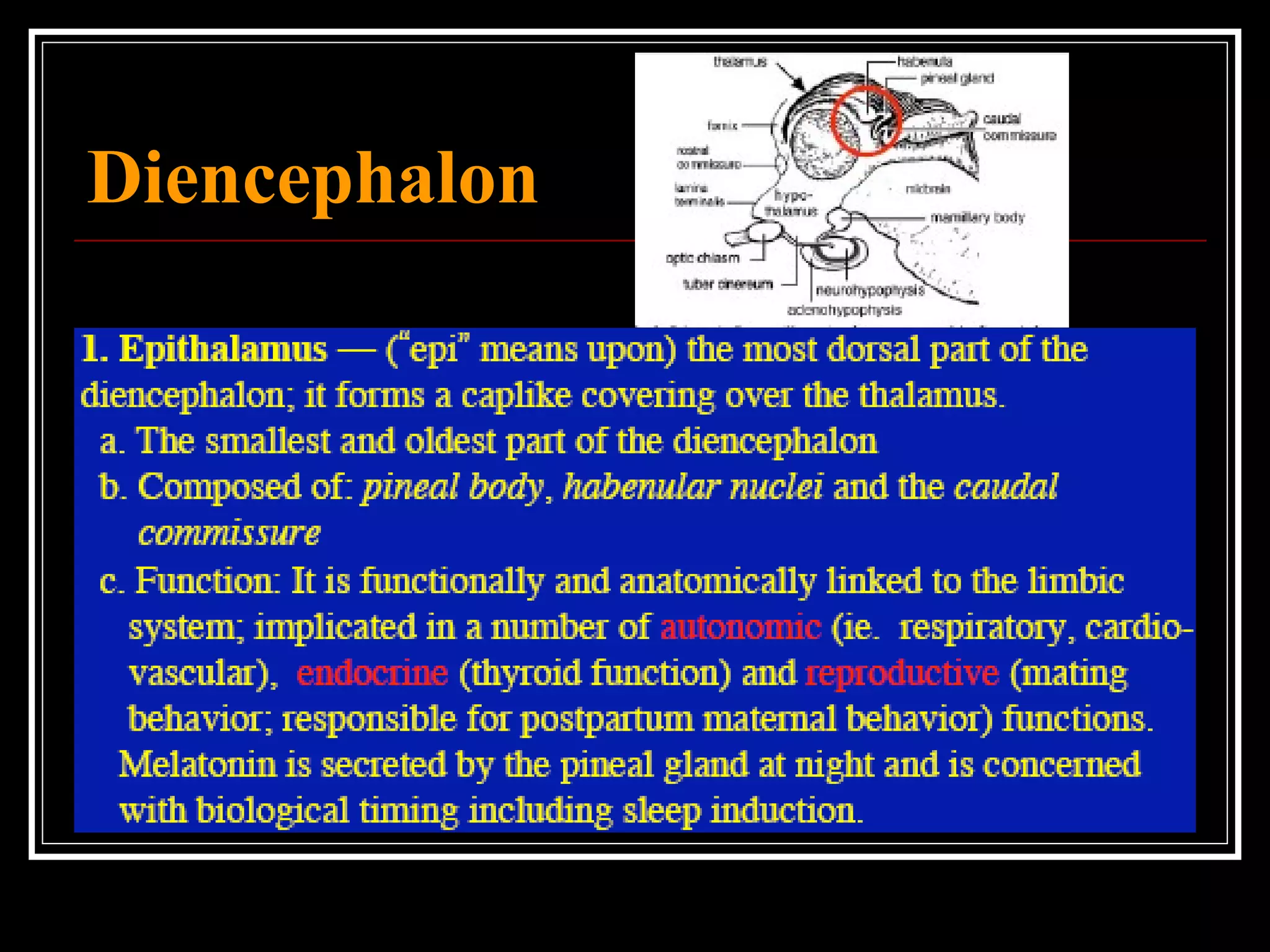
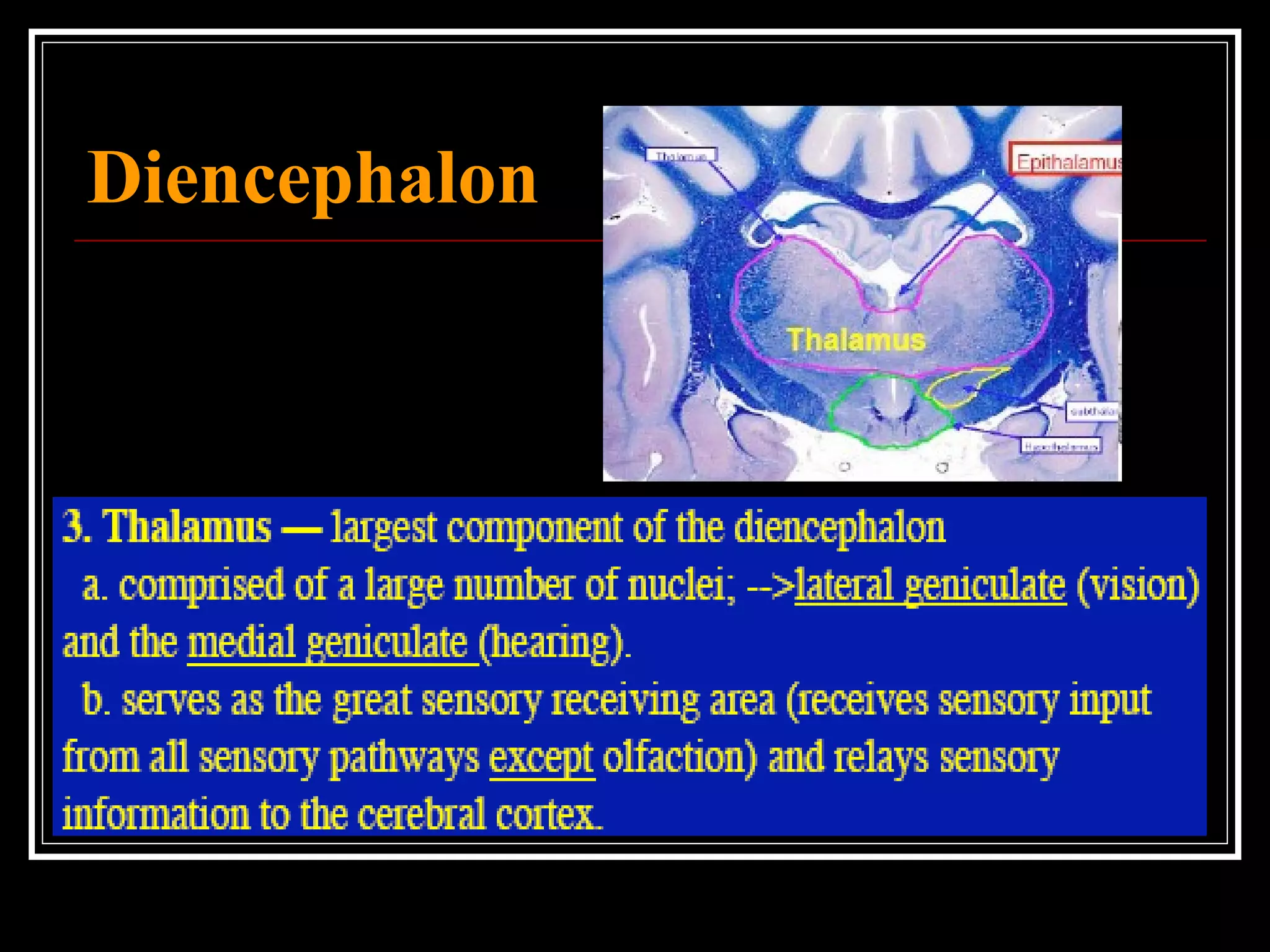
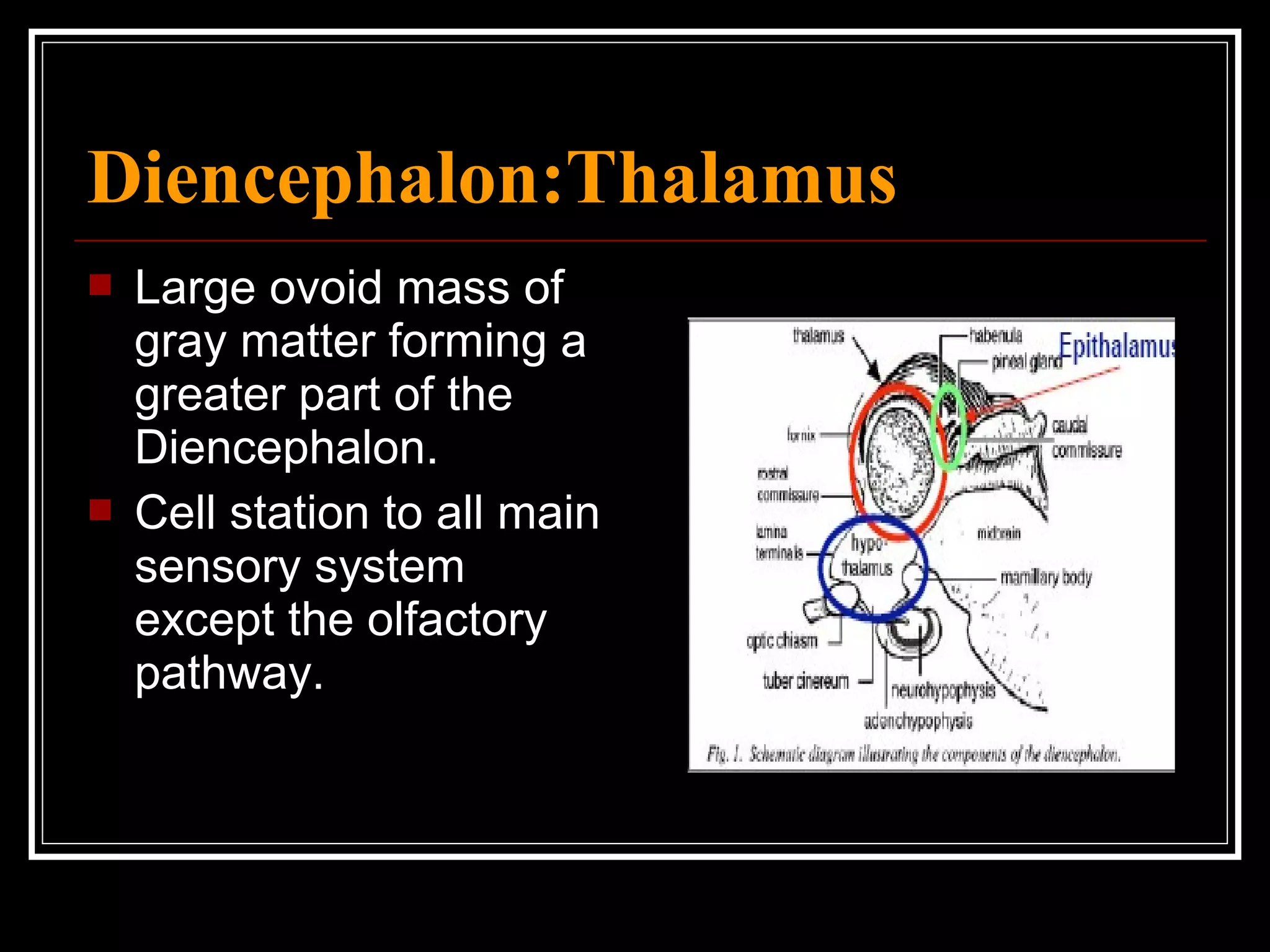
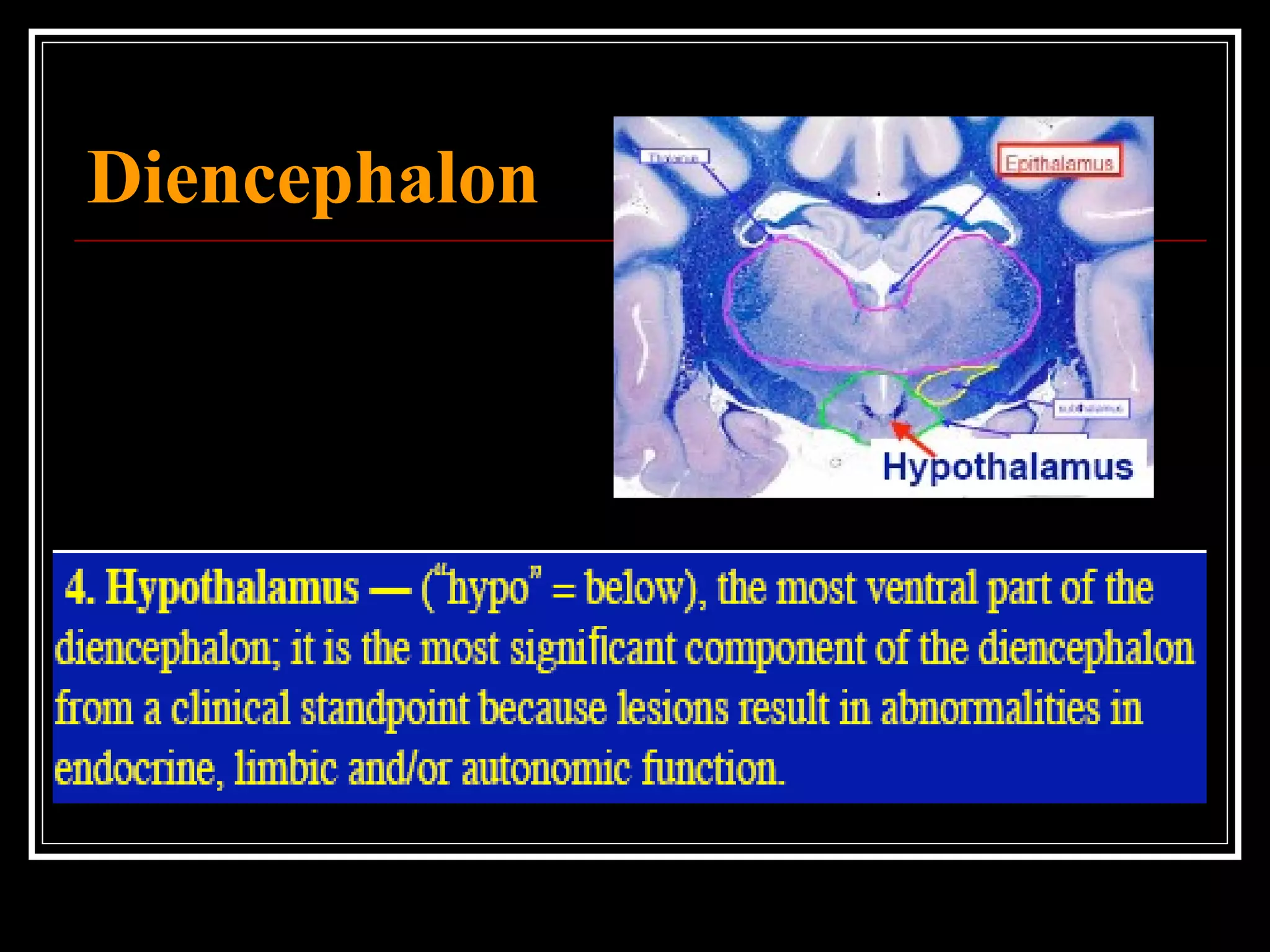
