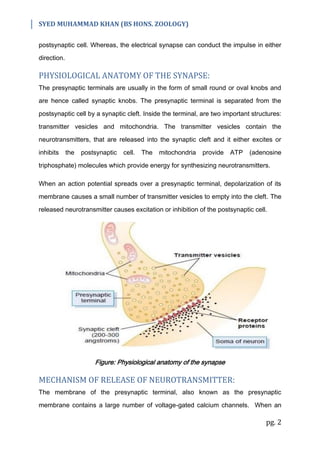
The document summarizes key aspects of synaptic transmission between neurons. There are two main types of synapses - chemical and electrical. At a chemical synapse, the presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft that act on receptors in the postsynaptic cell. This can excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. The electrical synapse allows direct ion flow between connected cells. Over 50 chemicals act as neurotransmitters, including amino acids, biogenic amines, purines, and peptides. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell, which can open ion channels or activate second messenger systems to have long-lasting effects on cell excitability.


![SYED MUHAMMAD KHAN (BS HONS. ZOOLOGY)
pg. 4
The G protein consists of three components: (1) alpha component (α) which is the
activator portion, (2) beta component (β), and (3) gamma component (γ). When it is
activated by a nerve impulse, the alpha portion of the G protein separates and
performs one or more of the following functions:
i. Opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell membrane
(which stays open for a long time).
ii. Activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) or cyclic guanosine
monophosphate (cGMP) in the cell (which alters the metabolism of the
cell).
iii. Activation of one or more intracellular enzymes.
iv. Activation of gene transcription.
Figure: Second Messenger system in which one neuron can activate a second
neuron by causing the release of G protein in the second neuron's cytoplasm. The G
protein can (1) open an ion channel, (2) activate an enzyme system [cAMP and
cGMP], (3) activate an intracellular enzyme system, and/or (4) cause gene
transcription.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synaptictransmission-201026111353/85/Synaptic-Transmission-4-320.jpg)
