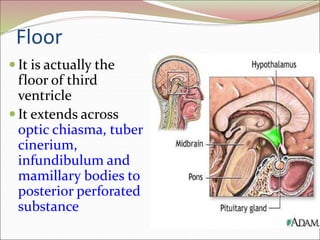
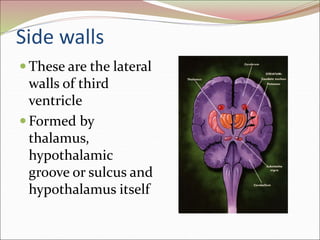
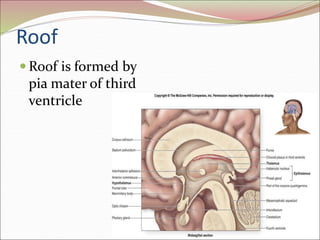
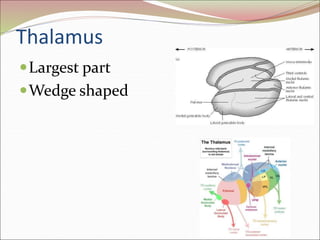
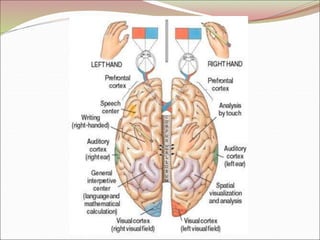
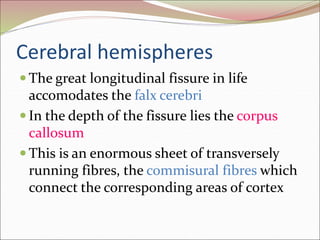
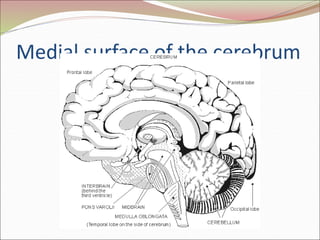
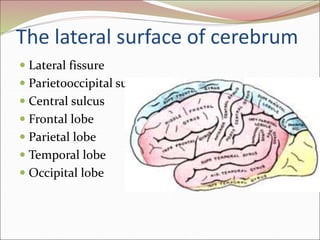
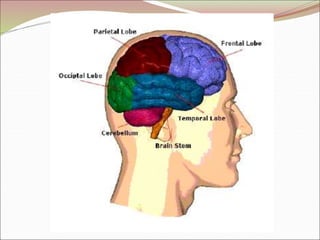
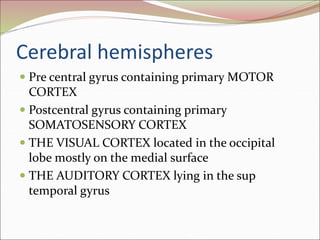
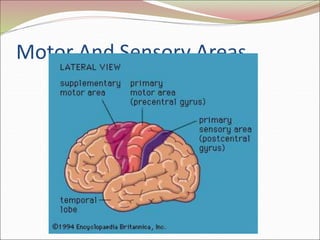
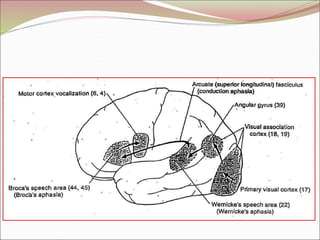
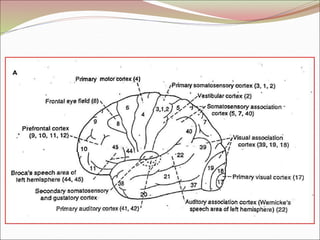
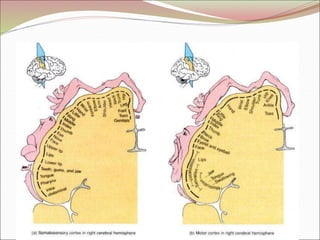
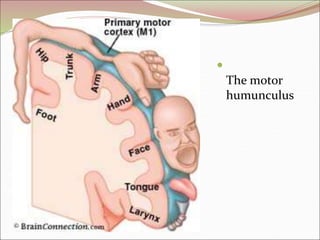
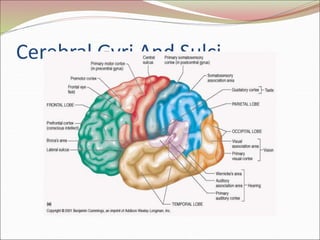
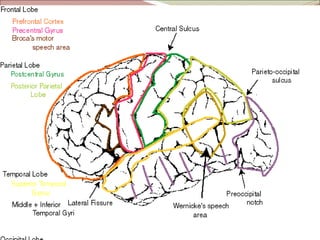
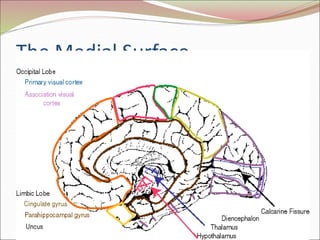
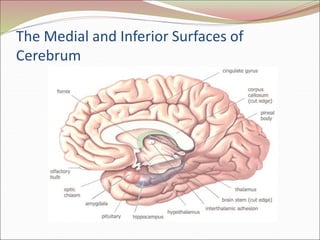
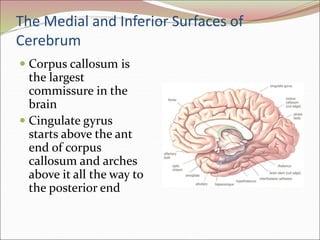
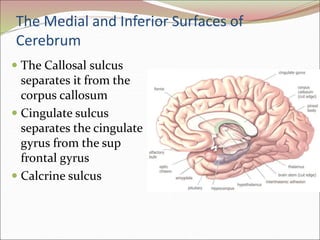
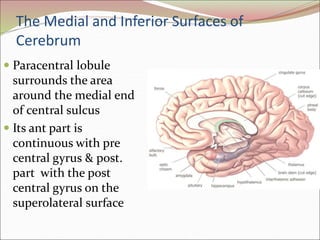
