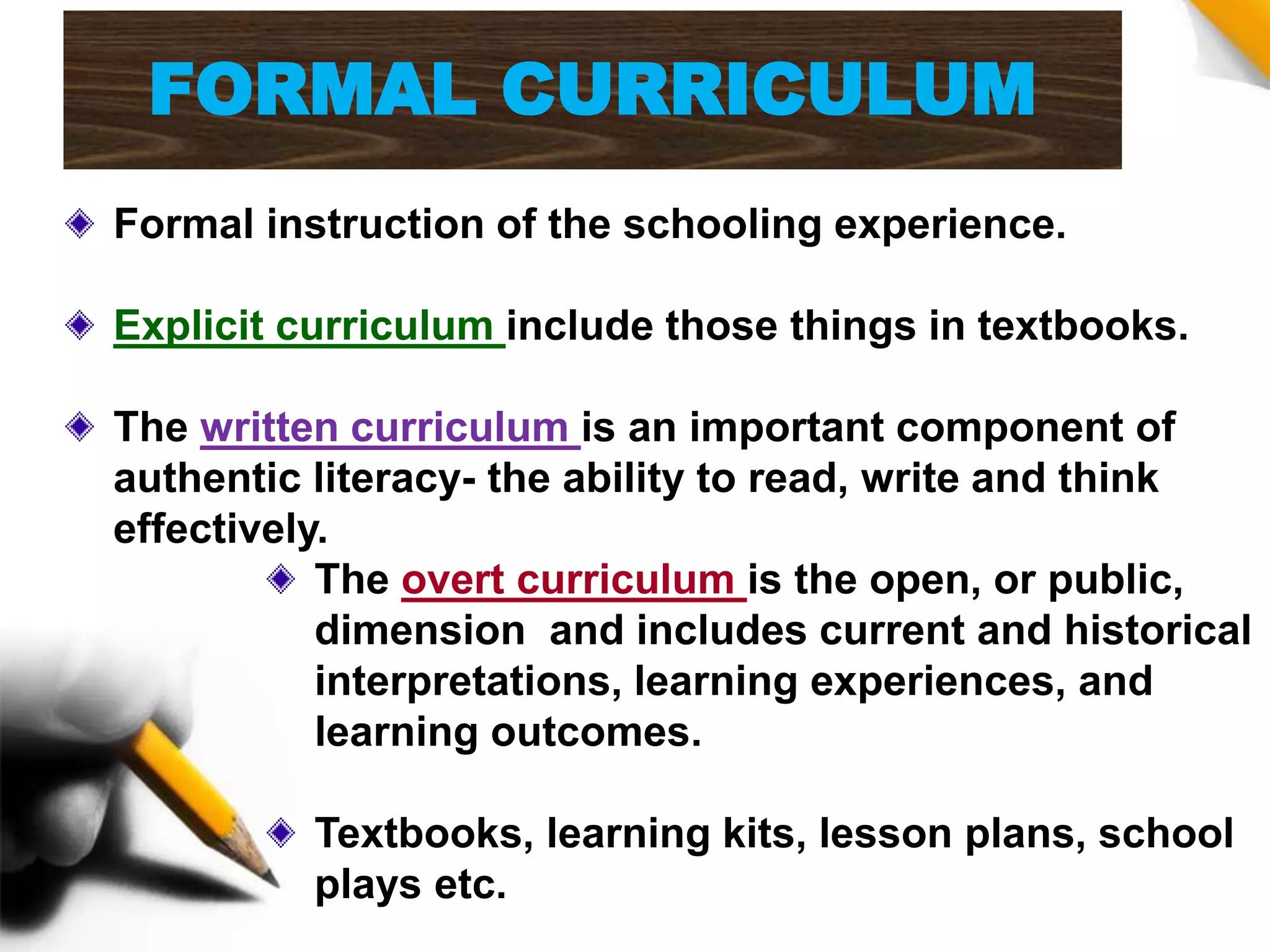
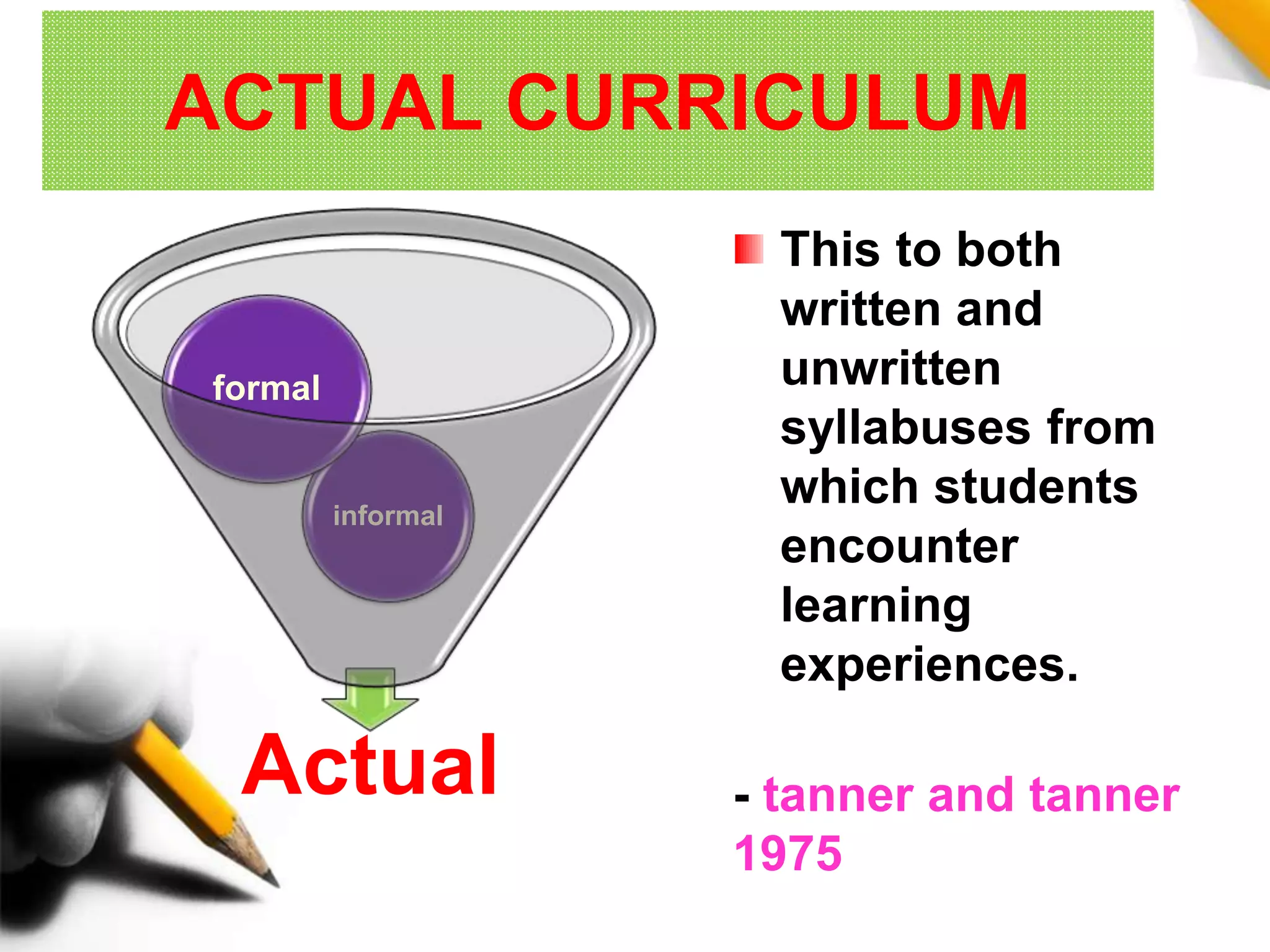
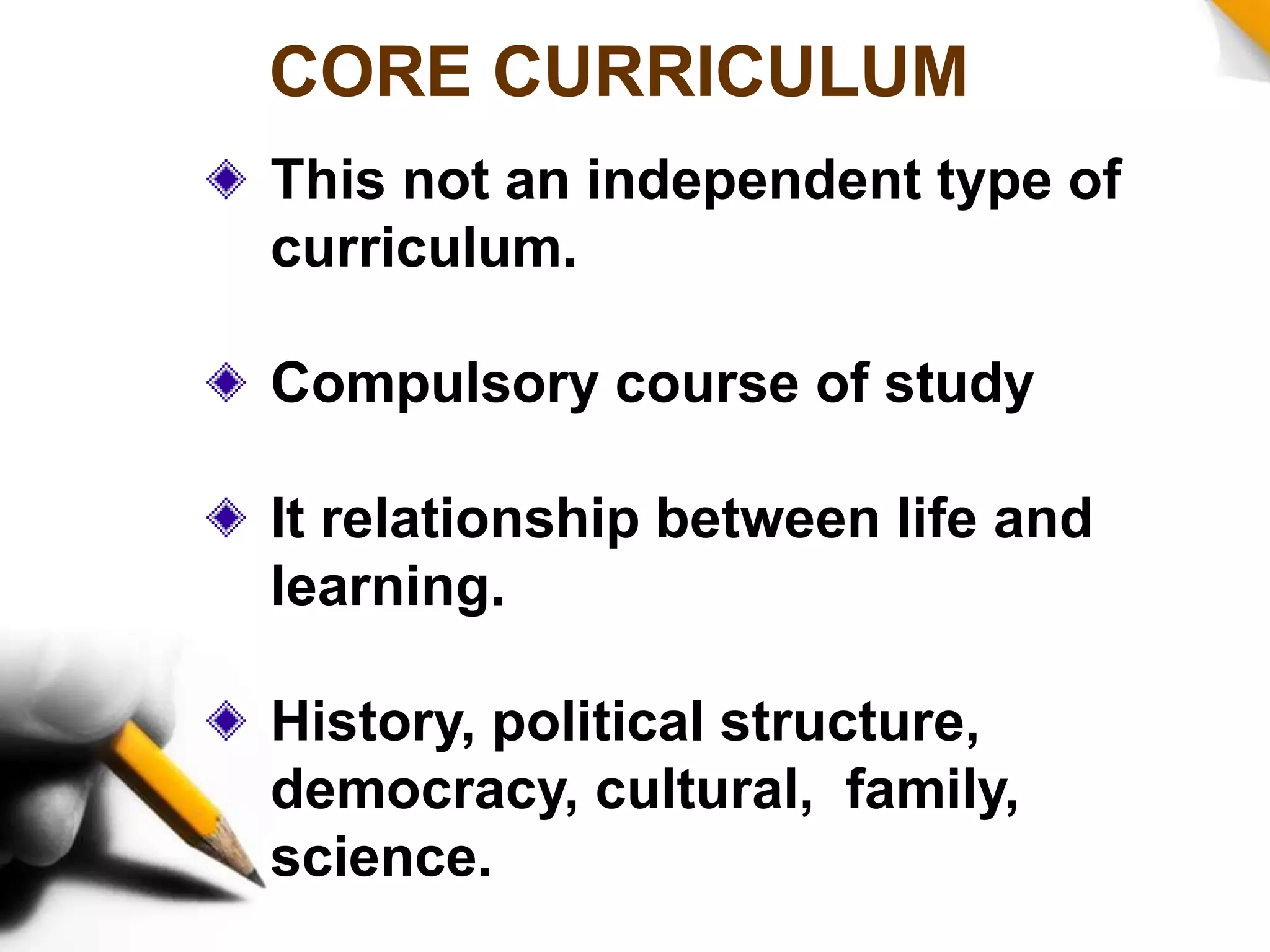
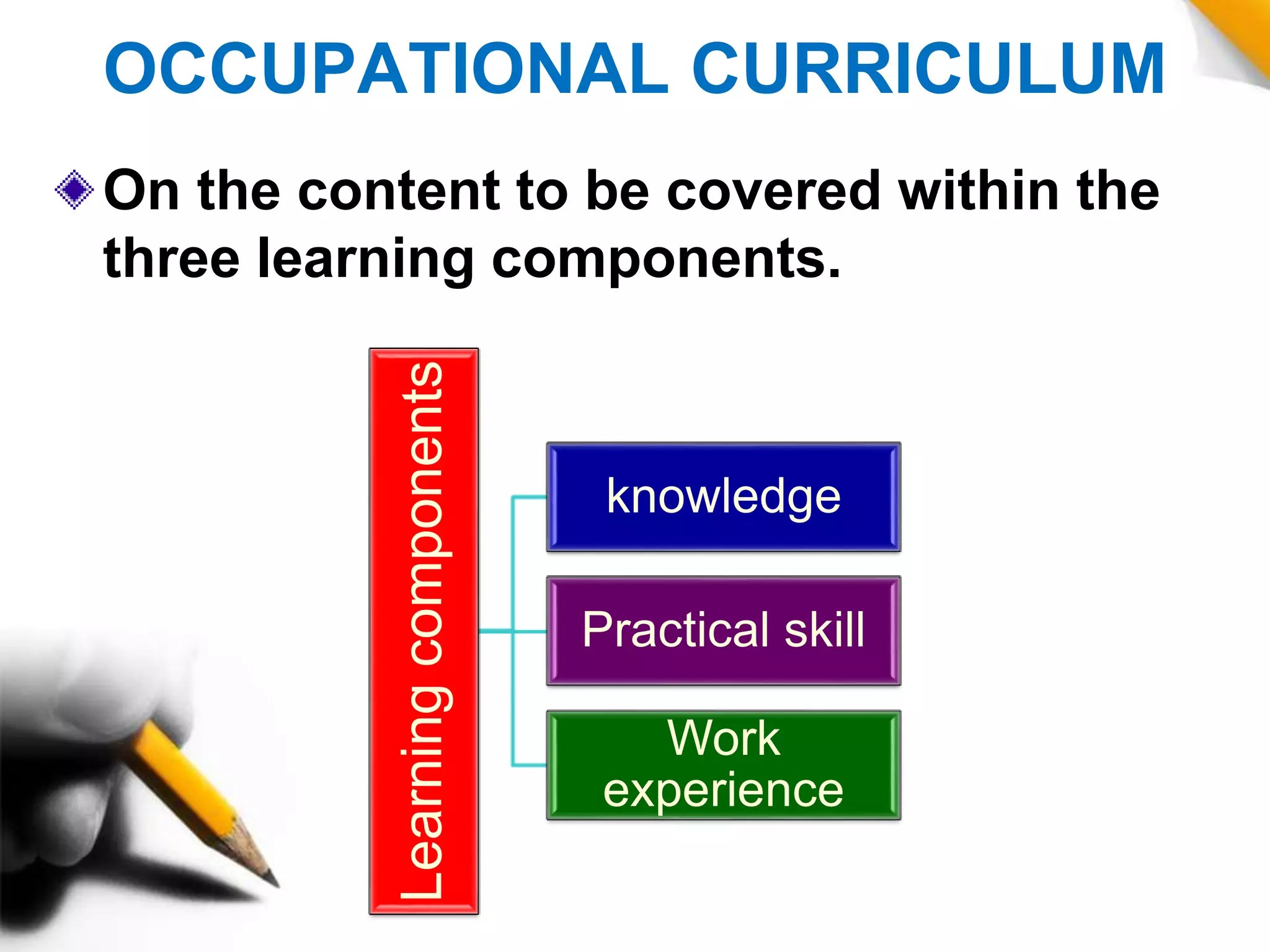
This document discusses different types of curriculum, including formal curriculum (written textbooks and lesson plans), informal curriculum (implicit lessons learned), null curriculum (what is not taught), actual curriculum (both written and unlearned lessons), subject curriculum (traditional organization by subjects), child curriculum (focusing on student experiences), core curriculum (compulsory common lessons), broad field curriculum (combining subjects), correlated curriculum (teaching subjects correlated to each other), task curriculum (project-based learning), intended curriculum (documented plans), extra-mural curriculum (non-official lessons), objective curriculum (focusing on objectives, experiences and behaviors), rhetorical curriculum (ideas from officials), phantom curriculum (lessons from media), concomitant curriculum