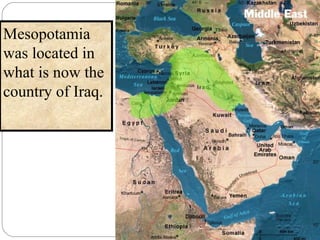
The Sumerian civilization originated in Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-day Iraq around 5500 BC. Mesopotamia was a fertile region where many city-states developed, including Ur, Uruk, Eridu, Lagash and Kish. The Sumerians made advances in writing, mathematics, astronomy, agriculture and engineering, developing irrigation systems, the wheel, plow and the world's first codified legal and administrative systems. However, constant warfare between the independent city-states drained Sumer's strength and it was eventually conquered by the Babylonians in 1759 BC, marking the end of the Sumerian civilization.