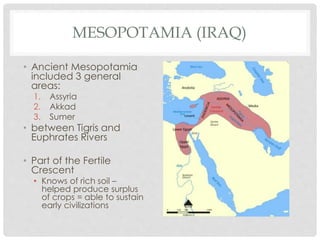
This document provides an overview of early human cultures and civilizations. It begins with definitions of culture and discusses the Paleolithic and Neolithic Ages. The Neolithic Revolution marked the beginning of settled societies based around agriculture and domestication of animals. This led to the emergence of early civilizations in places like Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Key features of early civilizations included organized government, religion, job specialization, social classes, art, architecture, writing, and trade. The Sumerians created the first Mesopotamian civilization based around city-states with temples, defenses, and the earliest writing system of cuneiform. Later, the Akkadians and