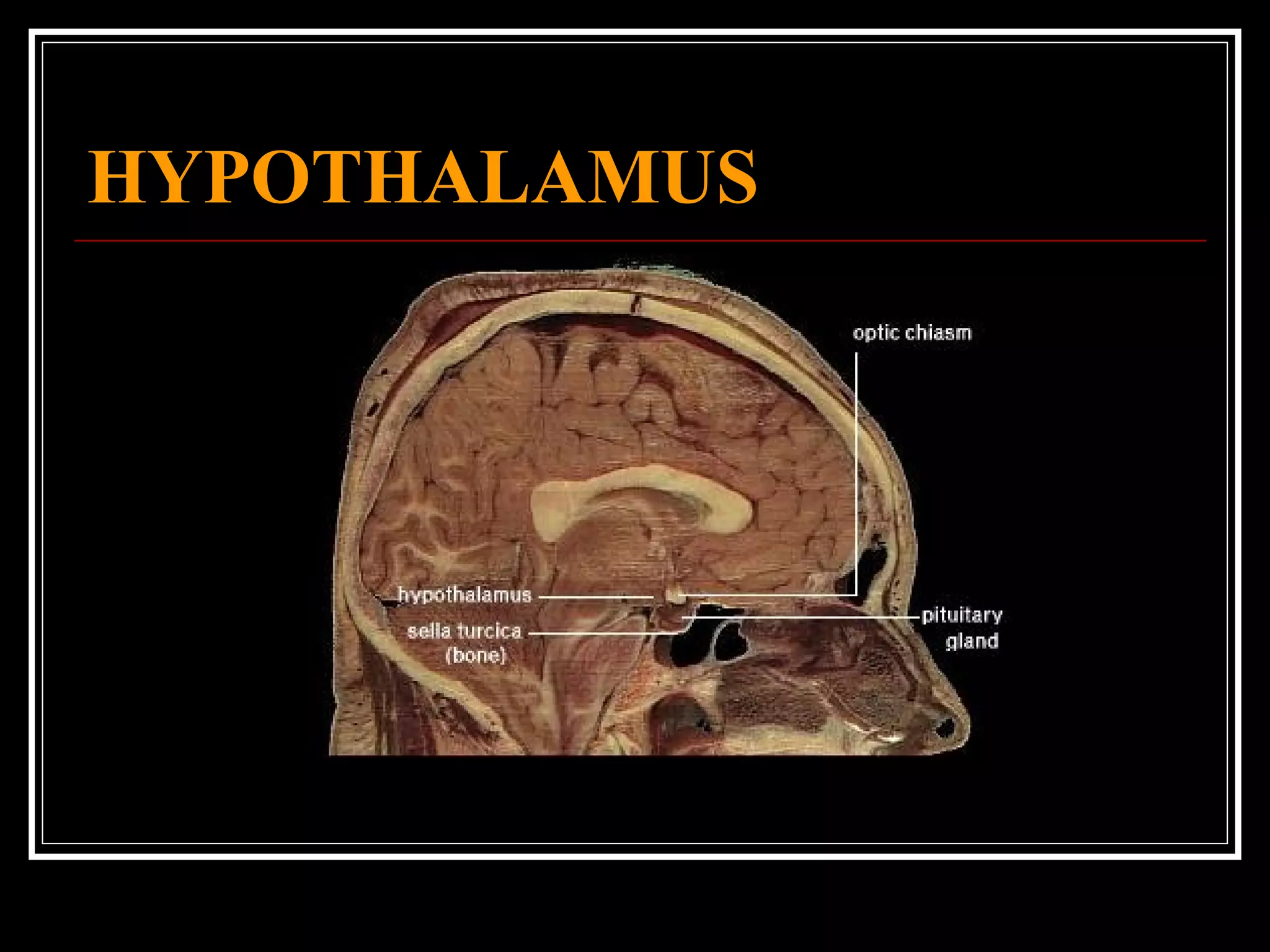
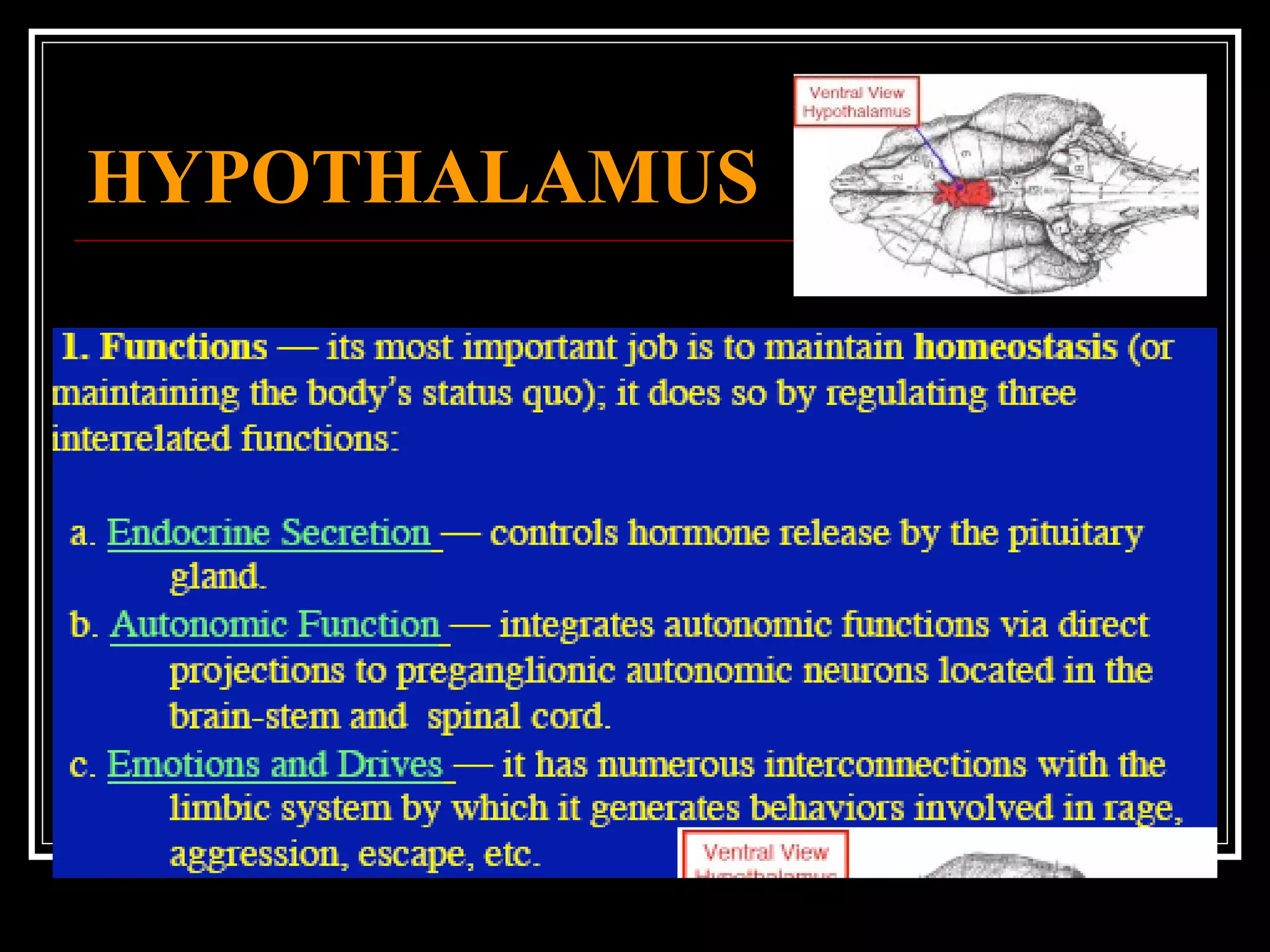
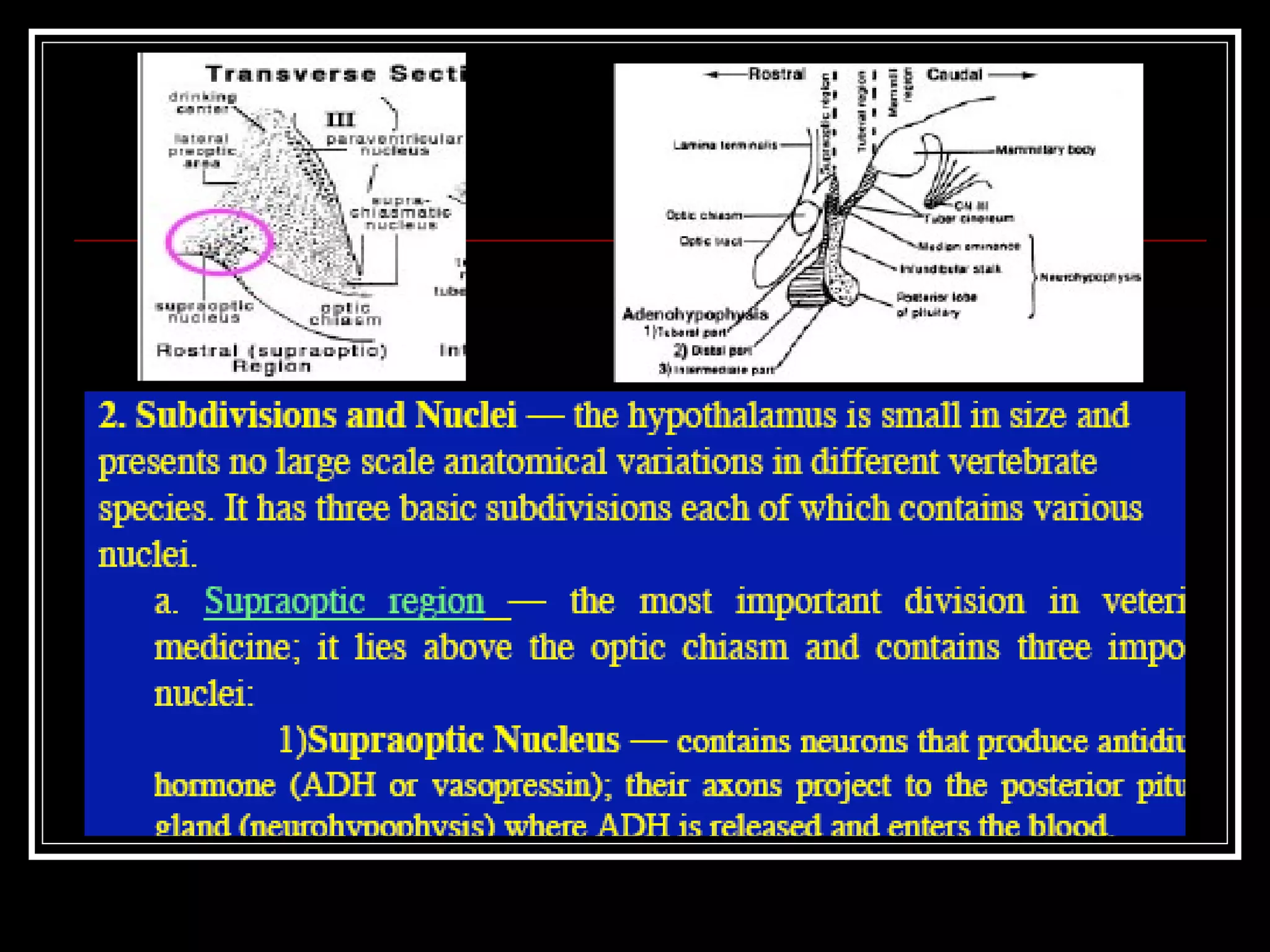
