Embed presentation
Downloaded 321 times
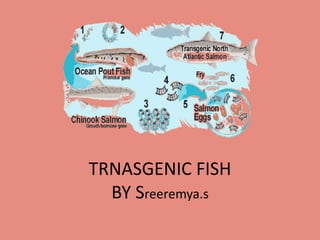

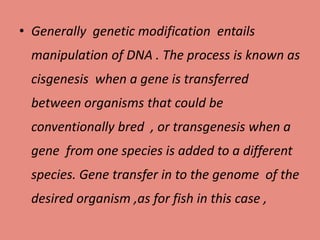






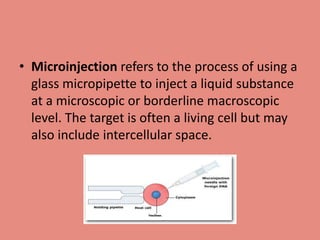
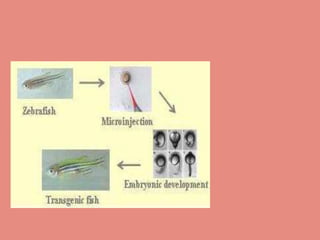


Transgenic fish, or genetically modified fish, are created through genetic engineering to introduce new traits, with FDA approval for some varieties. Techniques such as cisgenesis and transgenesis are used for gene transfer, often employing vectors or microinjection methods. Various fish species, including salmon and ornamental types like rainbow zebrafish, have been genetically engineered since the early 1980s.