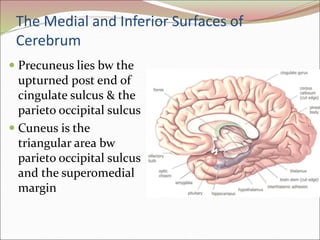
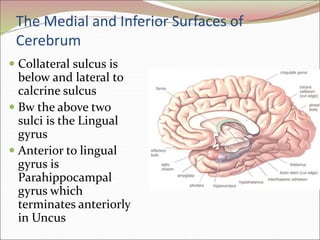
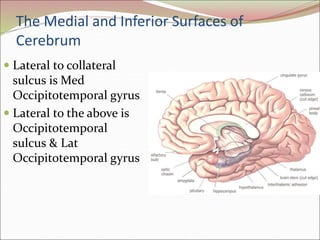
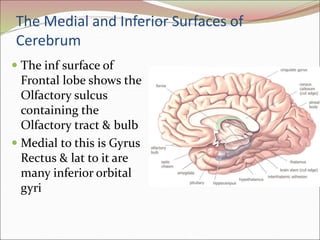
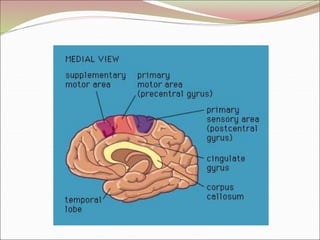
The diencephalon surrounds and forms the walls of the third ventricle. It contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus. The thalamus relays sensory information to the cortex and is involved in sensory and motor integration. The hypothalamus connects the nervous and endocrine systems and regulates autonomic functions and behaviors. The limbic system, which includes the hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala and limbic cortex, is involved in emotion, motivation and memory. The cerebral hemispheres are the largest part of the forebrain. They contain the cortex and underlying white matter. Sensory and motor areas of the cortex are involved in