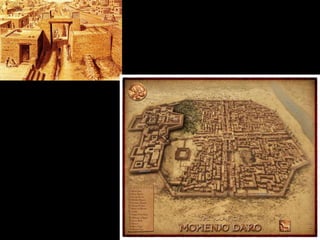
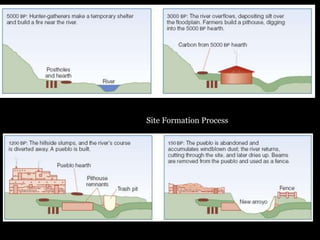
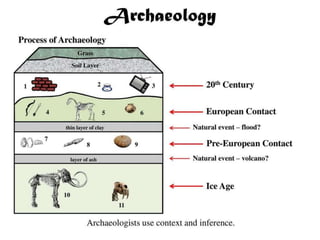
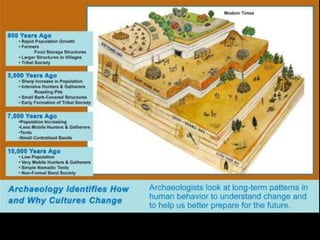
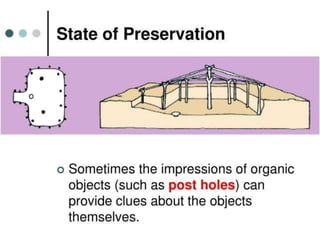
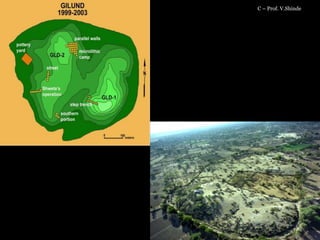
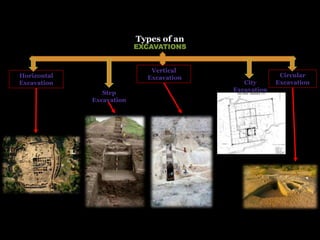
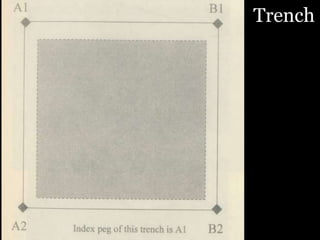
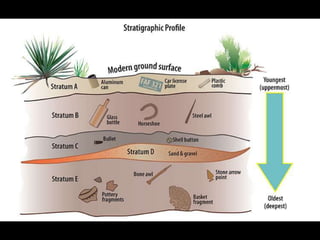
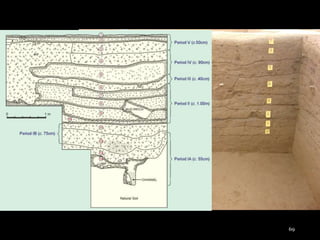
The document outlines the process and techniques of archaeological excavations, including planning, site identification, and types of excavations. It details various phases like pre-excavation, excavation, and post-excavation, including the roles of different team members and tools used. Additionally, it categorizes sites based on prehistoric, proto-historic, and historic phases, highlighting the diversity of artefacts and structures found.