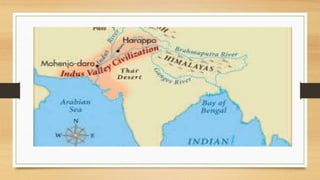
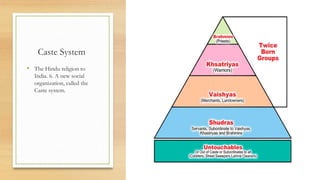
The ancient Indus Valley civilization developed along the Indus River in modern-day Pakistan from around 3000 BCE. Two major cities, Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, dominated the region by 2500 BCE, and the civilization traded with neighbors. The Harappans developed new technologies like wheeled vehicles and standardized weights and measures. Though the nature of their religion is unclear, they built large baths for ritual purification. Around 1500 BCE, nomadic Indo-European peoples called the Aryans migrated into the region, introducing iron and horses. They composed sacred texts called the Vedas and epics like the Ramayana, and also established social hierarchies later forming the caste system.