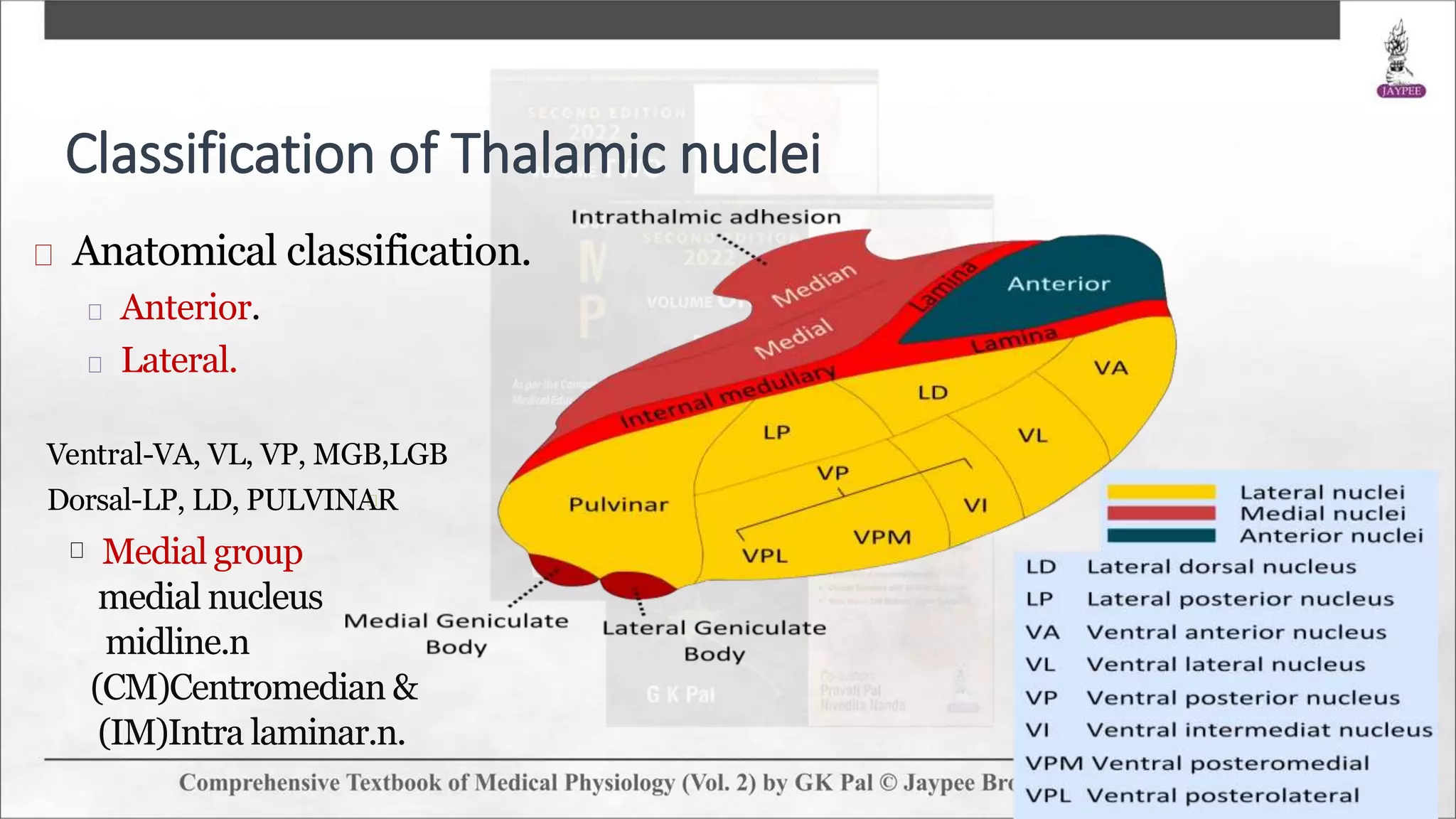
The thalamus is an egg-shaped structure atop the brain stem that acts as a sensory relay station. It is composed of several discrete nuclei that are classified anatomically and physiologically. Anatomically, the thalamus is divided into anterior, medial, and lateral groups of nuclei. Physiologically, the nuclei are grouped into specific relay nuclei, association nuclei, nonspecific nuclei, and motor nuclei. The thalamus receives ascending sensory inputs and projects them to sensory cortical areas, functioning as a relay for somatic sensations and special senses. It also plays roles in arousal, memory, emotion, motor functions, and sleep-wake cycles.