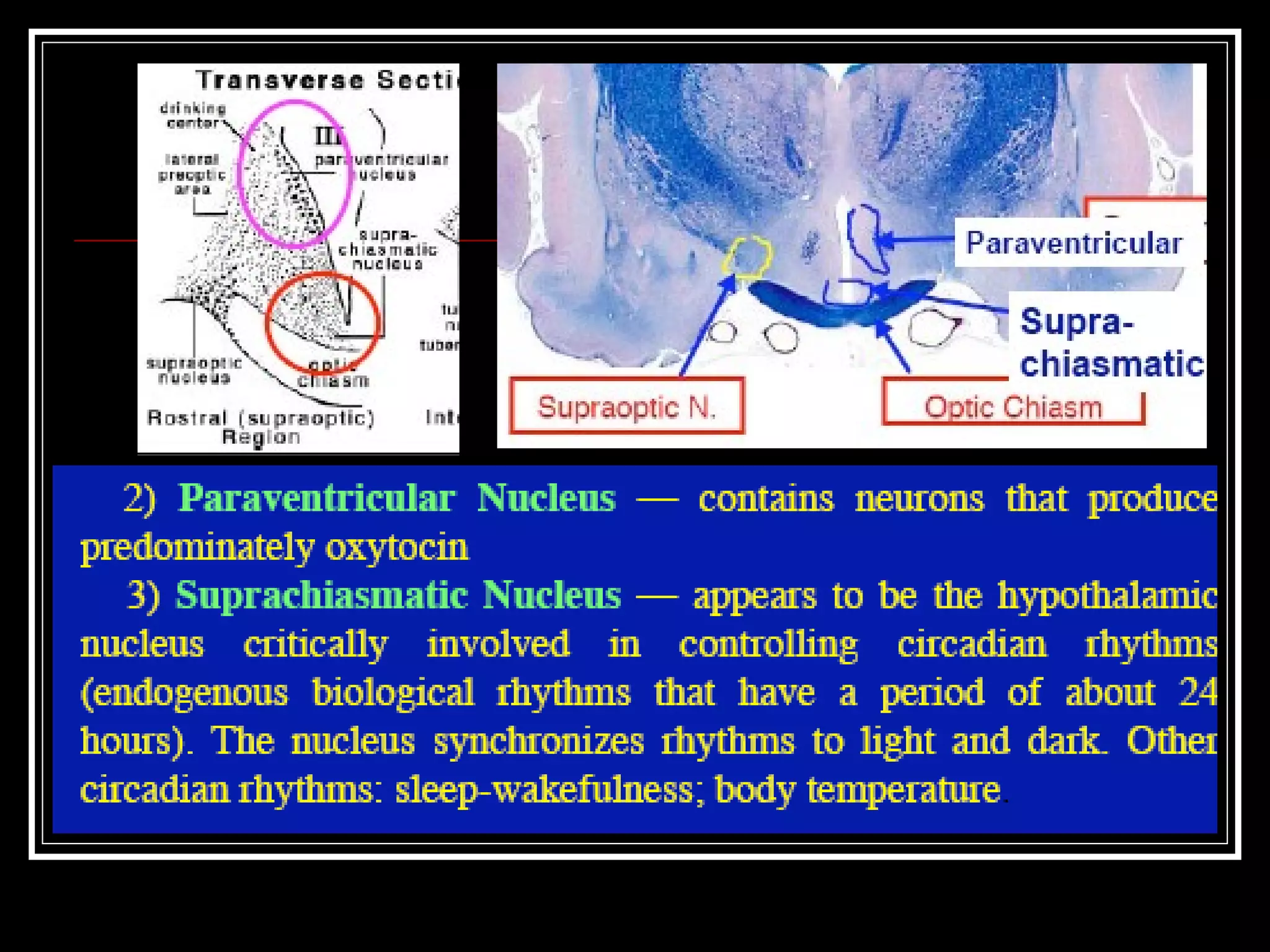
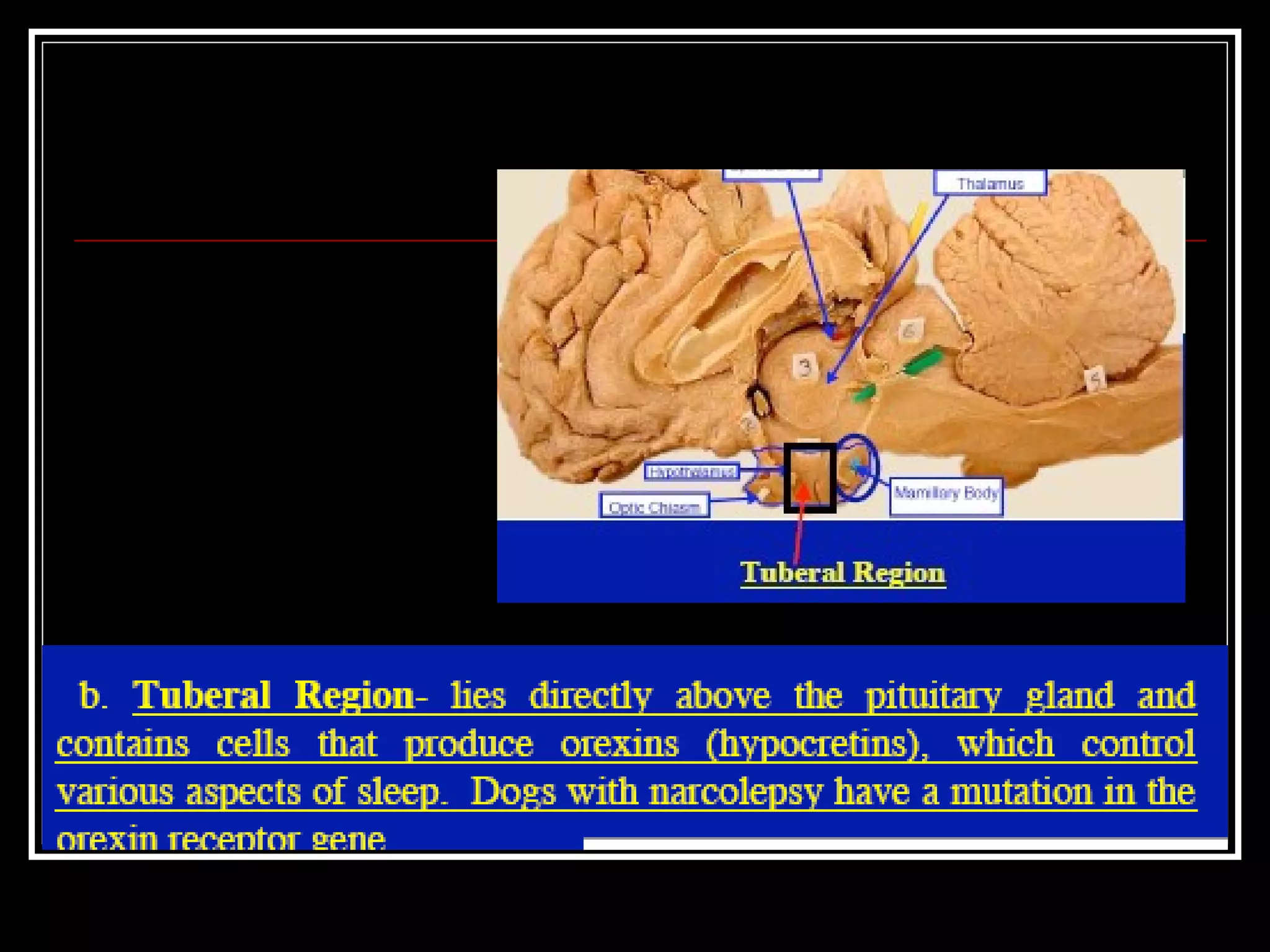
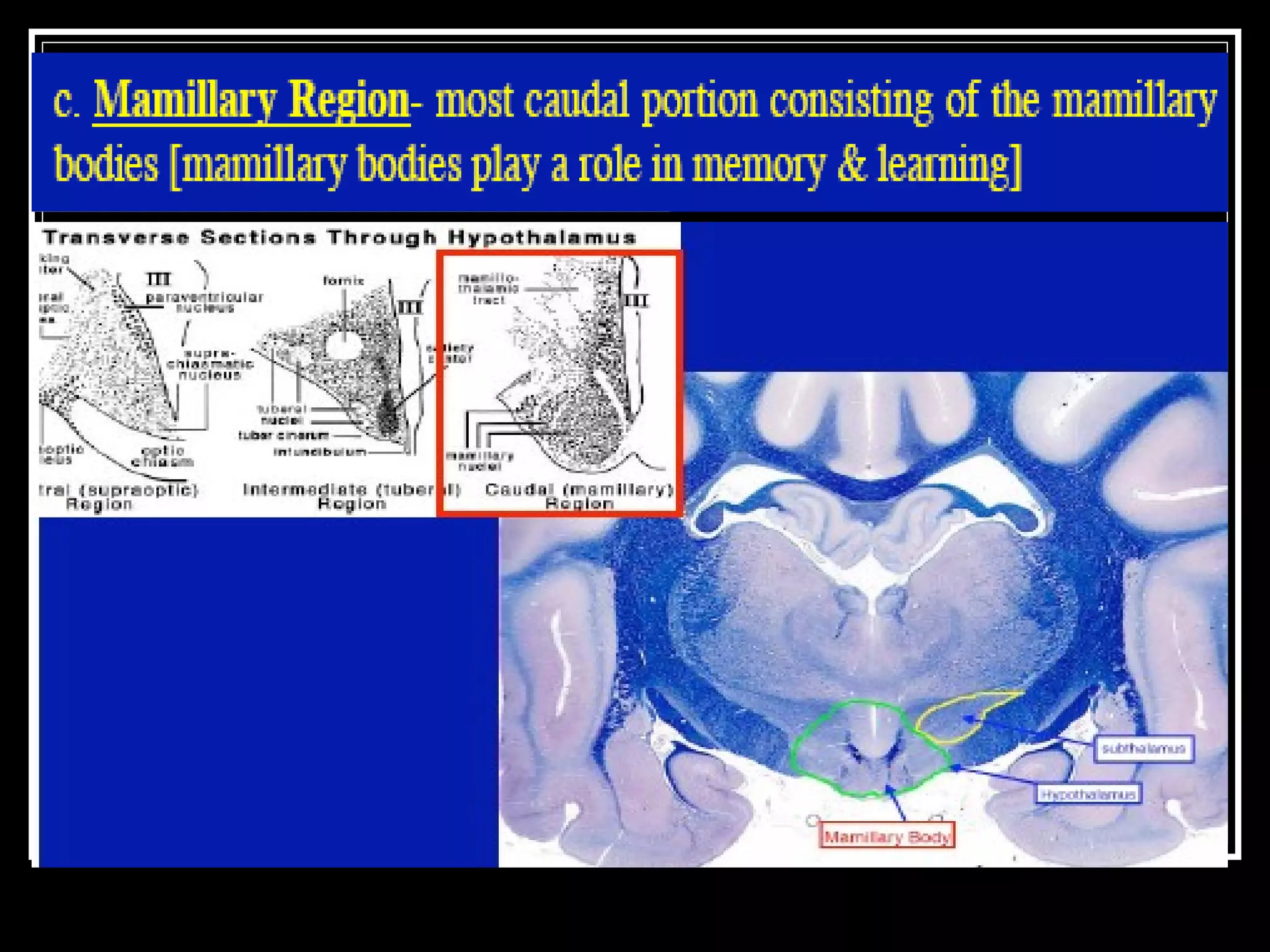
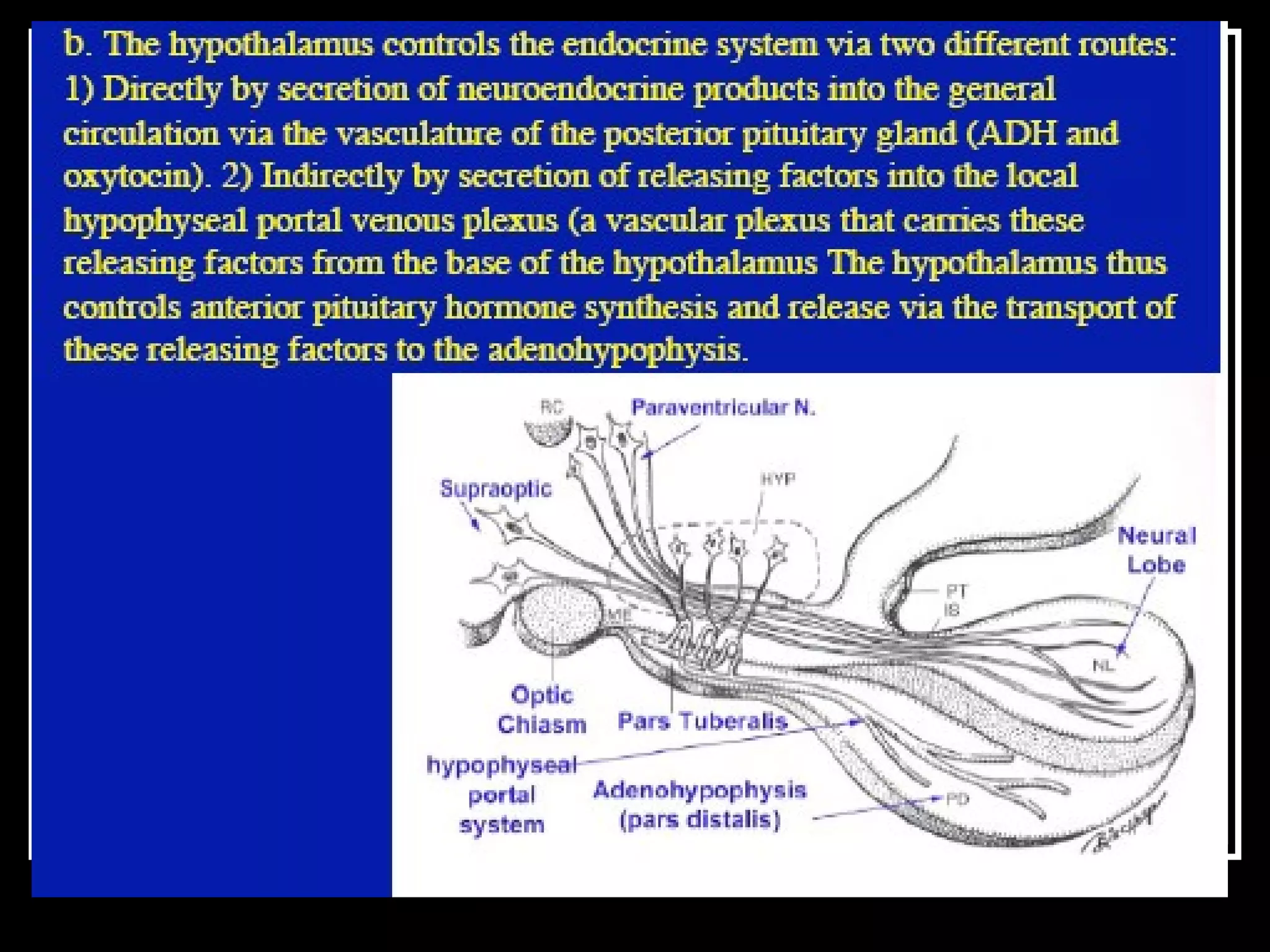
