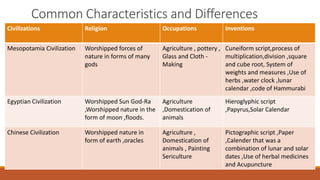
Civilization refers to advanced stages of social and cultural development characterized by progress in the arts, sciences, and forms of social organization. Early civilizations flourished along river valleys because they provided water, fertile soil, building materials, opportunities for fishing, transportation, trade, and a moderate climate. The Bronze Age saw the introduction of bronze, an alloy stronger than copper or tin alone, leading to improved tools and crafts. Notable early civilizations included those in Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and India, which developed writing systems, calendars, legal codes, herbal medicine, and other innovations while worshipping nature and engaging in agriculture.