This document discusses issues to consider when designing an entity-relationship (ER) diagram. It covers:
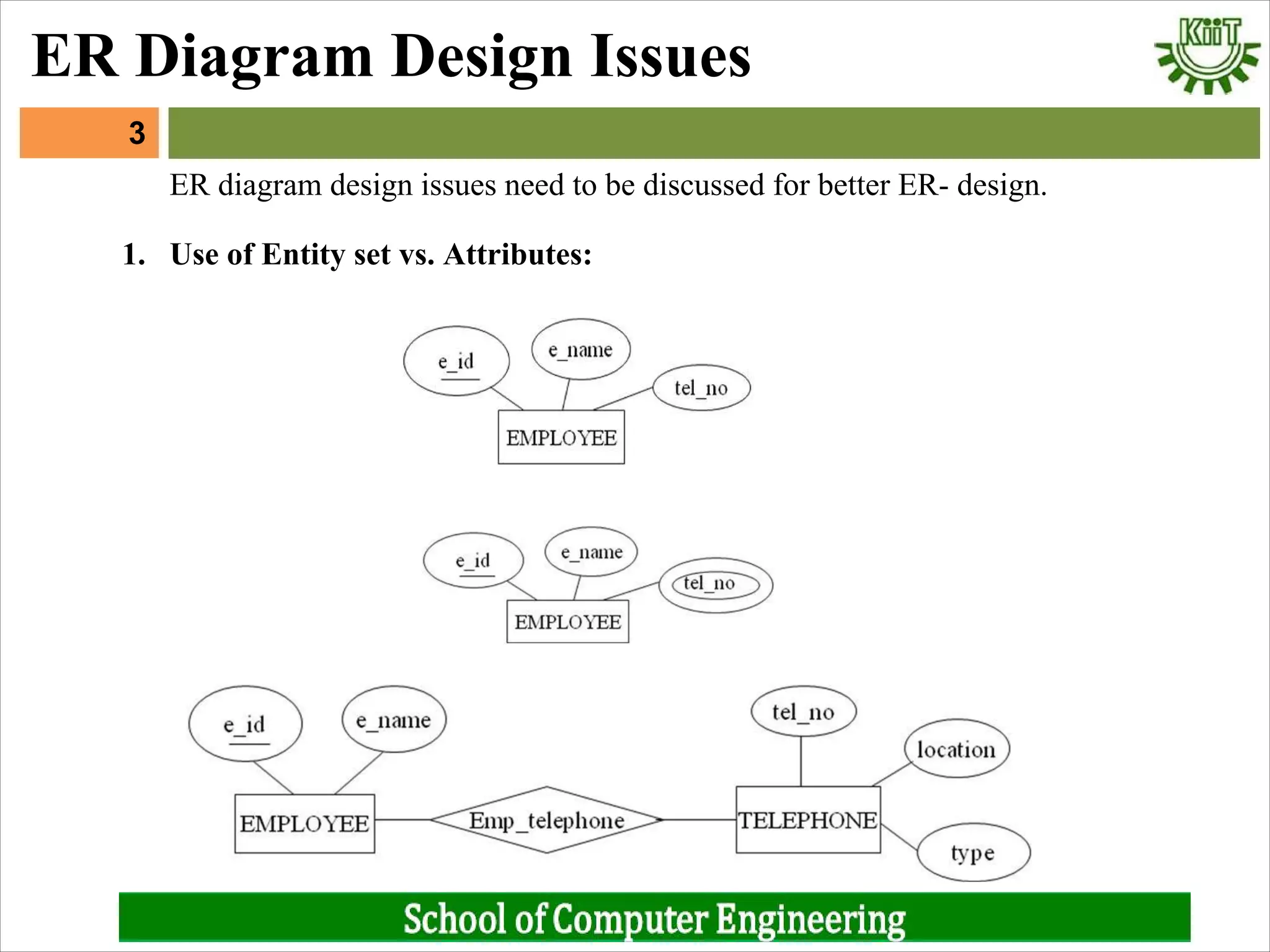
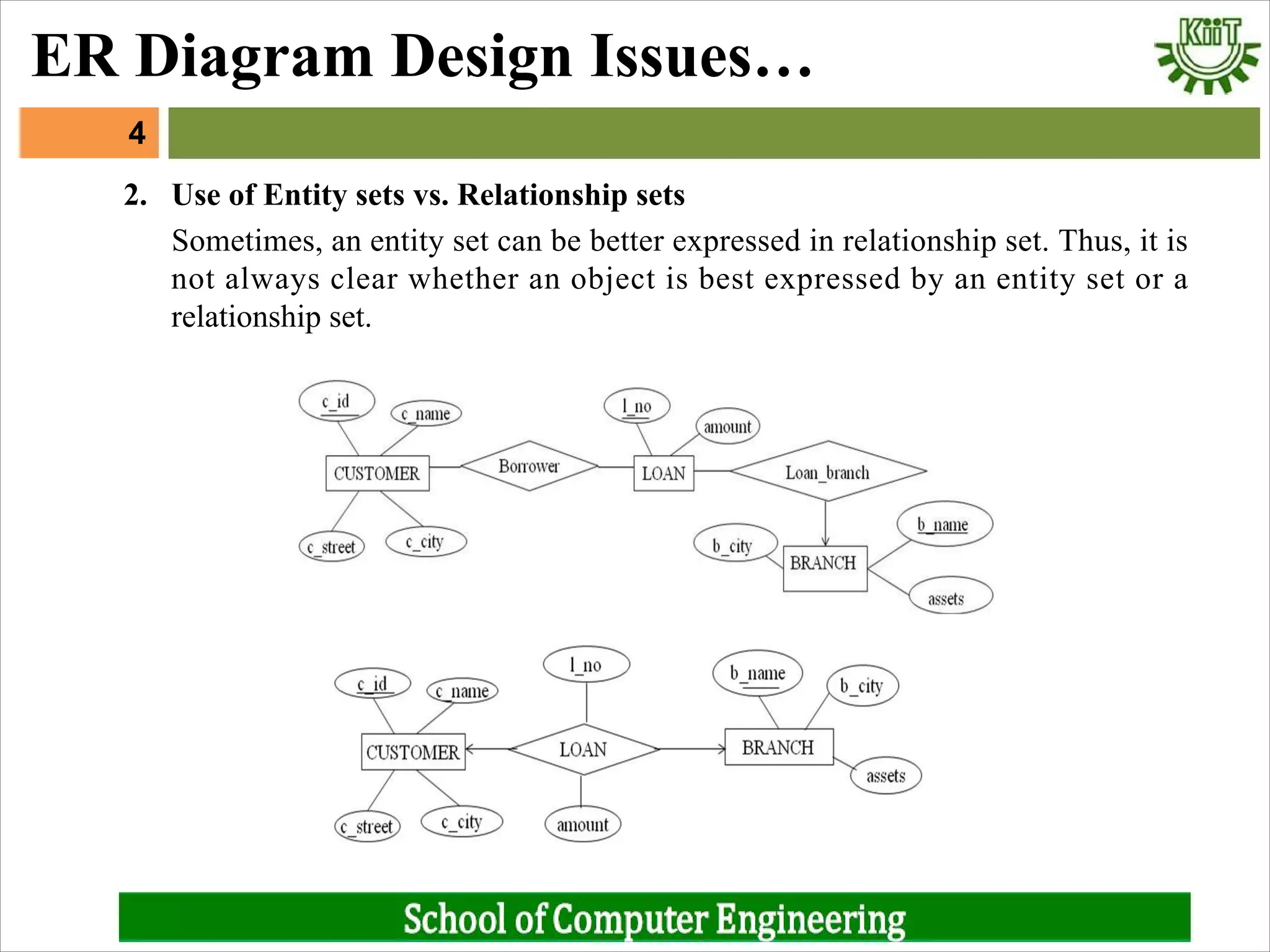
1. Whether to represent objects as entity sets or relationship sets.
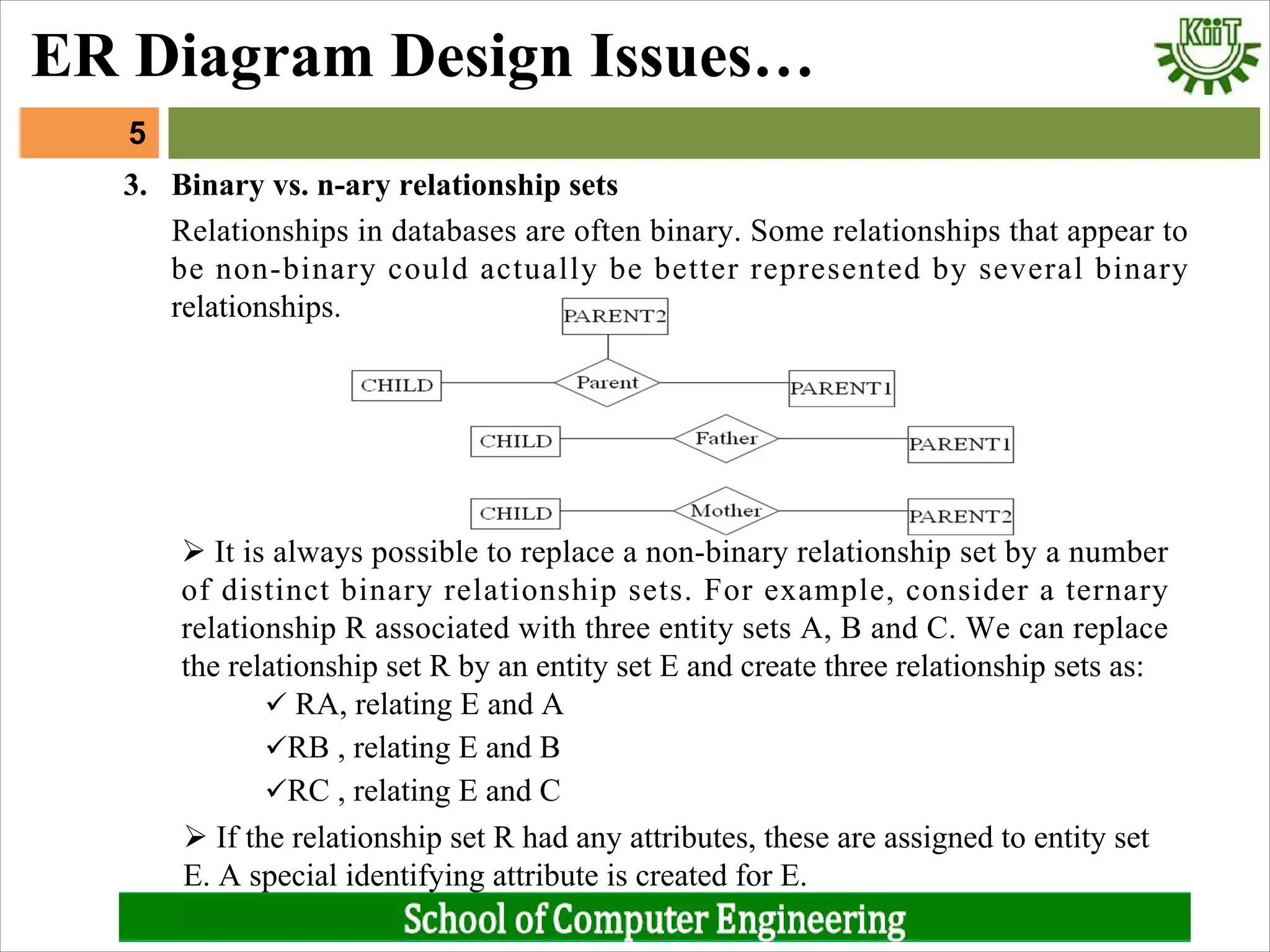
2. Whether relationships should be binary or n-ary. N-ary relationships can be represented as multiple binary relationships connected through a new entity set.
3. Where to place attributes of relationships, which may depend on the cardinality ratio of the relationship. For example, attributes of a one-to-many relationship can be placed on the "many" side.
![Dr. Amiya Ranjan Panda
Assistant Professor [II]
School of Computer Engineering,
Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT),
Deemed to be University,Odisha
ER Diagram Design Issues
KALINGA INSTITUTE OF INDUSTRIAL
TECHNOLOGY
School Of Computer
Engineering
4 Credit Lecture Note 07](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbms-7-210329065525/75/Dbms-7-ER-Diagram-Design-Issue-1-2048.jpg)