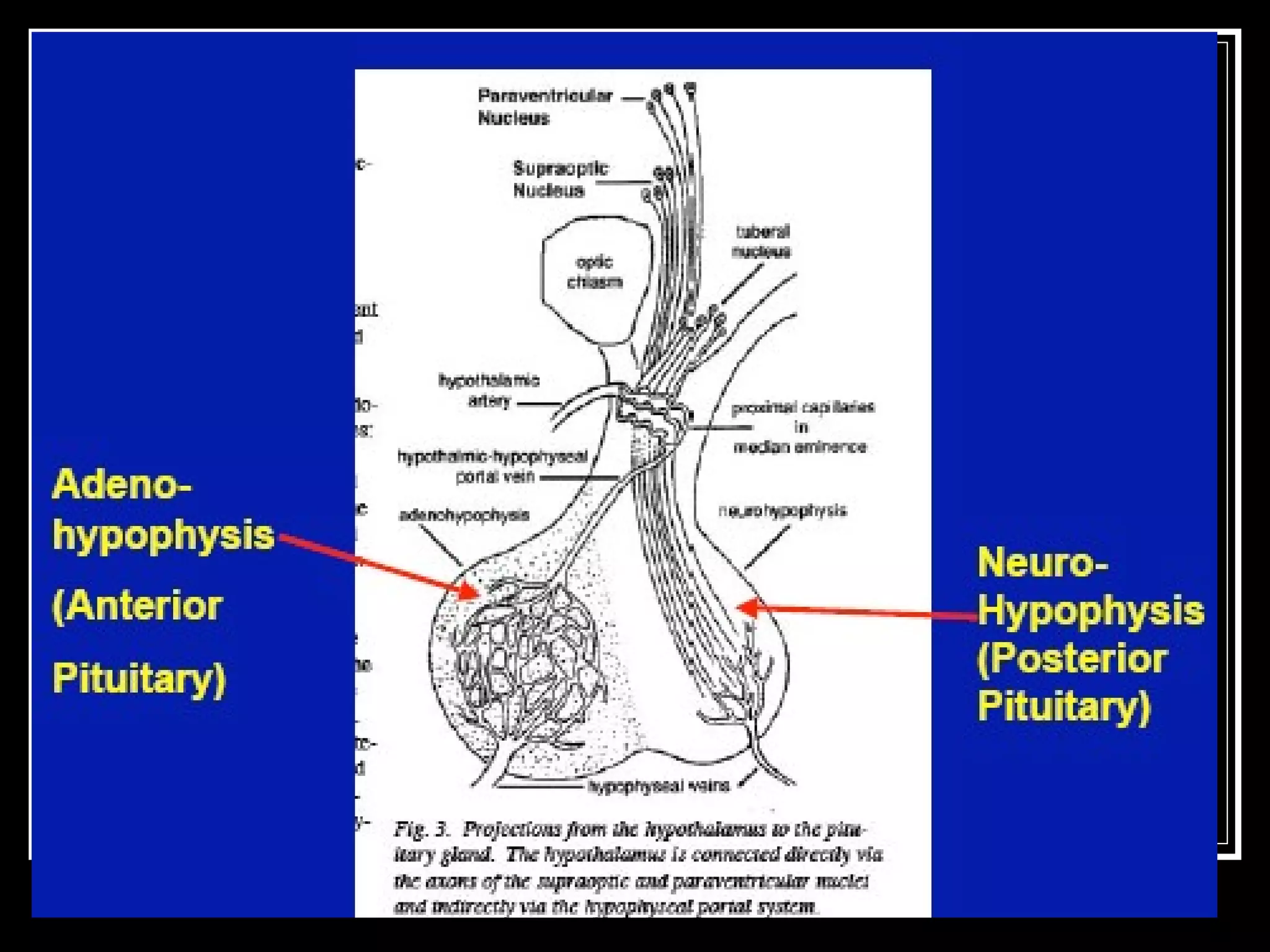
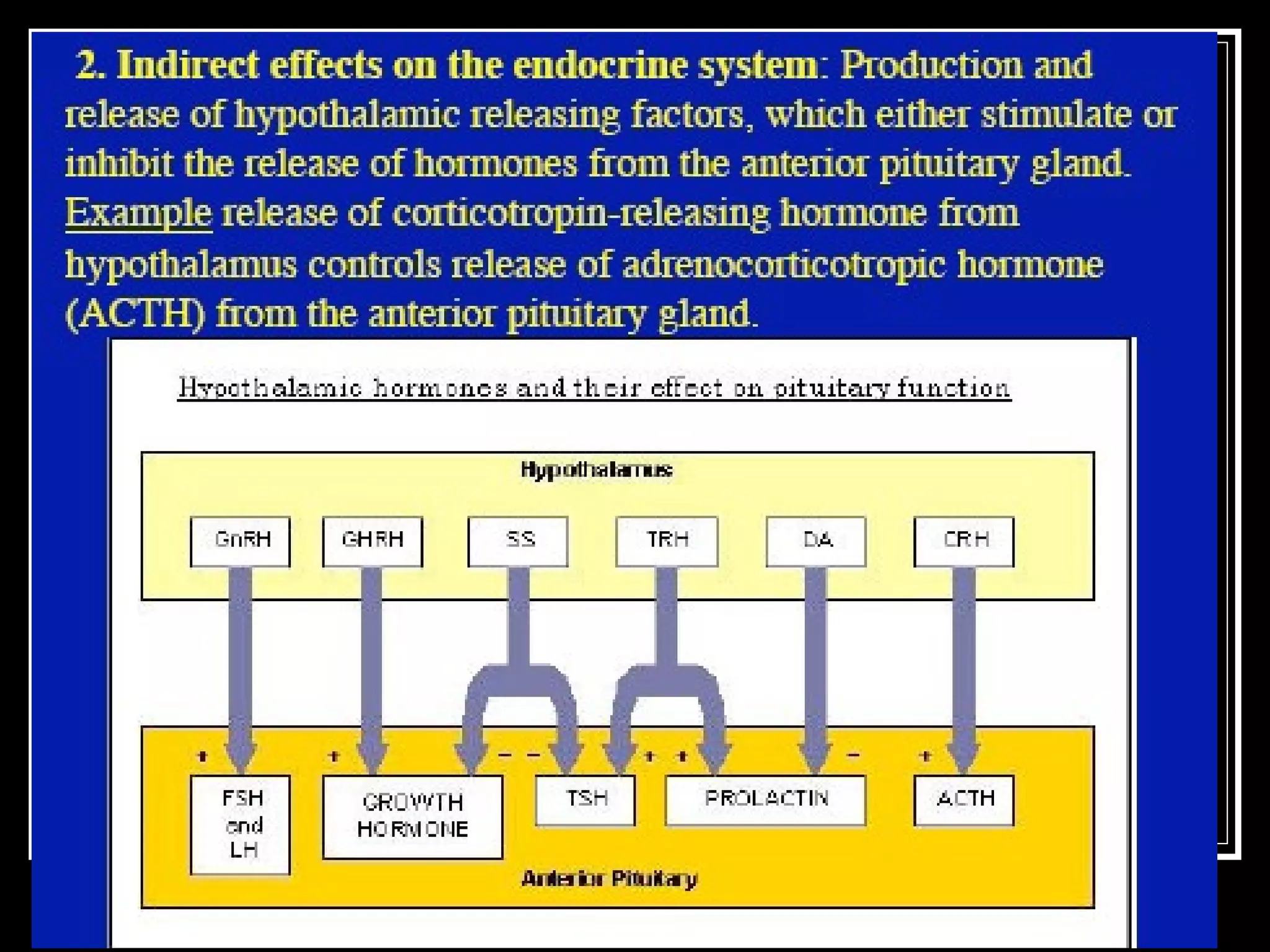
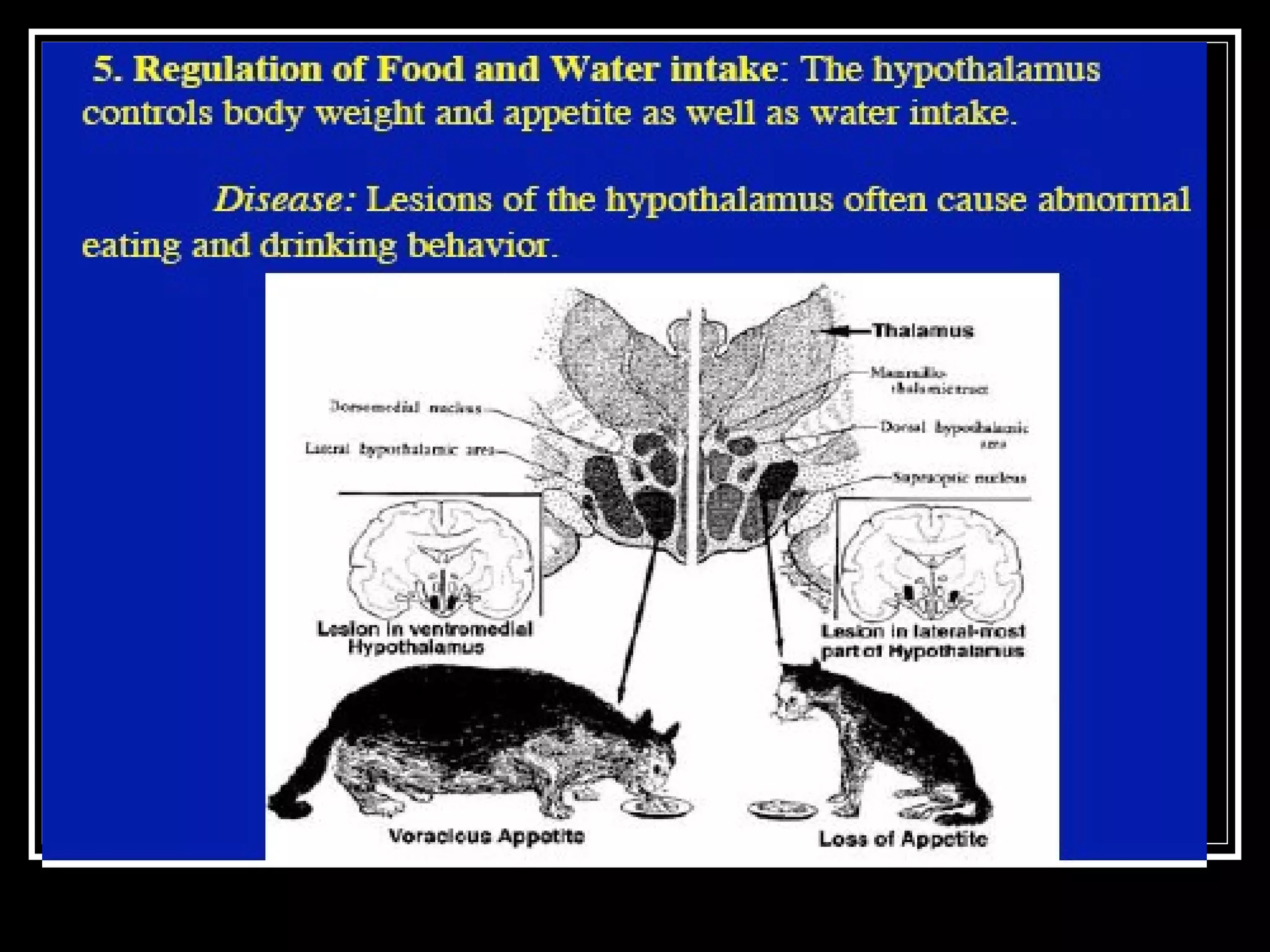
The document discusses the diencephalon, which is a region of the brain situated between the cerebrum and brainstem. It consists of four main parts: the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus. The thalamus acts as a gateway to the cerebral cortex by integrating sensory information and influencing mood and emotions. The hypothalamus regulates vital functions such as body temperature, hunger, and circadian rhythms. Examville.com is described as providing online practice tests, classes, tutoring, study guides, and premium content to help students prepare for exams.