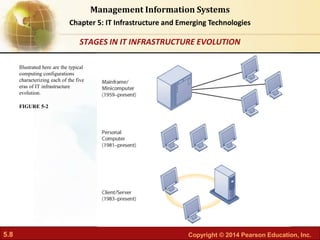
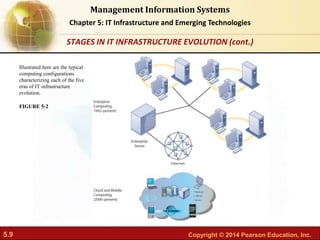
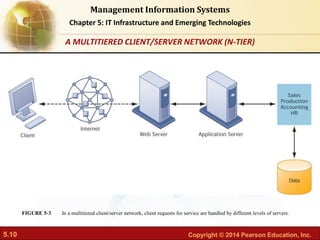
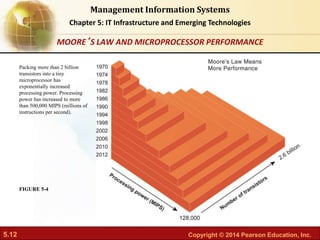
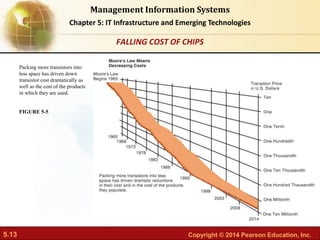
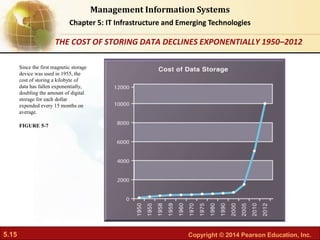
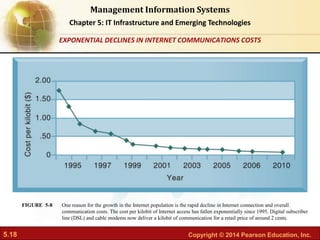
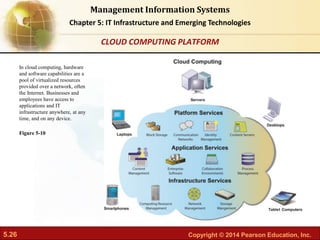
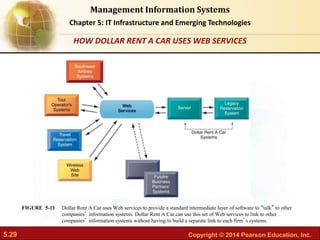
This document provides an overview of chapter 5 from the textbook "IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies". The chapter discusses IT infrastructure components and trends, including: the evolution of infrastructure through different eras like mainframe, client/server, and cloud/mobile computing; technology drivers like Moore's Law and declining communication costs; the seven main components of infrastructure; and contemporary hardware trends like smartphones, tablets, and e-readers. It also includes diagrams illustrating infrastructure concepts and case studies on organizations adapting their IT infrastructure.