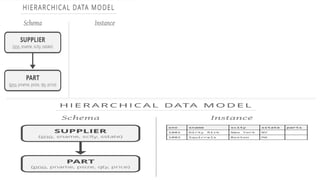
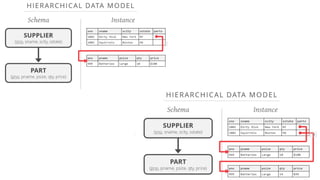
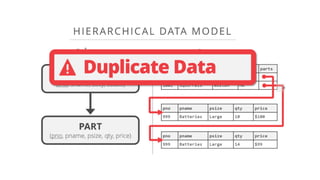
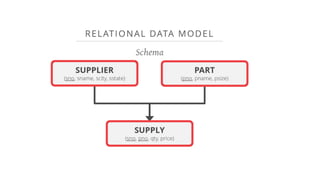
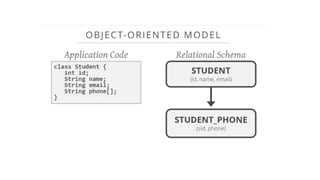
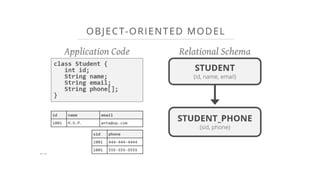
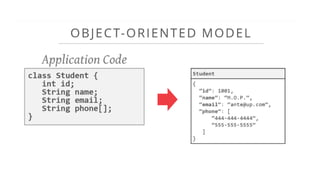
This document provides an overview of relational database management systems (RDBMS). It defines key database concepts like data, information, and database systems. It also explains the hierarchical structure of DBMS and compares flat file databases to relational databases. Relational databases incorporate multiple normalized tables that can be related to each other, while flat files put all data in a single table without relationships between files.