The document discusses lesson planning and provides guidance on developing effective lesson plans. It covers:
- The importance of having a lesson plan as the teacher's blueprint to guide activities and achieve objectives.
- The basic parts of a lesson plan including objectives, subject matter, materials, procedures, assignments and evaluation.
- Different types of lesson plans for different experience levels, from detailed plans for student teachers to brief outlines for experienced teachers.
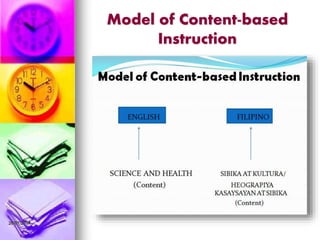
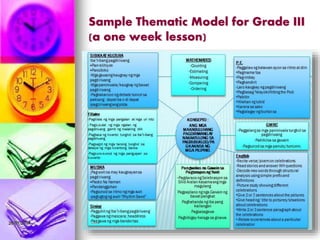
- Models for integrating subjects like using content areas to teach language skills and developing thematic units that combine multiple subjects.
The document emphasizes that lesson plans should be systematic, measurable, attainable, retainable and time-bound to effectively guide instruction.